Moore Model - mbits-mirafra/digitalDesignCourse GitHub Wiki
Moore model is a type of finite state machine used in digital logic design and computer science. It is named after its inventor, Edward F. Moore.
In a Moore machine, the output of the machine is determined solely by its current state. The next state of the machine is determined by the combination of the current state and the input applied to the machine.
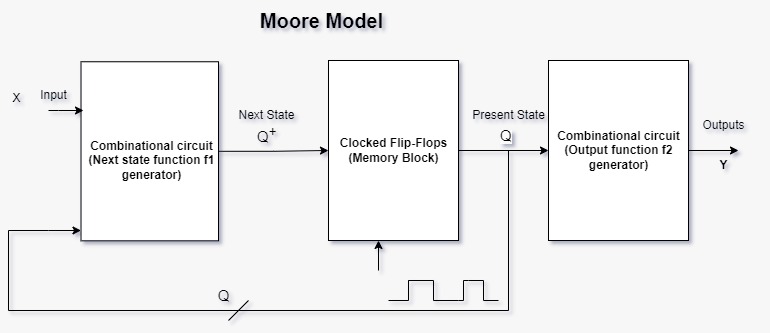
Q= Present state of the circuit
Q+=Next state of the circuit
X=Present input
Y=Outputs
The next state is a Boolean function of the present inputs and the present state
Q+=f1(X,Q)
The outputs are also the functions of present inputs and present state
Y=f2(Q)
Design a synchronous circuit using positive edge JK flip flop with minimal combinational gating to generate the following sequence 0-1-2-0 if input X=0 and 0-2-1-0 if input X=1. Provide an output which goes to high whenever the circuit is in non-zero states irrespective of the sequence. Is this a Moore machine?
Step 1:Draw the state diagram
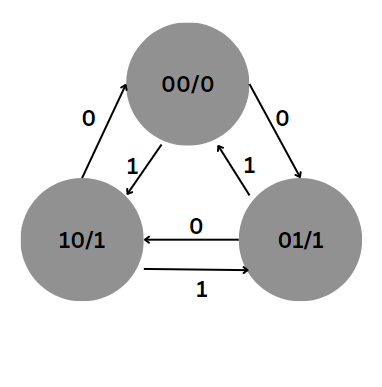
Step 2: Write the State table
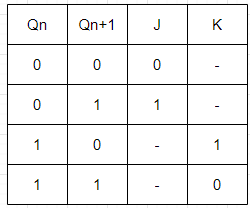
Step 3: Excitation table of JK Flip-Flop.
Step 4:Building truth table using state diagram.
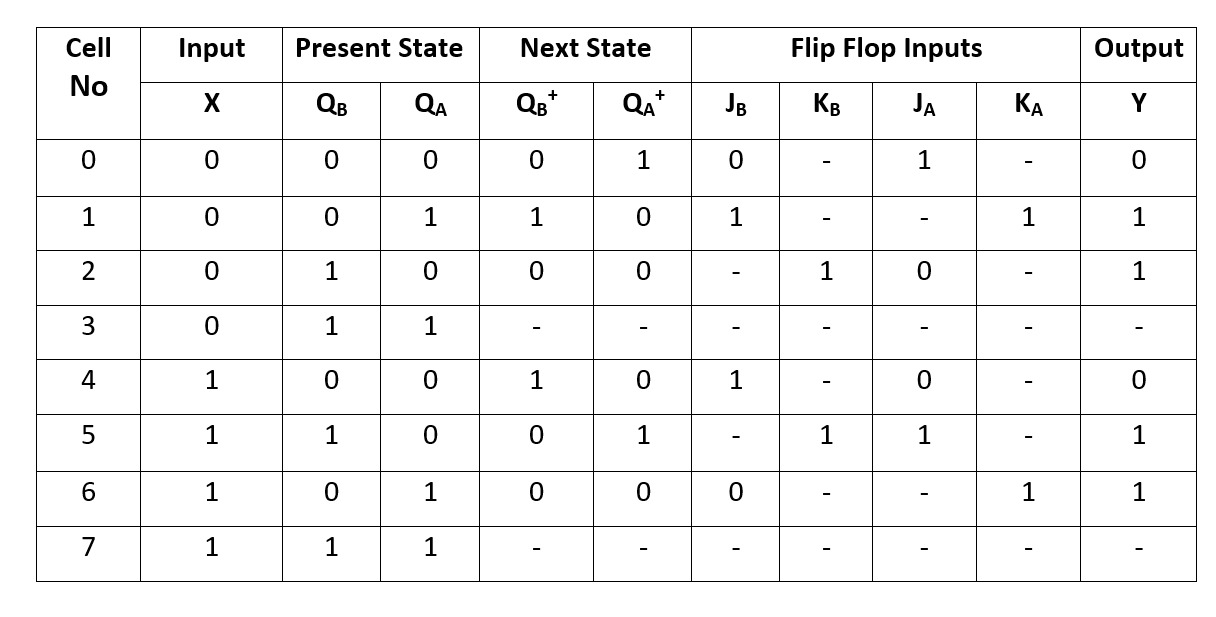
Step 5: Forming equations using K-maps.
