Image filter (NW.js) - chung-leong/zigar GitHub Wiki
In this example we're going to build a dekstop app that apply a filter on an image. We'll first implement just the user interface and with the image loading/saving functionalities. After getting the basics working, we'll bring in our Zig-powered image filter.
We begin by initializing the project:
mkdir filter
cd filter
npm init -y
npm install node-zigar
mkdir src img zigThen we add index.html to the src directory:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<title>Image filter</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="App">
<input id="fileOpen" type="file" class="hidden" accept="image/*">
<input id="fileSave" type="file" class="hidden" accept="image/*" nwsaveas>
<div class="contents">
<div class="pane align-right">
<canvas id="srcCanvas"></canvas>
</div>
<div class="pane align-left">
<canvas id="dstCanvas"></canvas>
<div class="controls">
Intensity: <input id="intensity" type="range" min="0" max="1" step="0.0001" value="0.3">
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Basically, we have two HTML canvases in our app, one for displaying the original image and the other the outcome. There's also a range input for controlling the intensity of the filter's effect. The two hidden file inputs give us a way to open the file open/save dialog boxes when the user chooses these options in the app menu.
Save the app code to index.js:
const { writeFile } = require('fs/promises');
const { resolve } = require('path');
const { pathToFileURL } = require('url');
const isMac = process.platform === 'darwin'
nw.Window.open('./src/index.html', { width: 800, height: 600, x: 10, y: 10 }, (browser) => {
// handle menu click
const onOpenClick = () => {
const { window: { document } } = browser;
document.getElementById('fileOpen').click();
};
const onSaveClick = () => {
const { window: { document } } = browser;
document.getElementById('fileSave').click();
};
const onCloseClick = () => {
browser.close();
};
// create menu bar
const menuBar = new nw.Menu({ type: 'menubar' });
const fileMenu = new nw.Menu();
fileMenu.append(new nw.MenuItem({ label: 'Open', click: onOpenClick }));
fileMenu.append(new nw.MenuItem({ label: 'Save', click: onSaveClick }));
fileMenu.append(new nw.MenuItem({ type: 'separator' }));
fileMenu.append(new nw.MenuItem({ label: (isMac) ? 'Close' : 'Quit', click: onCloseClick }));
menuBar.append(new nw.MenuItem({ label: 'File', submenu: fileMenu }));
browser.menu = menuBar;
browser.window.onload = async () => {
// find page elements
const { window: { document } } = browser;
const fileOpen = document.getElementById('fileOpen');
const fileSave = document.getElementById('fileSave');
const srcCanvas = document.getElementById('srcCanvas');
const dstCanvas = document.getElementById('dstCanvas');
const intensity = document.getElementById('intensity');
const params = { intensity: 0.3 };
// attach event handlers
fileOpen.onchange = async (evt) => {
const { target: { files: [ file ] } } = evt;
if (file) {
await loadImage(file.path);
}
};
fileSave.onchange = async (evt) => {
const { target: { files: [ file ] } } = evt;
if (file) {
await saveImage(file.path, file.type);
// clear value so onchange is fired again when the same file is selected
evt.target.value = '';
}
};
intensity.oninput = (evt) => {
const { target: { value } } = evt;
params.intensity = parseFloat(value);
applyFilter();
};
// load sample image
const path = resolve(__dirname, './img/sample.png');
await loadImage(path);
async function loadImage(path) {
const url = pathToFileURL(path);
const img = new Image;
img.src = url;
// img.decode() doesn't work for some reason
await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
img.onload = resolve;
img.onerror = reject;
});
const bitmap = await createImageBitmap(img);
srcCanvas.width = bitmap.width;
srcCanvas.height = bitmap.height;
const ctx = srcCanvas.getContext('2d', { willReadFrequently: true });
ctx.drawImage(bitmap, 0, 0);
applyFilter();
}
function applyFilter() {
const srcCTX = srcCanvas.getContext('2d', { willReadFrequently: true });
const { width, height } = srcCanvas;
const params = { intensity: parseFloat(intensity.value) };
const srcImageData = srcCTX.getImageData(0, 0, width, height);
dstCanvas.width = width;
dstCanvas.height = height;
const dstCTX = dstCanvas.getContext('2d');
dstCTX.putImageData(srcImageData, 0, 0);
}
async function saveImage(path, type) {
const blob = await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const callback = (result) => {
if (result) {
resolve(result);
} else {
reject(new Error('Unable to encode image'));
}
};
dstCanvas.toBlob(callback, type)
});
const buffer = await blob.arrayBuffer();
await writeFile(path, new DataView(buffer));
}
};
});The code above should be largely self-explanatory if you've worked with HTML canvas before.
