ERPLAB Studio Panels: Plot ERP Scalp Maps - ucdavis/erplab GitHub Wiki
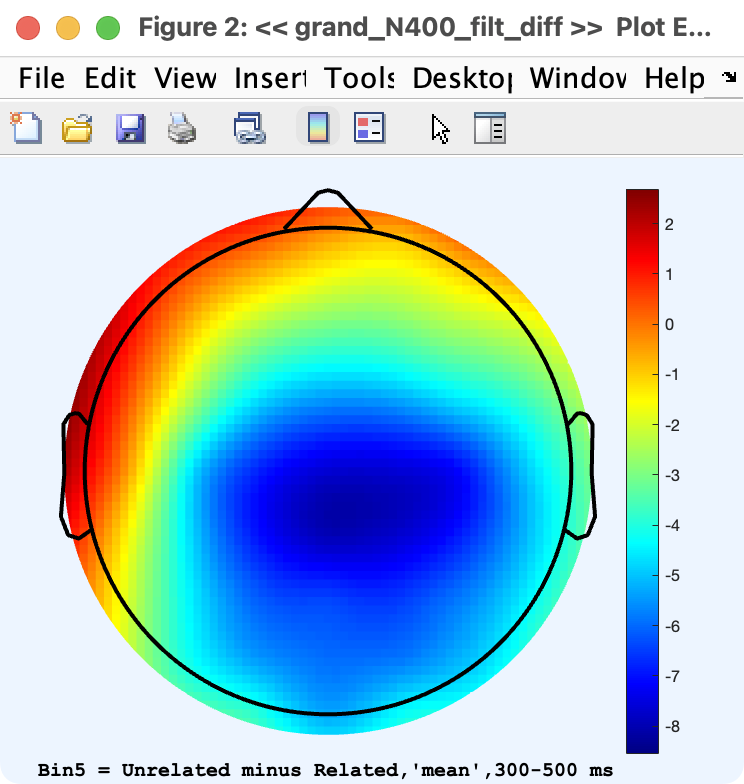
The Plot Scalp Maps panel in the ERP tab allows you to plot topographic maps of ERP data. This routine allows you to plot the data from one or more time period for a selected set of bins from the ERPset(s) that have been selected in the ERPsets panel. If multiple ERPsets are selected, a separate window will be created for each ERPset that shows the scalp maps from that ERPset. The panel is shown below, along with an example of the output (taken from the unrelated-minus-related difference wave in the ERP CORE N400 experiment).
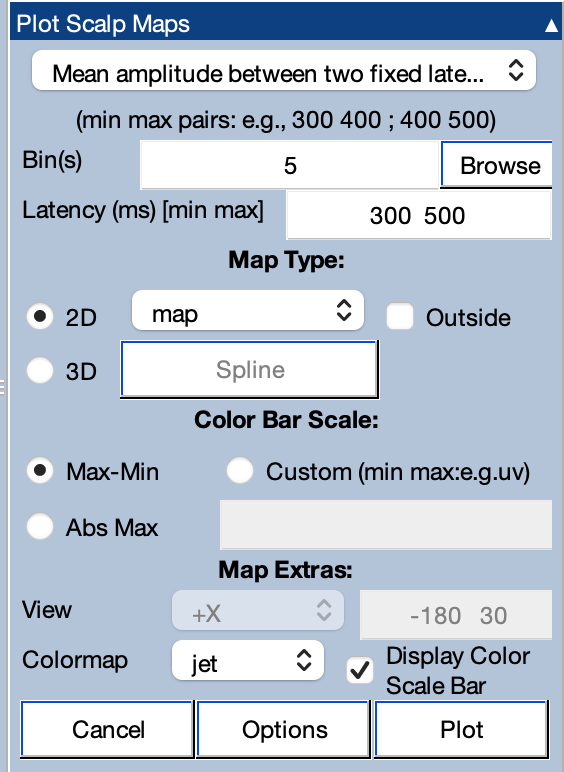
To plot a set of topographic maps, you start by selecting what kinds of values to plot. The options are:
-
Instantaneous amplitude- The amplitude at a single time point (e.g., 300 ms)
-
Mean amplitude between two fixed latencies- The mean voltage in a time period (e.g., 300-500 ms)
-
Instantaneous amplitude Laplacian- Instantaneous amplitude of the surface Laplacian
-
Mean amplitude between two fixed latencies- Mean amplitude of the surface Laplacian
-
Root mean square value- This is the RMS of the voltage values over the specified time range
For instantaneous amplitude, you provide a set of one or more latencies in the Latency text box (e.g., "100 150 200 250 300" or equivalently "100:50:300"). For mean or RMS amplitude, you provide one or more sets of time periods. For example, you would specify 300 500 to plot the scalp distribution of the mean voltage between 300 and 500 ms. You can also specify multiple time periods, separated by semicolons (e.g., "200 300 ; 300 400; 400 500" to plot maps of mean amplitude from 200-300, 300-400, and 400-500).
