Sighash and TX Signing
The op_codes CHECKSIG, CHECKSIGVERIFY, CHECKMULTISIG, CHECKMULTISIGVERIFY all verify signatures together with an non-script one-byte sighash argument, which indicates which part of the transaction the signature specifically endorses.
The input signature can endorse an entire transaction with a fixed set of inputs and outputs. The signature can also be selectively applied to specific outputs, so the transaction can include further outputs not endorsed by the signature.
| Sighash Type | Marker | Description | Libbitcoin API |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL | 0x01 | Signs all inputs and outputs | sighash_algorithm::all |
| NONE | 0x02 | Signs all inputs, outputs modifiable | sighash_algorithm::none |
| SINGLE | 0x03 | Signs all inputs and single output, other outputs modifiable | sighash_algorithm::single |
Note: Selectively endorsing inputs is done with the ANYONECANPAY sighash modifier, which is covered later in this chapter.
The illustration below illustrates the signature derivation for an input with the sighash set to ALL:
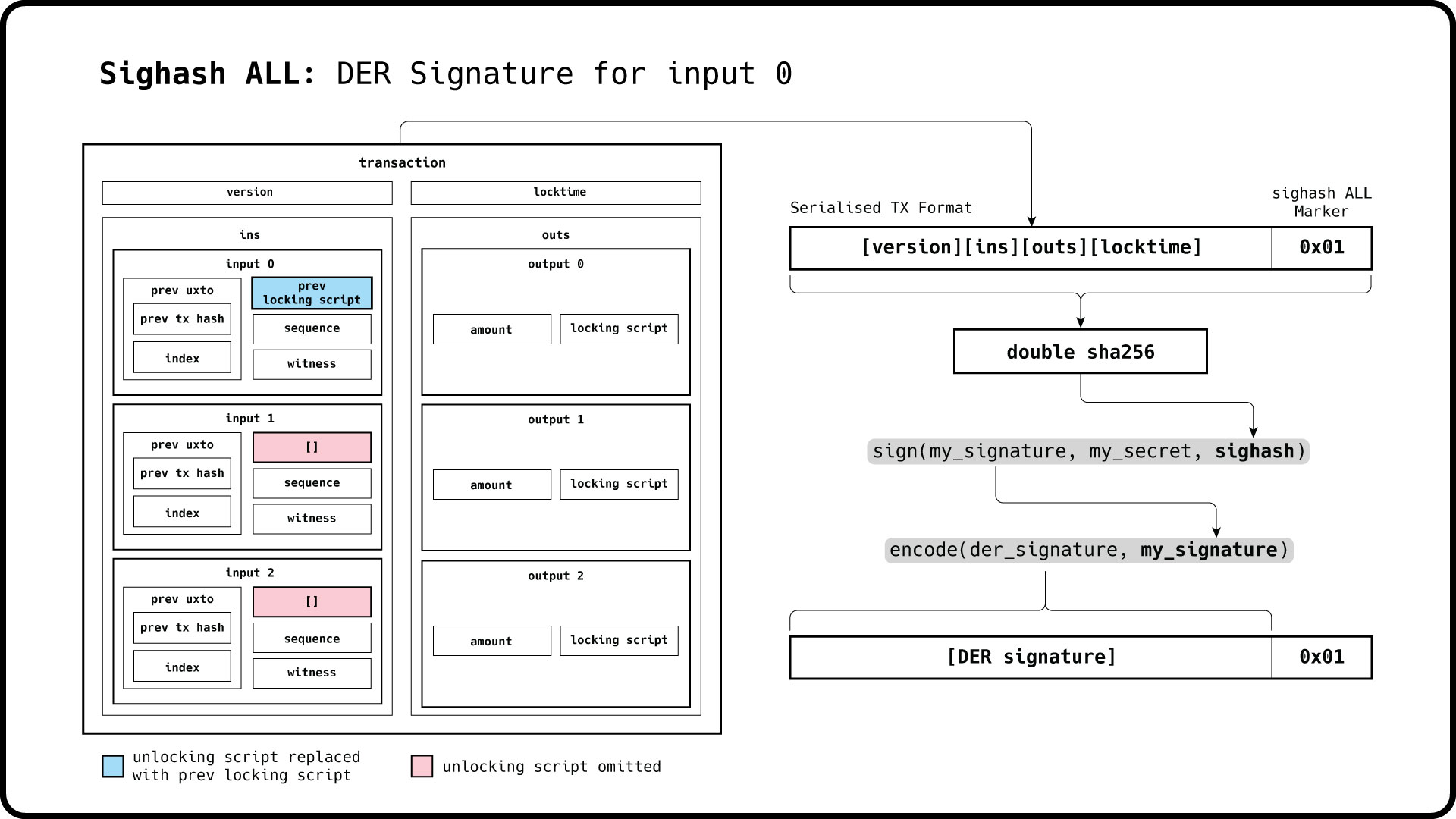
Since the entire transaction is included in the sighash that is signed, we must first construct the complete set of inputs and outputs before the signatures are created.