Replace the content of index.css with the following:
:root {
font-family: Inter, system-ui, Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
line-height: 1.5;
font-weight: 400;
color-scheme: light dark;
color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.87);
background-color: #242424;
font-synthesis: none;
text-rendering: optimizeLegibility;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
}
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
}
body {
margin: 0;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
place-items: center;
min-width: 320px;
min-height: 100vh;
}
#root {
flex: 1 1 100%;
width: 100%;
}
.App {
display: flex;
position: relative;
flex-direction: column;
width: 100%;
height: 100%;
}
.App .nav {
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
color: #000000;
background-color: #999999;
font-weight: bold;
flex: 0 0 auto;
padding: 2px 2px 1px 2px;
}
.App .nav .button {
padding: 2px;
cursor: pointer;
}
.App .nav .button:hover {
color: #ffffff;
background-color: #000000;
padding: 2px 10px 2px 10px;
}
.App .contents {
display: flex;
width: 100%;
margin-top: 1em;
}
.App .contents .pane {
flex: 1 1 50%;
padding: 5px 5px 5px 5px;
}
.App .contents .pane CANVAS {
border: 1px dotted rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.10);
max-width: 100%;
max-height: 90vh;
}
.App .contents .pane .controls INPUT {
vertical-align: middle;
width: 50%;
}
@media screen and (max-width: 600px) {
.App .contents {
flex-direction: column;
}
.App .contents .pane {
padding: 1px 2px 1px 2px;
}
.App .contents .pane .controls {
padding-left: 4px;
}
}
.hidden {
position: absolute;
visibility: hidden;
z-index: -1;
}
.align-left {
text-align: left;
}
.align-right {
text-align: right;
}We need to adjust main in package.json:
"main": "src/index.js",We also need a sample image. Either download the following or choose one of your own:

Save it in img.
Now we're ready to go:
[NW.js directory]/nw .You should see something like this:
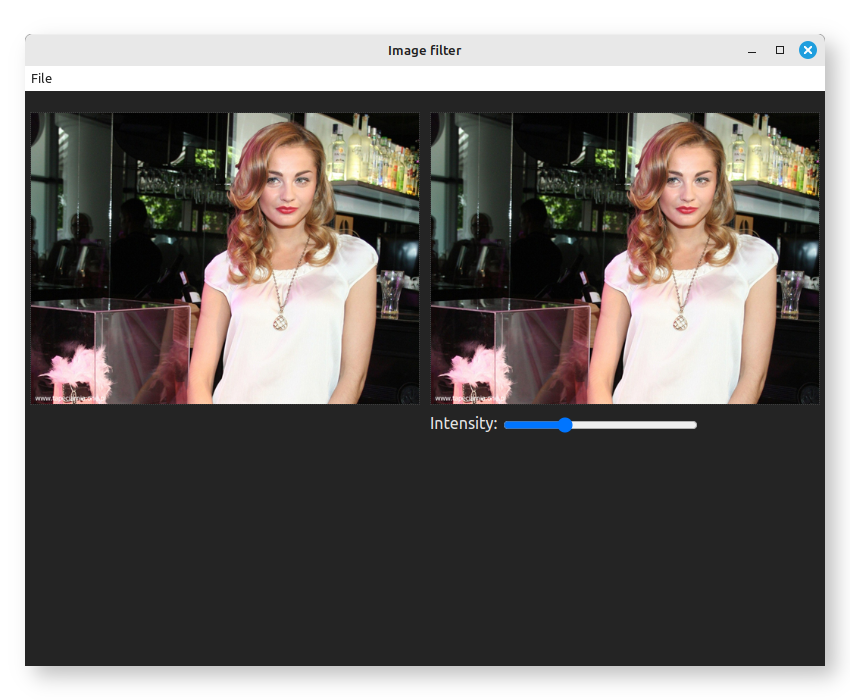
Moving the slider won't do anything but image loading and saving should work.
