FPFA - mbits-mirafra/digitalDesignCourse GitHub Wiki
FPGA
What is FPGA
FPGA stands for Field-Programmable Gate Array. It is an integrated circuit that can be programmed by a user after manufacturing. Unlike Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), which are designed for a specific purpose and cannot be reprogrammed, FPGAs are flexible and can be reprogrammed for different applications. An FPGA contains an array of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) that can be programmed to perform specific functions. These blocks can be interconnected to create custom digital circuits. In addition to CLBs, an FPGA also contains programmable interconnects, I/O blocks, and other components to support a wide range of applications.
FPGA Architecture
An FPGA has a regular structure of logic cells or modules and interlinks which is under the developers and designers complete control. The FPGA is built with mainly three major blocks such as Configurable Logic Block (CLB), I/O Blocks or Pads and Switch Matrix/ Interconnection Wires.
Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs): These are the fundamental building blocks of an FPGA. They consist of a set of lookup tables (LUTs-A lookup table is a digital circuit that can be used to implement any Boolean function in FPGA design. It consists of a series of input variables and a corresponding output value, which is determined by the input variables.) and flip-flops that can be programmed to perform digital logic operations. The LUTs can be configured to implement any Boolean function, and the flip-flops can be used to store state information.
Input/Output Blocks (IOBs): These blocks provide the interface between the FPGA and the outside world. They consist of input and output pins that can be configured to interface with a wide range of external devices and protocols, such as Ethernet, USB, and PCI.
Programmable Interconnects: These are the routing resources that connect the CLBs and IOBs. They consist of a network of programmable switches that can be used to connect any combination of CLBs and IOBs.
Why FPGA ?
FPGAs offer high performance and can execute complex operations at high speeds. They can be used to implement custom logic circuits that perform tasks much faster than software running on general-purpose processors. It can be reprogrammed to perform different tasks and functions, making them ideal for prototyping and testing new designs. They can also be used to implement a wide range of functions, from simple logic circuits to complex digital signal processing algorithms. FPGAs is be less expensive than ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits) for low to medium volume production runs. They also have shorter design and development times, which can save on engineering costs.
How FPGA works?
In an FPGA board, the FPGA chip is typically the main component that performs the desired logic functions. The FPGA chip itself contains a large array of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) that can be programmed to implement a wide range of digital logic functions. To use the FPGA on an FPGA board, the user typically creates a design using a hardware description language (HDL) such as Verilog or VHDL, and then uses software tools to synthesize, place, and route the design onto the FPGA. This process involves mapping the digital logic functions in the design to the CLBs on the FPGA, and configuring the interconnects between the CLBs. Once the design is loaded onto the FPGA, the FPGA begins performing the desired logic functions in real-time. The input and output signals to and from the FPGA can be accessed using the I/O pins on the FPGA board, which typically include digital inputs and outputs, as well as analog inputs and outputs.
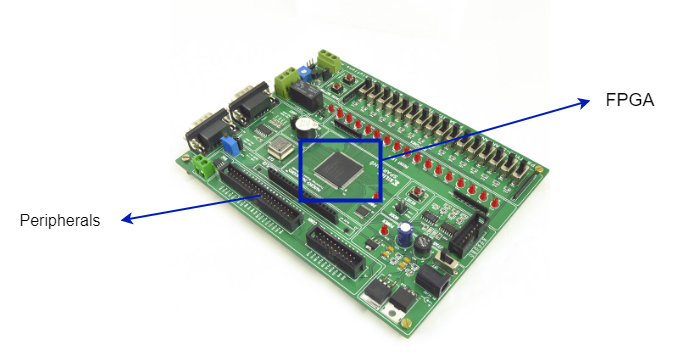
FPGA Board Where FPGA is used? FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays) are used in a wide range of applications across various industries, where high-performance digital signal processing or custom logic functions are required. Some of the common applications of FPGAs include:
- Digital signal processing: FPGAs are commonly used in digital signal processing applications like audio and video processing, where high-speed computation and signal processing is required.
- Embedded systems: FPGAs are used in embedded systems to provide flexible hardware configurations that can be customized to meet specific application requirements.
- High-performance computing: FPGAs are used in high-performance computing applications like scientific simulations and modeling, where they can be used to accelerate computationally intensive algorithms.
Advantages
- Flexibility: FPGAs are highly flexible and can be programmed to perform a wide range of digital functions. They can be reprogrammed to support new features or functionalities without having to redesign the hardware.
- Speed: FPGAs can perform complex computations in parallel, which makes them much faster than microcontrollers or general-purpose processors.
- High reliability: FPGAs are more reliable than software-based solutions, as they are less susceptible to software bugs, viruses, and hacking.
- Customizability: FPGAs can be customized to meet specific application requirements, which can lead to improved performance and reduced cost.
Disadvantages
- Cost: FPGAs are generally more expensive than microcontrollers or general-purpose processors, which can be a barrier to adoption, especially for low-volume applications.
- Complexity: FPGAs can be complex to program and require specialized knowledge of hardware design languages like VHDL or Verilog.
For more details regarding FPGA tap here