Note that for each input signing, we place the previous transaction's scriptPubKey or locking script in the scriptSig field of the respective input
//Namespace
using namespace bc;
using namespace machine; //opcode
using namespace chain; //transaction, inputs, outputs, script// Not shown:
// Construction of inputs and outputs.
// Finalise TX - can't be modified later.
tx.inputs().push_back(input_0); //first input
tx.inputs().push_back(input_1); //second input
//...nth input
tx.outputs().push_back(output_0); //first output
tx.outputs().push_back(output_1); //second output
//...nth output
// Construct previous output script of input_0 & input_1.
script prevout_script0 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address0.hash());
script prevout_script1 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address1.hash());
// TX signature for input_0.
endorsement sig_0;
uint8_t input0_index(0u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_0, my_secret0, prevout_script0, tx,
input0_index, sighash_algorithm::all);
// TX signature for input_1.
endorsement sig_1;
uint8_t input1_index(1u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_1, my_secret1, prevout_script1, tx,
input1_index, sighash_algorithm::all);
// Construct input script_0.
operation::list sig_script_0;
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(sig_0));
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey0)));
script input_script0(sig_script_0);
// Construct input script_1.
operation::list sig_script_1;
sig_script_1.push_back(operation(sig_1));
sig_script_1.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey1)));
script input_script1(sig_script_1);
// Add unlockingscript to TX.
tx.inputs()[input0_index].set_script(input_script0);
tx.inputs()[input1_index].set_script(input_script1);
// ALL: We cannot modify TX after signing.We then verify the input scripts and the included endorsements. If necessary, you can consult the documentation chapters on script verification and the script machine.
witness empty_witness; // Only verified in a p2w tx.
uint64_t prevout_amount(1); // Only verified in a p2w endorsement.
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 0.
auto ec_input0 = script::verify(tx, input0_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script0, empty_witness, prevout_script0,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input0.message() << std::endl;
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 1.
auto ec_input1 = script::verify(tx, input1_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script1, empty_witness, prevout_script1,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input1.message() << std::endl;Signing an input with the sighash marker set to NONE omits all outputs in the sighash which is signed.