Okay, we'll now put in the Zig-powered image filter. Save the following code as sepia.zig in
the zig directory:
// Pixel Bender kernel "Sepia" (translated using pb2zig)
const std = @import("std");
pub const kernel = struct {
// kernel information
pub const namespace = "AIF";
pub const vendor = "Adobe Systems";
pub const version = 2;
pub const description = "a variable sepia filter";
pub const parameters = .{
.intensity = .{
.type = f32,
.minValue = 0.0,
.maxValue = 1.0,
.defaultValue = 0.0,
},
};
pub const inputImages = .{
.src = .{ .channels = 4 },
};
pub const outputImages = .{
.dst = .{ .channels = 4 },
};
// generic kernel instance type
fn Instance(comptime InputStruct: type, comptime OutputStruct: type, comptime ParameterStruct: type) type {
return struct {
params: ParameterStruct,
input: InputStruct,
output: OutputStruct,
outputCoord: @Vector(2, u32) = @splat(0),
// output pixel
dst: @Vector(4, f32) = undefined,
// functions defined in kernel
pub fn evaluatePixel(self: *@This()) void {
const intensity = self.params.intensity;
const src = self.input.src;
const dst = self.output.dst;
self.dst = @splat(0.0);
var rgbaColor: @Vector(4, f32) = undefined;
var yiqaColor: @Vector(4, f32) = undefined;
const YIQMatrix: [4]@Vector(4, f32) = .{
.{
0.299,
0.596,
0.212,
0.0,
},
.{
0.587,
-0.275,
-0.523,
0.0,
},
.{
0.114,
-0.321,
0.311,
0.0,
},
.{ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 },
};
const inverseYIQ: [4]@Vector(4, f32) = .{
.{ 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.0 },
.{
0.956,
-0.272,
-1.1,
0.0,
},
.{
0.621,
-0.647,
1.7,
0.0,
},
.{ 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 },
};
rgbaColor = src.sampleNearest(self.outCoord());
yiqaColor = @"M * V"(YIQMatrix, rgbaColor);
yiqaColor[1] = intensity;
yiqaColor[2] = 0.0;
self.dst = @"M * V"(inverseYIQ, yiqaColor);
dst.setPixel(self.outputCoord[0], self.outputCoord[1], self.dst);
}
pub fn outCoord(self: *@This()) @Vector(2, f32) {
return .{ @as(f32, @floatFromInt(self.outputCoord[0])) + 0.5, @as(f32, @floatFromInt(self.outputCoord[1])) + 0.5 };
}
};
}
// kernel instance creation function
pub fn create(input: anytype, output: anytype, params: anytype) Instance(@TypeOf(input), @TypeOf(output), @TypeOf(params)) {
return .{
.input = input,
.output = output,
.params = params,
};
}
// built-in Pixel Bender functions
fn @"M * V"(m1: anytype, v2: anytype) @TypeOf(v2) {
const ar = @typeInfo(@TypeOf(m1)).Array;
var t1: @TypeOf(m1) = undefined;
inline for (m1, 0..) |column, c| {
inline for (0..ar.len) |r| {
t1[r][c] = column[r];
}
}
var result: @TypeOf(v2) = undefined;
inline for (t1, 0..) |column, c| {
result[c] = @reduce(.Add, column * v2);
}
return result;
}
};
pub const Input = KernelInput(u8, kernel);
pub const Output = KernelOutput(u8, kernel);
pub const Parameters = KernelParameters(kernel);
pub fn createOutput(allocator: std.mem.Allocator, width: u32, height: u32, input: Input, params: Parameters) !Output {
return createPartialOutput(allocator, width, height, 0, height, input, params);
}
pub fn createPartialOutput(allocator: std.mem.Allocator, width: u32, height: u32, start: u32, count: u32, input: Input, params: Parameters) !Output {
