Multiplier - mbits-mirafra/digitalDesignCourse GitHub Wiki
What is multiplier?
A multiplier is an electronic circuit or computer program that performs the multiplication of two numbers. It can take two binary numbers as inputs and produce the product of those two numbers as output. Multipliers are essential building blocks in many digital signal processing (DSP) applications and are used in various digital systems such as microprocessors, digital signal processors, and communication systems.
Why do we need to learn this topic?
Learning about multipliers is important for several reasons.
Firstly, multipliers are widely used in digital signal processing (DSP) applications such as audio and video signal processing, wireless communication systems, and digital image processing. Understanding how multipliers work is essential for designing efficient and high-performance DSP systems.
Secondly, multipliers are an essential building block for designing complex digital circuits such as microprocessors, microcontrollers, and digital signal processors. A good understanding of how multipliers work is therefore necessary for anyone interested in digital circuit design.
Finally, understanding multipliers is important for anyone interested in computer architecture, as multiplication is a fundamental operation in many computer algorithms and applications. By understanding how multipliers work, one can gain a deeper understanding of the inner workings of computer systems.
Advantages of multiplier
- Speed: Multipliers can perform multiplication operations much faster than a series of additions.
- Efficiency: Multiplication can be done using much fewer resources (transistors) than a series of additions.