The Karnaugh maps for simplifying flip-flop inputs and the output are shown below
Kmap for JB:

JB=X|QA+XQ|A
JB=X^QA
Kmap for KB:

KB=1
Kmap for JA:

JA=X'QB' + XQB
JA=(X^QB)'
Kmap for KA:

KA=1
Kmap for Y:
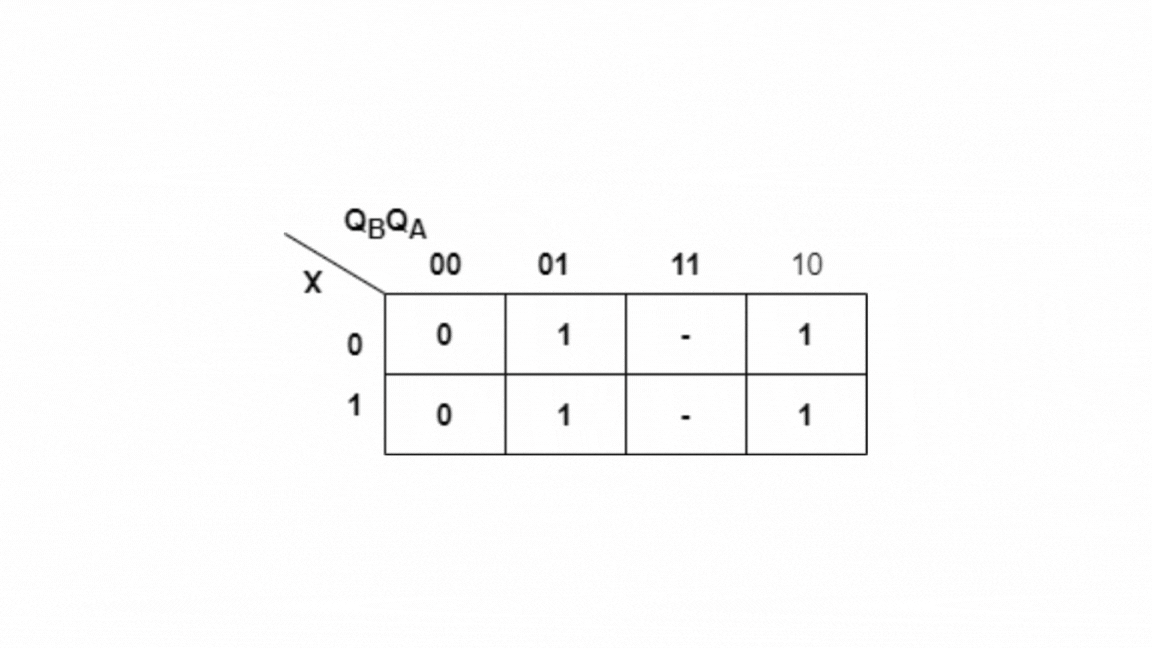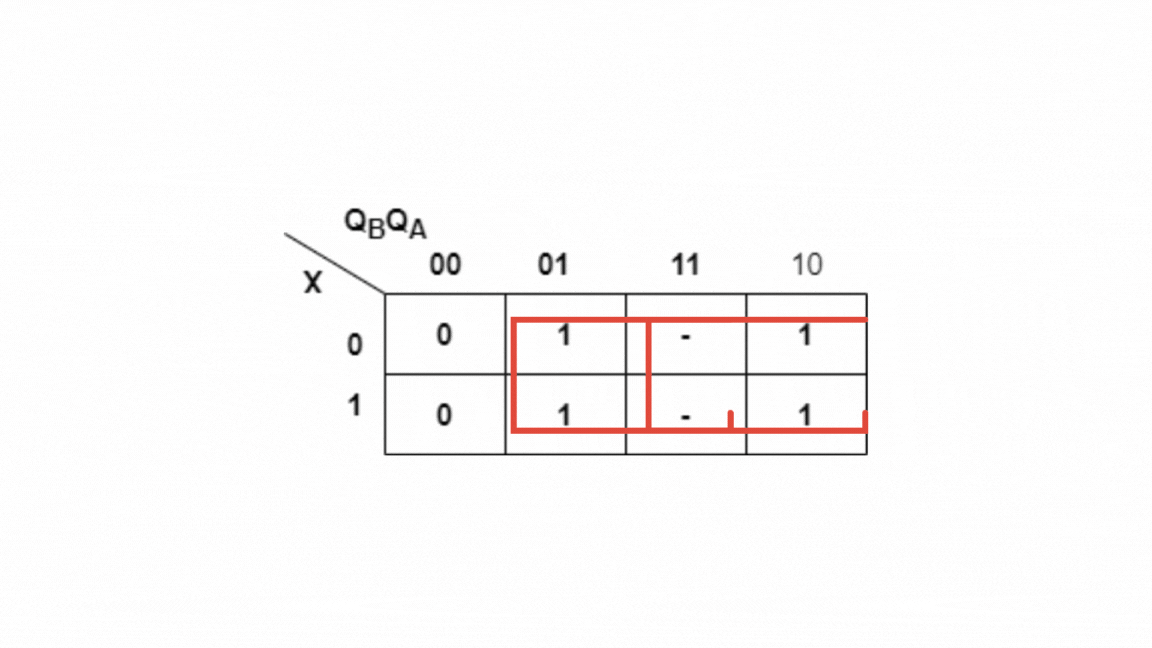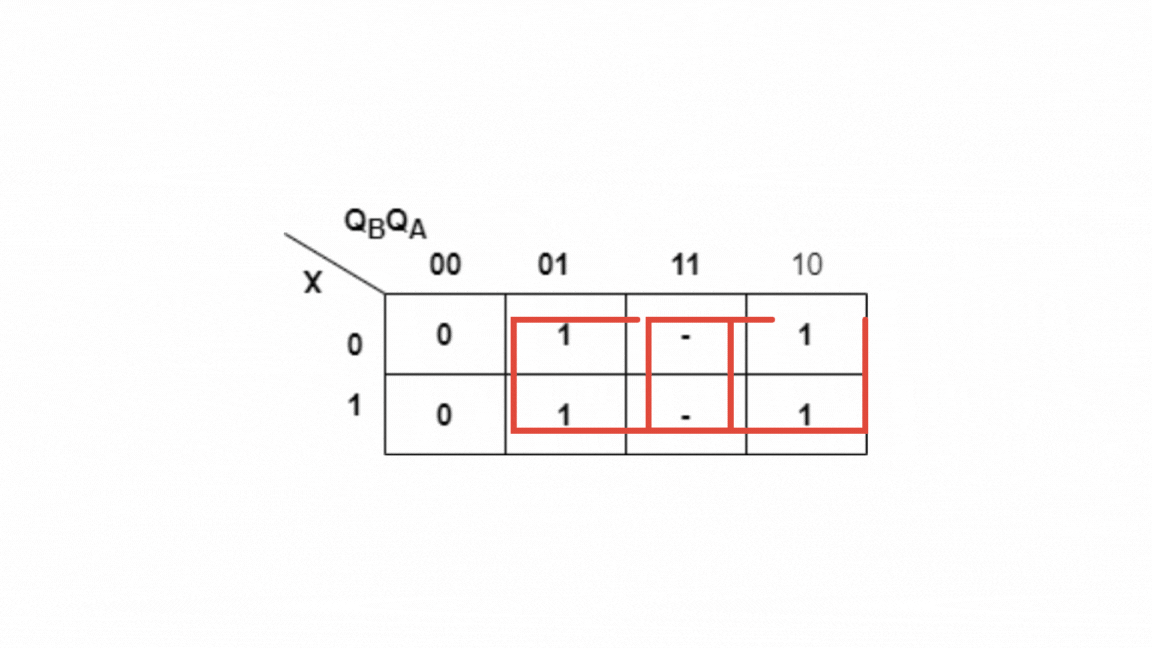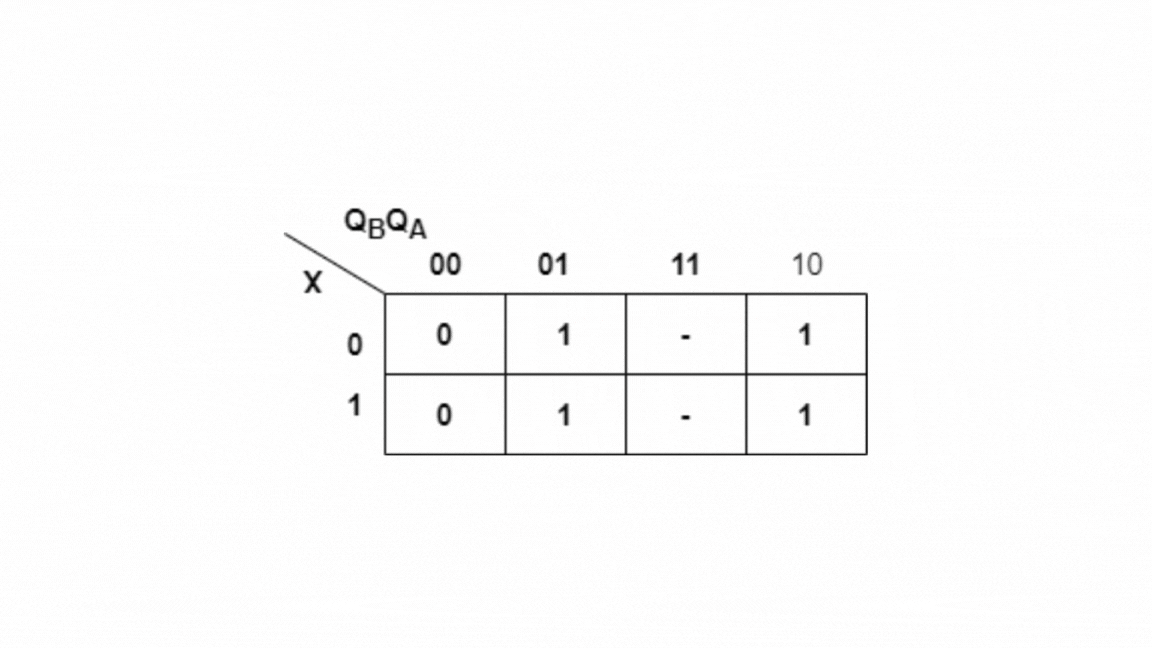
Y=QB+QA
Step 6:Circuit diagram using k-map equations.