var output: Output = undefined;
inline for (std.meta.fields(Output)) |field| {
const ImageT = @TypeOf(@field(output, field.name));
@field(output, field.name) = .{
.data = try allocator.alloc(ImageT.Pixel, count * width),
.width = width,
.height = height,
.offset = start * width,
};
}
var instance = kernel.create(input, output, params);
if (@hasDecl(@TypeOf(instance), "evaluateDependents")) {
instance.evaluateDependents();
}
const end = start + count;
instance.outputCoord[1] = start;
while (instance.outputCoord[1] < end) : (instance.outputCoord[1] += 1) {
instance.outputCoord[0] = 0;
while (instance.outputCoord[0] < width) : (instance.outputCoord[0] += 1) {
instance.evaluatePixel();
}
}
return output;
}
const ColorSpace = enum { srgb, @"display-p3" };
pub fn Image(comptime T: type, comptime len: comptime_int, comptime writable: bool) type {
return struct {
pub const Pixel = @Vector(4, T);
pub const FPixel = @Vector(len, f32);
pub const channels = len;
data: if (writable) []Pixel else []const Pixel,
width: u32,
height: u32,
colorSpace: ColorSpace = .srgb,
offset: usize = 0,
fn constrain(v: anytype, min: f32, max: f32) @TypeOf(v) {
const lower: @TypeOf(v) = @splat(min);
const upper: @TypeOf(v) = @splat(max);
const v2 = @select(f32, v > lower, v, lower);
return @select(f32, v2 < upper, v2, upper);
}
fn pbPixelFromFloatPixel(pixel: Pixel) FPixel {
if (len == 4) {
return pixel;
}
const mask: @Vector(len, i32) = switch (len) {
1 => .{0},
2 => .{ 0, 3 },
3 => .{ 0, 1, 2 },
else => @compileError("Unsupported number of channels: " ++ len),
};
return @shuffle(f32, pixel, undefined, mask);
}
fn floatPixelFromPBPixel(pixel: FPixel) Pixel {
if (len == 4) {
return pixel;
}
const alpha: @Vector(1, T) = if (len == 1 or len == 3) .{1} else undefined;
const mask: @Vector(len, i32) = switch (len) {
1 => .{ 0, 0, 0, -1 },
2 => .{ 0, 0, 0, 1 },
3 => .{ 0, 1, 2, -1 },
else => @compileError("Unsupported number of channels: " ++ len),
};
return @shuffle(T, pixel, alpha, mask);
}
fn pbPixelFromIntPixel(pixel: Pixel) FPixel {
const numerator: FPixel = switch (len) {
1 => @floatFromInt(@shuffle(T, pixel, undefined, @Vector(1, i32){0})),
2 => @floatFromInt(@shuffle(T, pixel, undefined, @Vector(2, i32){ 0, 3 })),
3 => @floatFromInt(@shuffle(T, pixel, undefined, @Vector(3, i32){ 0, 1, 2 })),
4 => @floatFromInt(pixel),
else => @compileError("Unsupported number of channels: " ++ len),
};
const denominator: FPixel = @splat(@floatFromInt(std.math.maxInt(T)));
return numerator / denominator;
}
fn intPixelFromPBPixel(pixel: FPixel) Pixel {
const max: f32 = @floatFromInt(std.math.maxInt(T));
const multiplier: FPixel = @splat(max);
const product: FPixel = constrain(pixel * multiplier, 0, max);
const maxAlpha: @Vector(1, f32) = .{std.math.maxInt(T)};
return switch (len) {
1 => @intFromFloat(@shuffle(f32, product, maxAlpha, @Vector(4, i32){ 0, 0, 0, -1 })),
2 => @intFromFloat(@shuffle(f32, product, undefined, @Vector(4, i32){ 0, 0, 0, 1 })),
3 => @intFromFloat(@shuffle(f32, product, maxAlpha, @Vector(4, i32){ 0, 1, 2, -1 })),