There are several options for determining the scale of the maps. If you select Max-Min, the routine automatically chooses a scale for each bin on the basis of the minimum and maximum voltages found in that bin (e.g., the chosen scale might go from -4 µV to +9 µV). If you select Abs Max, the routine finds the minimum and maximum values, and creates a symmetrical scale depending on which has a greater absolute value (e.g., the chosen scale might go from -9 µV to +9 µV). For these two options, each bin is scaled separately. A third option is Custom, which allows you to specify the minimum and maximum values (e.g., you might put -5 +5 in the text box). In this case, the scale is the same for each bin. There are a variety of additional plotting options (e.g., turning on or off electrode markers) that are accessed with the Options button.
The topographic plotting routine requires that the location of each electrode is specified (not just the name, but the 3-D coordinates). These can be set using the Edit/Delete Channels & Locations panel (in the EEG tab prior to averaging or the ERP tab after averaging).
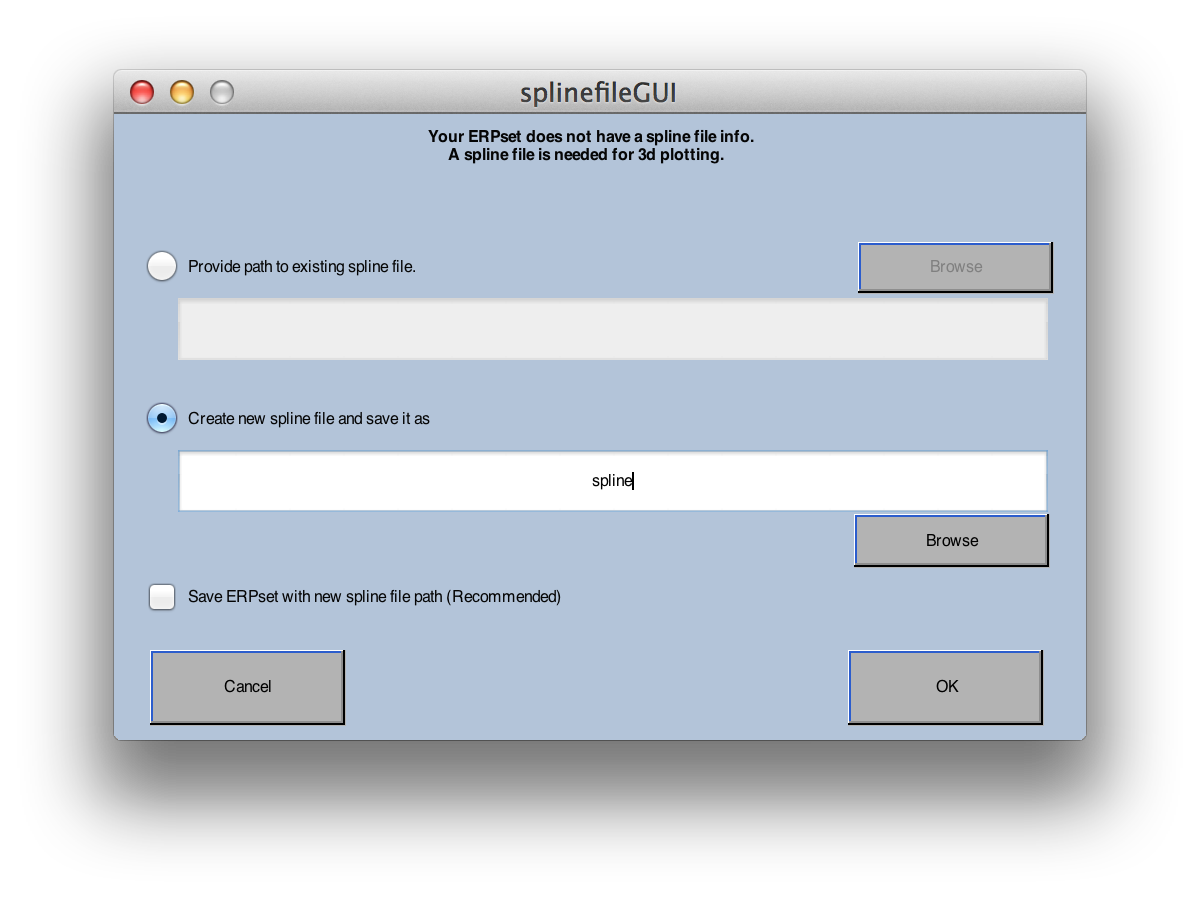
You can choose between 2D maps (which always use a top viewpoint) and 3D maps (which allow you to specify the viewpoint). Plotting 3D maps requires creating a spline file (which is used in the interpolation of values across the model head). If you don’t already have a spline file integrated into the current ERPset, click the Spline button to get the window shown in the screenshot below. If you've already created a spline file for this set of electrodes, you can specify its location. If you haven't already created the spline file, you will tell it to create a new one and give a name for the file. If you check Save ERPset with new spline file path to disk, it will save a new version of your ERPset with information about how to find the spline file in the future.