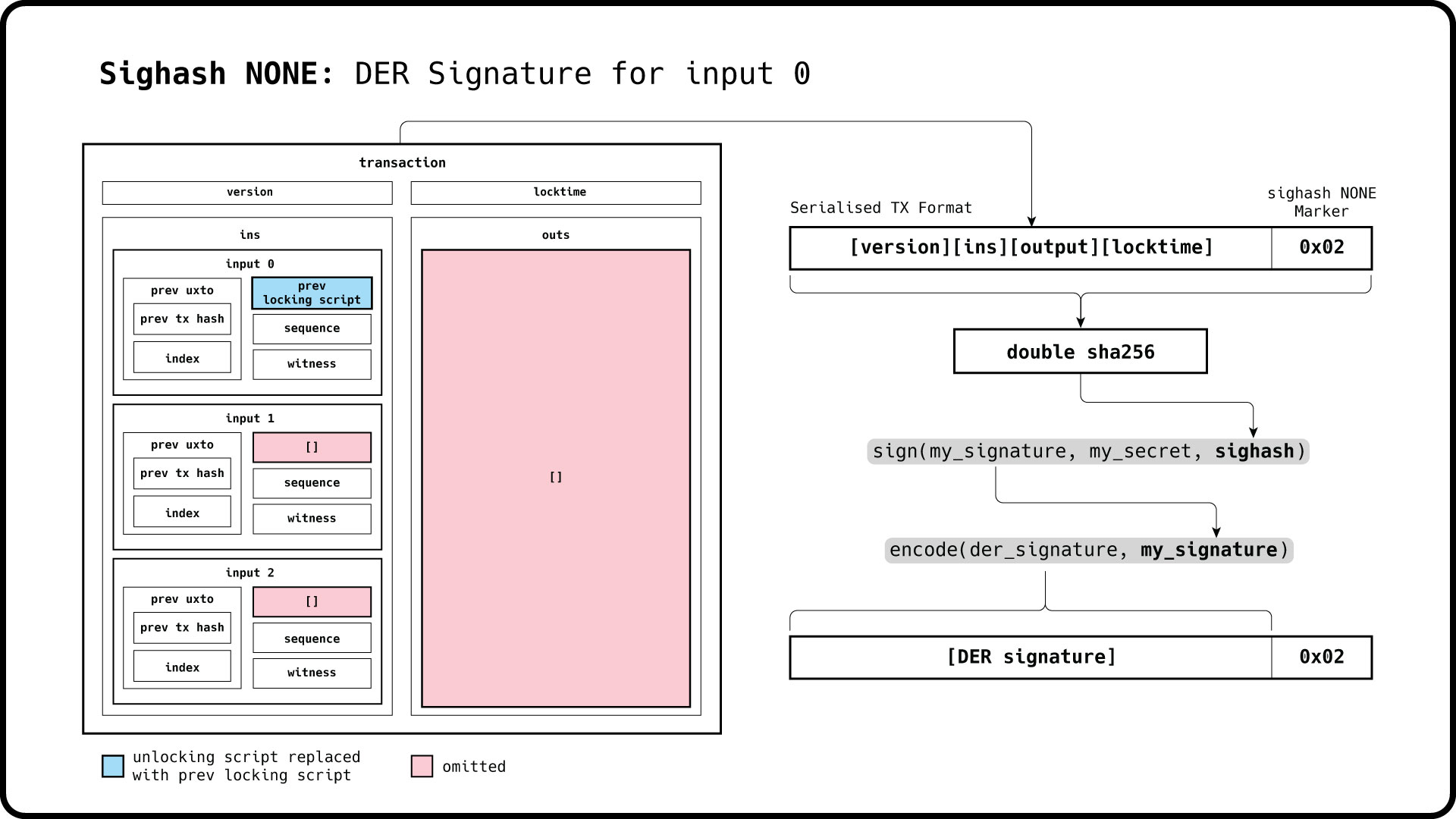
We can therefore modify any output after the input signatures are created.
// Not shown:
// Construction of inputs and outputs.