4 => @intFromFloat(product),
else => @compileError("Unsupported number of channels: " ++ len),
};
}
fn getPixel(self: @This(), x: u32, y: u32) FPixel {
const index = (y * self.width) + x - self.offset;
const src_pixel = self.data[index];
const pixel: FPixel = switch (@typeInfo(T)) {
.Float => pbPixelFromFloatPixel(src_pixel),
.Int => pbPixelFromIntPixel(src_pixel),
else => @compileError("Unsupported type: " ++ @typeName(T)),
};
return pixel;
}
fn setPixel(self: @This(), x: u32, y: u32, pixel: FPixel) void {
if (comptime !writable) {
return;
}
const index = (y * self.width) + x - self.offset;
const dst_pixel: Pixel = switch (@typeInfo(T)) {
.Float => floatPixelFromPBPixel(pixel),
.Int => intPixelFromPBPixel(pixel),
else => @compileError("Unsupported type: " ++ @typeName(T)),
};
self.data[index] = dst_pixel;
}
fn pixelSize(self: @This()) @Vector(2, f32) {
_ = self;
return .{ 1, 1 };
}
fn pixelAspectRatio(self: @This()) f32 {
_ = self;
return 1;
}
inline fn getPixelAt(self: @This(), coord: @Vector(2, f32)) FPixel {
const left_top: @Vector(2, f32) = .{ 0, 0 };
const bottom_right: @Vector(2, f32) = .{ @floatFromInt(self.width - 1), @floatFromInt(self.height - 1) };
if (@reduce(.And, coord >= left_top) and @reduce(.And, coord <= bottom_right)) {
const ic: @Vector(2, u32) = @intFromFloat(coord);
return self.getPixel(ic[0], ic[1]);
} else {
return @splat(0);
}
}
fn sampleNearest(self: @This(), coord: @Vector(2, f32)) FPixel {
return self.getPixelAt(@floor(coord));
}
fn sampleLinear(self: @This(), coord: @Vector(2, f32)) FPixel {
const c = coord - @as(@Vector(2, f32), @splat(0.5));
const c0 = @floor(c);
const f0 = c - c0;
const f1 = @as(@Vector(2, f32), @splat(1)) - f0;
const w: @Vector(4, f32) = .{
f1[0] * f1[1],
f0[0] * f1[1],
f1[0] * f0[1],
f0[0] * f0[1],
};
const p00 = self.getPixelAt(c0);
const p01 = self.getPixelAt(c0 + @as(@Vector(2, f32), .{ 0, 1 }));
const p10 = self.getPixelAt(c0 + @as(@Vector(2, f32), .{ 1, 0 }));
const p11 = self.getPixelAt(c0 + @as(@Vector(2, f32), .{ 1, 1 }));
var result: FPixel = undefined;
comptime var i = 0;
inline while (i < len) : (i += 1) {
const p: @Vector(4, f32) = .{ p00[i], p10[i], p01[i], p11[i] };
result[i] = @reduce(.Add, p * w);
}
return result;
}
};
}
pub fn KernelInput(comptime T: type, comptime Kernel: type) type {
const input_fields = std.meta.fields(@TypeOf(Kernel.inputImages));
comptime var struct_fields: [input_fields.len]std.builtin.Type.StructField = undefined;
inline for (input_fields, 0..) |field, index| {
const input = @field(Kernel.inputImages, field.name);
const ImageT = Image(T, input.channels, false);
const default_value: ImageT = undefined;
struct_fields[index] = .{
.name = field.name,
.type = ImageT,
.default_value = @ptrCast(&default_value),
.is_comptime = false,
.alignment = @alignOf(ImageT),
};
}
return @Type(.{
.Struct = .{
.layout = .auto,
.fields = &struct_fields,
.decls = &.{},
.is_tuple = false,
},
});
}
pub fn KernelOutput(comptime T: type, comptime Kernel: type) type {
const output_fields = std.meta.fields(@TypeOf(Kernel.outputImages));
comptime var struct_fields: [output_fields.len]std.builtin.Type.StructField = undefined;