- Precision: Multipliers can perform multiplication with greater precision than a series of additions, especially for large numbers.
Disadvantages of multiplier
- Complexity: Multipliers can be complex to design and implement.
- Area: Multipliers can require a significant amount of chip area, which can limit their use in small or low-power devices.
- Power consumption: Multipliers can consume more power than a series of additions.
When is multiplier used?
Multipliers are used in the following scenarios
- Digital signal processing: Multipliers are extensively used in digital signal processing applications, such as audio and video processing, speech recognition, and radar systems. They are used to perform complex mathematical operations such as filtering, convolution, and Fourier transforms.
- Cryptography: Multipliers are also used in cryptography applications, such as encryption and decryption algorithms. They are used to generate keys and perform mathematical operations on large prime numbers.
- Graphics Processing: Multipliers are used in graphics processing units (GPUs) to perform matrix multiplication and other linear algebra operations. These operations are essential for rendering images and videos, which require high-speed processing of large amounts of data.
How is multiplier used?
A multiplier is used to multiply two numbers together. It takes two inputs, which are typically represented in binary format, and produces an output that is the product of the two inputs.
The circuit diagram and Truth table for the multiplier are shown below.
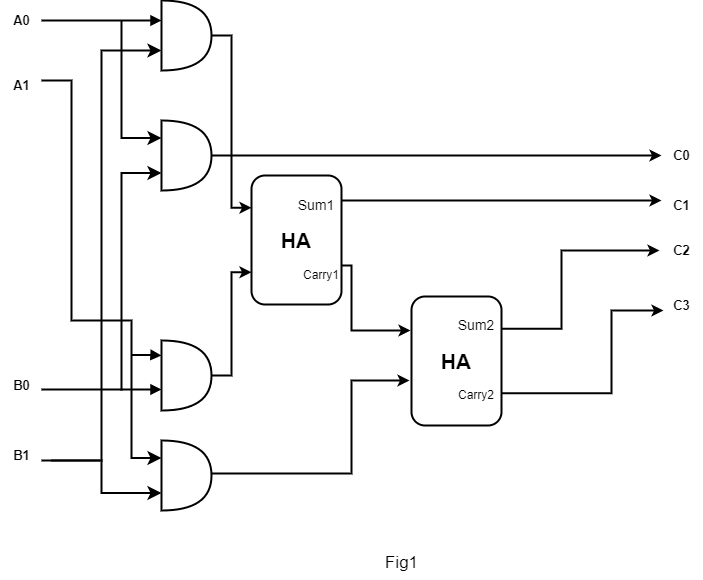