// We only need to finalise inputs. Outputs can be modified after signing.
tx.inputs().push_back(input_0); //first input
tx.inputs().push_back(input_1); //second input
//...nth input
// Construct previous output script of input_0 & input_1
script prevout_script0 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address0.hash());
script prevout_script1 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address1.hash());
// TX signature for input_0.
endorsement sig_0;
uint8_t input0_index(0u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_0, my_secret0, prevout_script0, tx,
input0_index, sighash_algorithm::none);
// TX signature for input_1.
endorsement sig_1;
uint8_t input1_index(1u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_1, my_secret1, prevout_script1, tx,
input1_index, sighash_algorithm::none);
// Construct input script_0.
operation::list sig_script_0;
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(sig_0));
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey0)));
script input_script0(sig_script_0);
// Construct input script_1.
operation::list sig_script_1;
sig_script_1.push_back(operation(sig_1));
sig_script_1.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey1)));
script input_script1(sig_script_1);
// Add unlockingscript to TX.
tx.inputs()[input0_index].set_script(input_script0);
tx.inputs()[input1_index].set_script(input_script1);
// NONE: We can modify all outputs after signing
tx.outputs().push_back(output_0); //first output
tx.outputs().push_back(output_1); //second output
//...nth output
witness empty_witness; // Only verified in a p2w tx.
uint64_t prevout_amount(1); // Only verified in a p2w endorsement.
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 0.
auto ec_input0 = script::verify(tx, input0_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script0, empty_witness, prevout_script0,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input0.message() << std::endl;
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 1.
auto ec_input1 = script::verify(tx, input1_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script1, empty_witness, prevout_script1,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input1.message() << std::endl;A signature with the sighash marker set to SINGLE will only endorse or fix a single output with the same index as the input being signed. All other outputs can be modified later.
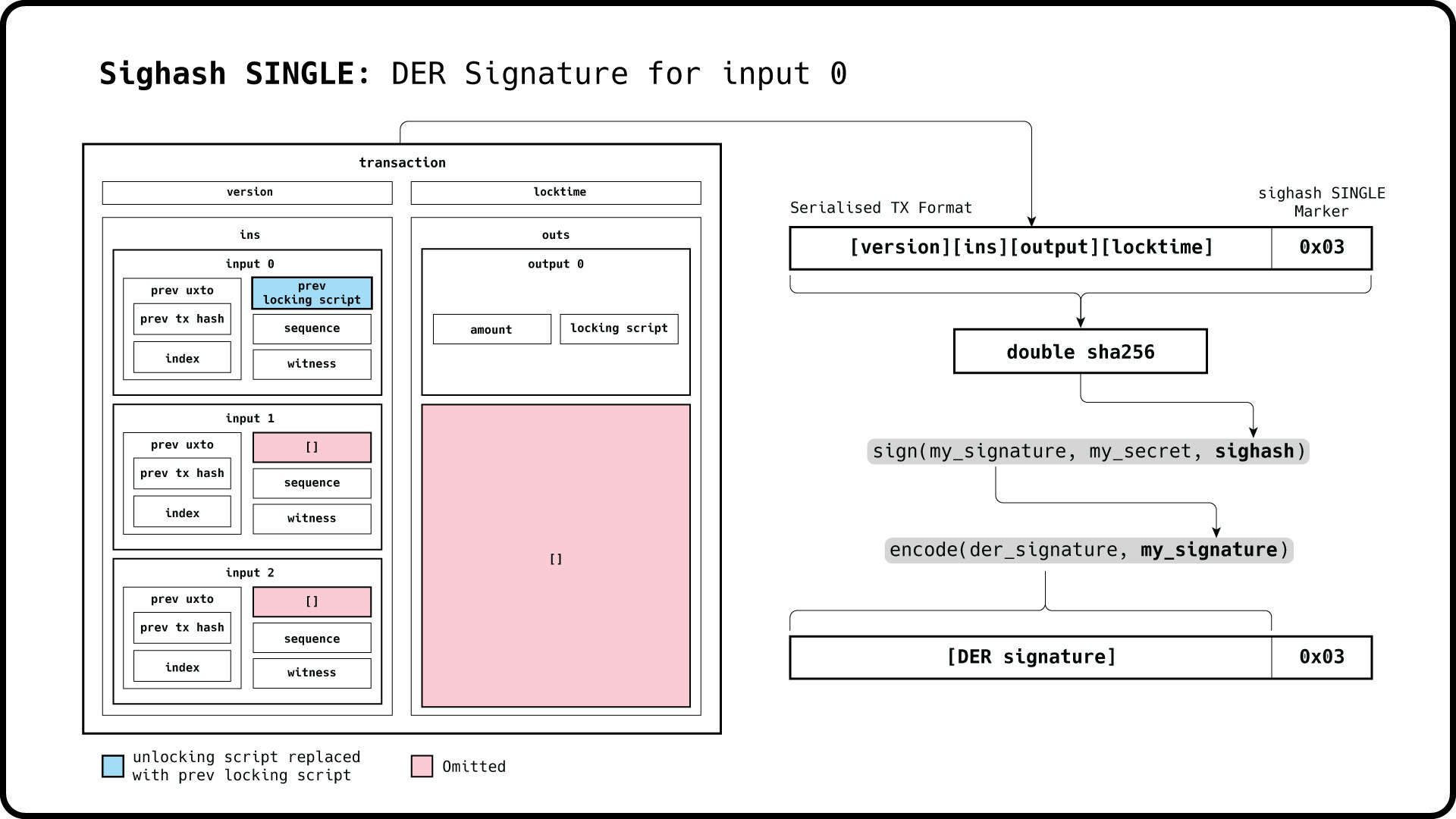
In the following example, we will sign a transaction with 2 inputs and 2 outputs, but add further outputs later on.
// Not shown:
// Construction of inputs and outputs.
// We sign all inputs and single output with same index.
tx.inputs().push_back(input_0); //first input
tx.outputs().push_back(output_0); //first output