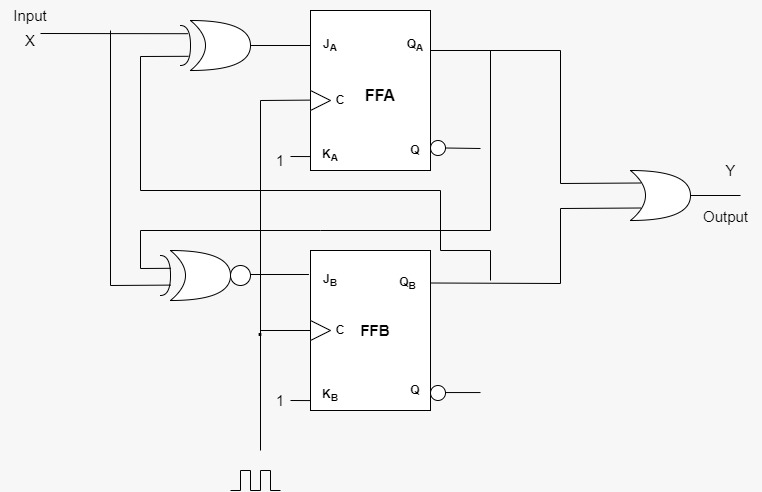
Therefore the synchronous circuit is Moore machine
In Moore Model state reduction is not possible because the output is not directly dependent on the input given.