Here HA represents Half Adder. Fig1 can also be drawn as-
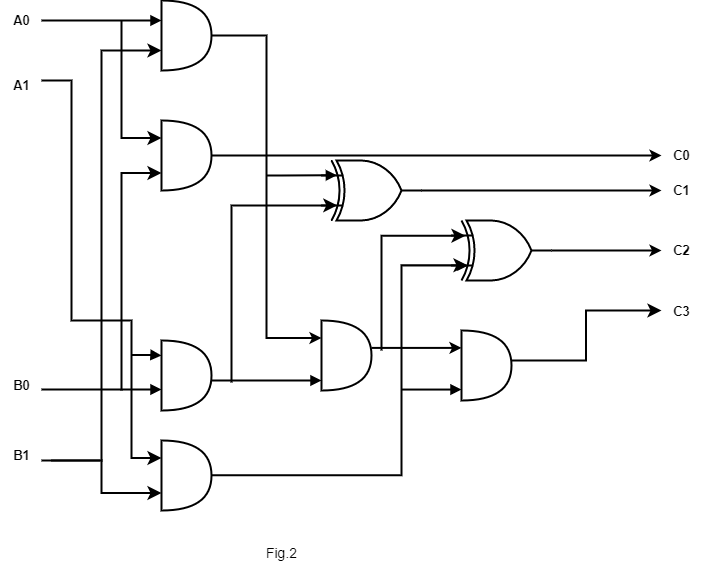
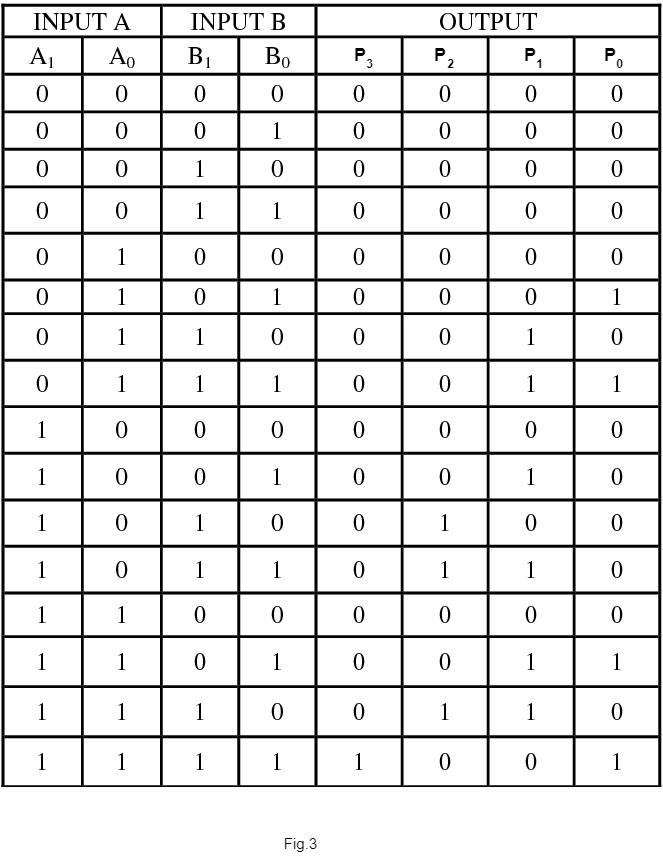
KMAP
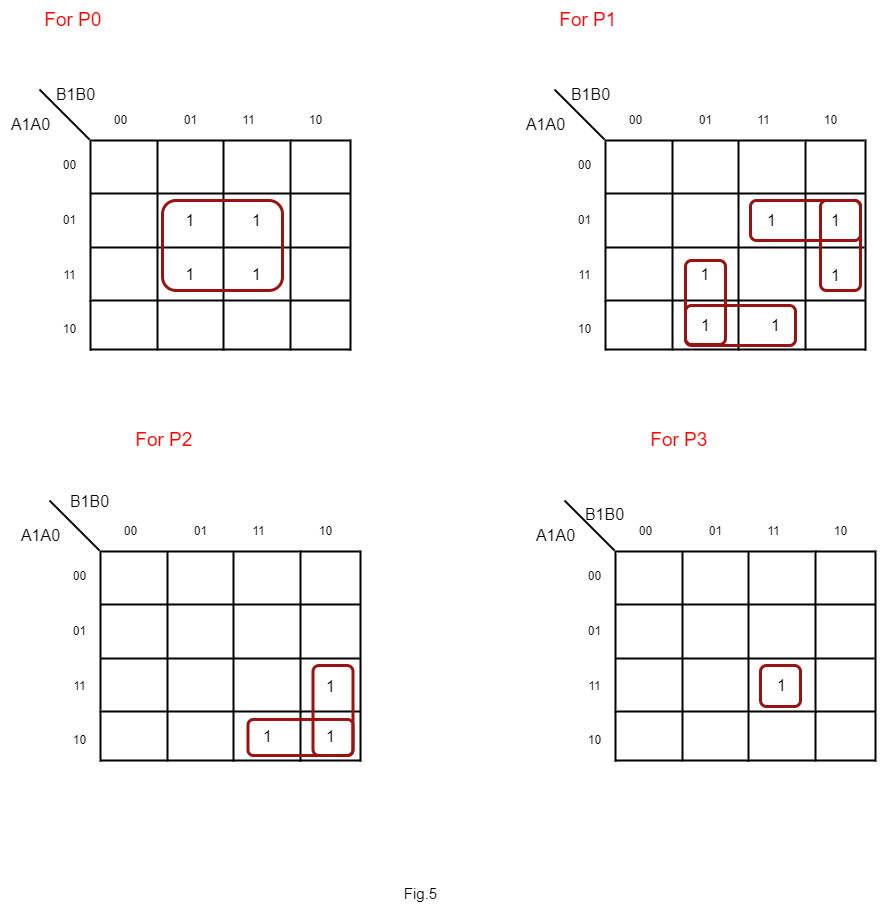
Output equations are given as
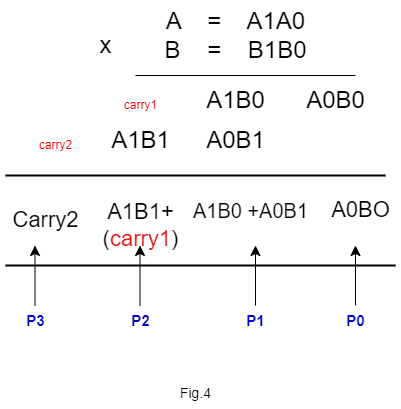
C0= A0B0
C1= A1B0+A0B1
C2= A1B1 + Carry1
C3= Carry 2
Similarly 4x4 Multiplier can be built
4X4 Multiplier
4x4 bit multiplication can be done as shown

Based on the above equation circuit diagram can be drawn as shown
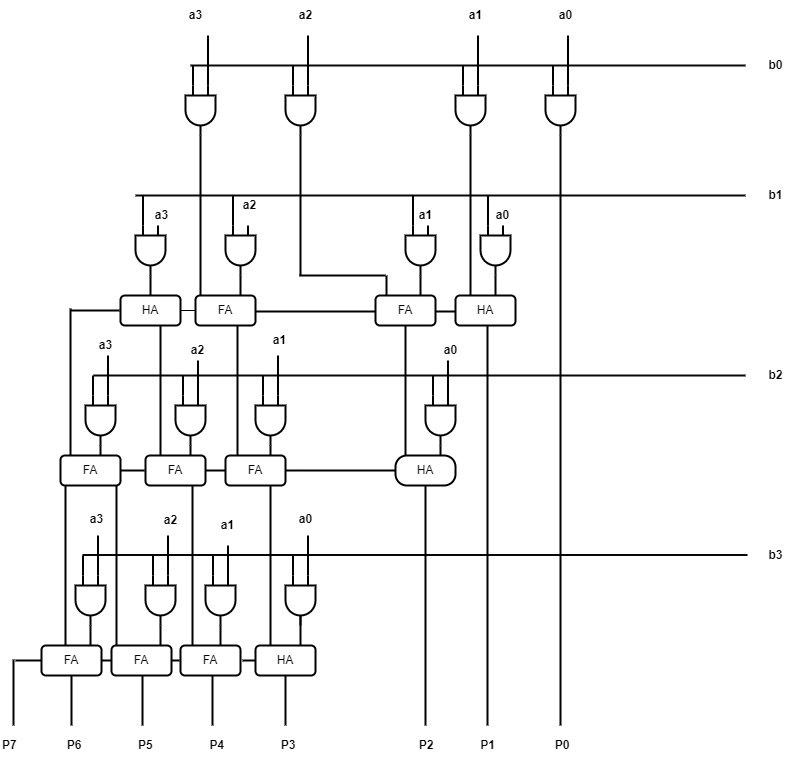
Click this for code files of 4-bit Binary Multiplier
Multiplier using shift register
Multiplier can also be implemented using shift registers
- It consists of shift registers(accumulator, multiplier), Adder, Mux & clock
- Accumulator stores the sum from the adder.
- Initially accumulator value is 0, multiplier & multiplicand are given with required values.
- LSB of the multiplier shift register decides whether to give output of mux as multiplicand or 0 as it is given input to the select line.
- During the posedge of the clock accumulator is loaded with the sum (which also acts as input to the addder)
- During negative edge of clock accumulator and multiplier is right shifted.
- The product is the final output from accumulator and multiplier combined.
Figure below shows multiplication of 2x2 bit.
- Here 11 is multiplier and 11 is multiplicand
- During first posedge clock the accumulator is loaded with sum 11.
- During negative edge clock, the shift registers are right shifted.
- Carry generated is the MSB.
Note:
For M x N bit multiplication, the number of bits for the product is M + N.
For example: Consider 11 x 111, the product is 10101 which is 2+3= 5 bit.