inline for (output_fields, 0..) |field, index| {
const output = @field(Kernel.outputImages, field.name);
const ImageT = Image(T, output.channels, true);
const default_value: ImageT = undefined;
struct_fields[index] = .{
.name = field.name,
.type = ImageT,
.default_value = @ptrCast(&default_value),
.is_comptime = false,
.alignment = @alignOf(ImageT),
};
}
return @Type(.{
.Struct = .{
.layout = .auto,
.fields = &struct_fields,
.decls = &.{},
.is_tuple = false,
},
});
}
pub fn KernelParameters(comptime Kernel: type) type {
const param_fields = std.meta.fields(@TypeOf(Kernel.parameters));
comptime var struct_fields: [param_fields.len]std.builtin.Type.StructField = undefined;
inline for (param_fields, 0..) |field, index| {
const param = @field(Kernel.parameters, field.name);
const default_value: ?*const anyopaque = get_def: {
const value: param.type = if (@hasField(@TypeOf(param), "defaultValue"))
param.defaultValue
else switch (@typeInfo(param.type)) {
.Int, .Float => 0,
.Bool => false,
.Vector => @splat(0),
else => @compileError("Unrecognized parameter type: " ++ @typeName(param.type)),
};
break :get_def @ptrCast(&value);
};
struct_fields[index] = .{
.name = field.name,
.type = param.type,
.default_value = default_value,
.is_comptime = false,
.alignment = @alignOf(param.type),
};
}
return @Type(.{
.Struct = .{
.layout = .auto,
.fields = &struct_fields,
.decls = &.{},
.is_tuple = false,
},
});
}The above code was translated from a Pixel Bender filter using pb2zig. Consult the intro page for an explanation of how it works.
In index.js, add these require statements at the top:
require('node-zigar/cjs');
const { createOutput } = require('../zig/sepia.zig');Add the following function:
function createImageData(width, height, source, params) {
const input = { src: source };
const output = createOutput(width, height, input, params);
const ta = output.dst.data.typedArray;
const clampedArray = new Uint8ClampedArray(ta.buffer, ta.byteOffset, ta.byteLength);
return new ImageData(clampedArray, width, height);
}The Zig function createOutput() has the follow declaration:
pub fn createOutput(
allocator: std.mem.Allocator,
width: u32,
height: u32,
input: Input,
params: Parameters,
) !Outputallocator is automatically provided by Zigar. We get width and height from the source canvas.
params contains a single f32: intensity. We get that from the HTML range input/slider.
Input is a parameterized type:
pub const Input = KernelInput(u8, kernel);Which expands to:
pub const Input = struct {
src: Image(u8, 4, false);
};Then further to:
pub const Input = struct {
src: struct {
pub const Pixel = @Vector(4, u8);
pub const FPixel = @Vector(4, f32);
pub const channels = 4;
data: []const Pixel,
width: u32,
height: u32,
colorSpace: ColorSpace = .srgb,
offset: usize = 0,
};
};Image was purposely defined in a way so that it is compatible with the browser's
ImageData. Its
data field is []const @Vector(4, u8), a slice pointer that accepts a Uint8ClampedArray
as target without casting. We can therefore simply pass { src: source } to createOutput as
input.
Like Input, Output is a parameterized type. It too can potentially contain multiple images. In
this case (and most cases), there's only one:
pub const Output = struct {
dst: {
pub const Pixel = @Vector(4, u8);
pub const FPixel = @Vector(4, f32);
pub const channels = 4;
data: []Pixel,
width: u32,
height: u32,
colorSpace: ColorSpace = .srgb,
offset: usize = 0,
},
};The typedArray property of output.dst.data gives us a Uint8Array. ImageData wants a
Uint8ClampedArray so we need to convert it before passing it to the constructor:
const ta = output.dst.data.typedArray;
const clampedArray = new Uint8ClampedArray(ta.buffer, ta.byteOffset, ta.byteLength);
return new ImageData(clampedArray, width, height);Now it's just a matter of inserting a call into applyFilter:
const srcImageData = srcCTX.getImageData(0, 0, width, height);
const dstImageData = createImageData(width, height, srcImageData, params);
dstCanvas.width = width;
dstCanvas.height = height;
const dstCTX = dstCanvas.getContext('2d');
dstCTX.putImageData(dstImageData, 0, 0);That's it! When you start the app again, , a message will appear informing you that the Node-API addon and the module "sepia" are being built. After a minute or so you should see this:
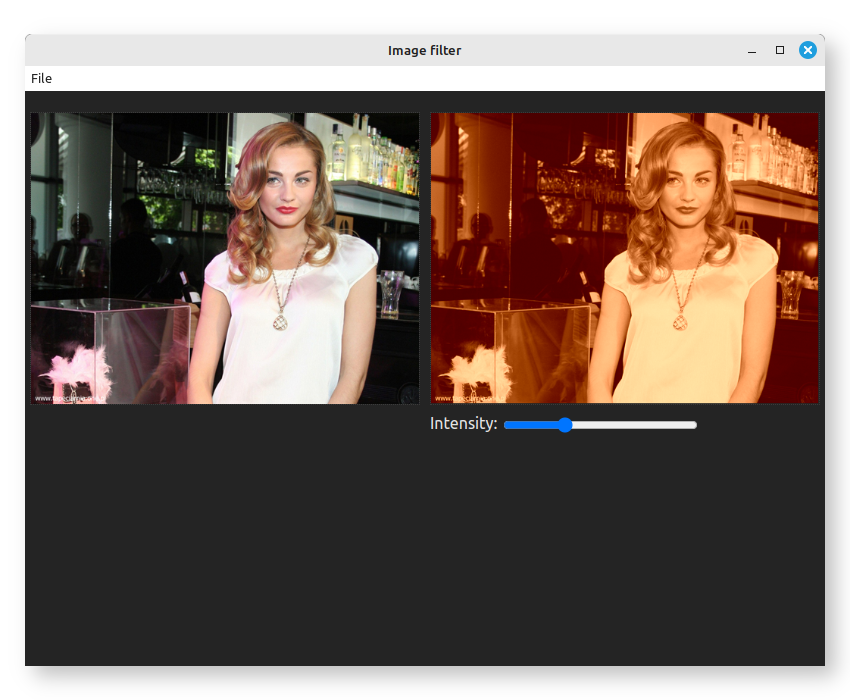
We're going to follow the same steps as described in the hello world tutorial. First, we'll alter the require statement so it references a node-zigar module instead of a Zig file:
const { createOutput } = require('../lib/sepia.zigar');Then we add node-zigar.config.json to the app's root directory:
{
"optimize": "ReleaseFast",
"sourceFiles": {
"lib/sha1.zigar": "zig/sepia.zig"
},
"targets": [
{ "platform": "win32", "arch": "x64" },
{ "platform": "win32", "arch": "arm64" },
{ "platform": "win32", "arch": "ia32" },
{ "platform": "linux", "arch": "x64" },
{ "platform": "linux", "arch": "arm64" },
{ "platform": "darwin", "arch": "x64" },
{ "platform": "darwin", "arch": "arm64" }
]
}We build the library files:
npx node-zigar buildThe app can now be packaged for distribution.
You can find the complete source code for this example here.
One of the key advantages that NW.js has over Electron is how UI code and "backend" code are housed in the same thread. There's is no need to transfer data from one side to another. This makes this example significantly simpler than the Electron counterpart. Deployment of Electron apps is far easier though. Overall, it might still be a more attractive platform.
The image filter employed for this example is very rudimentary. Check out pb2zig's project page to see more advanced code.
That's it for now. I hope this tutorial is enough to get you started with using Zigar.