tx.inputs().push_back(input_1); //second input
tx.outputs().push_back(output_1); //second output
//...nth input
//...nth output
// Construct previous output scripts of input_0 & input_1.
script prevout_script0 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address0.hash());
script prevout_script1 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address1.hash());
// TX signature for input_0.
endorsement sig_0;
uint8_t input0_index(0u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_0, my_secret0, prevout_script0, tx,
input0_index, sighash_algorithm::single);
// TX signature for input_1.
endorsement sig_1;
uint8_t input1_index(1u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_1, my_secret1, prevout_script1, tx,
input1_index, sighash_algorithm::single);
// Construct input script_0.
operation::list sig_script_0;
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(sig_0));
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey0)));
script input_script0(sig_script_0);
// Construct input script_1.
operation::list sig_script_1;
sig_script_1.push_back(operation(sig_1));
sig_script_1.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey1)));
script input_script1(sig_script_1);
// Add unlockingscript to TX.
tx.inputs()[input0_index].set_script(input_script0);
tx.inputs()[input1_index].set_script(input_script1);
// SINGLE: We can add additional outputs after signing.
tx.outputs().push_back(output_2); //third output
//...nth output
witness empty_witness; // Only verified in a p2w tx.
uint64_t prevout_amount(1); // Only verified in a p2w endorsement.
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 0.
auto ec_input0 = script::verify(tx, input0_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script0, empty_witness, prevout_script0,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input0.message() << std::endl;
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 1.
auto ec_input1 = script::verify(tx, input1_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script1, empty_witness, prevout_script1,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input1.message() << std::endl;The sighash modifier ANYONECANPAY enables inputs to be modified after signing, and can be combined with the previous sighash markers.
| Sighash Type | Marker | Description | Libbitcoin API |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALL + ANYONECANPAY | 0x81 | Signs single input and all outputs, inputs modifiable | sighash_algorithm::all_anyone_can_pay |
| NONE + ANYONECANPAY | 0x82 | Signs single input, inputs & outputs modifiable | sighash_algorithm::none_anyone_can_pay |
| SINGLE + ANYONECANPAY | 0x83 | Signs single input, and single output, other inputs & outputs modifiable | sighash_algorithm::single_anyone_can_pay |
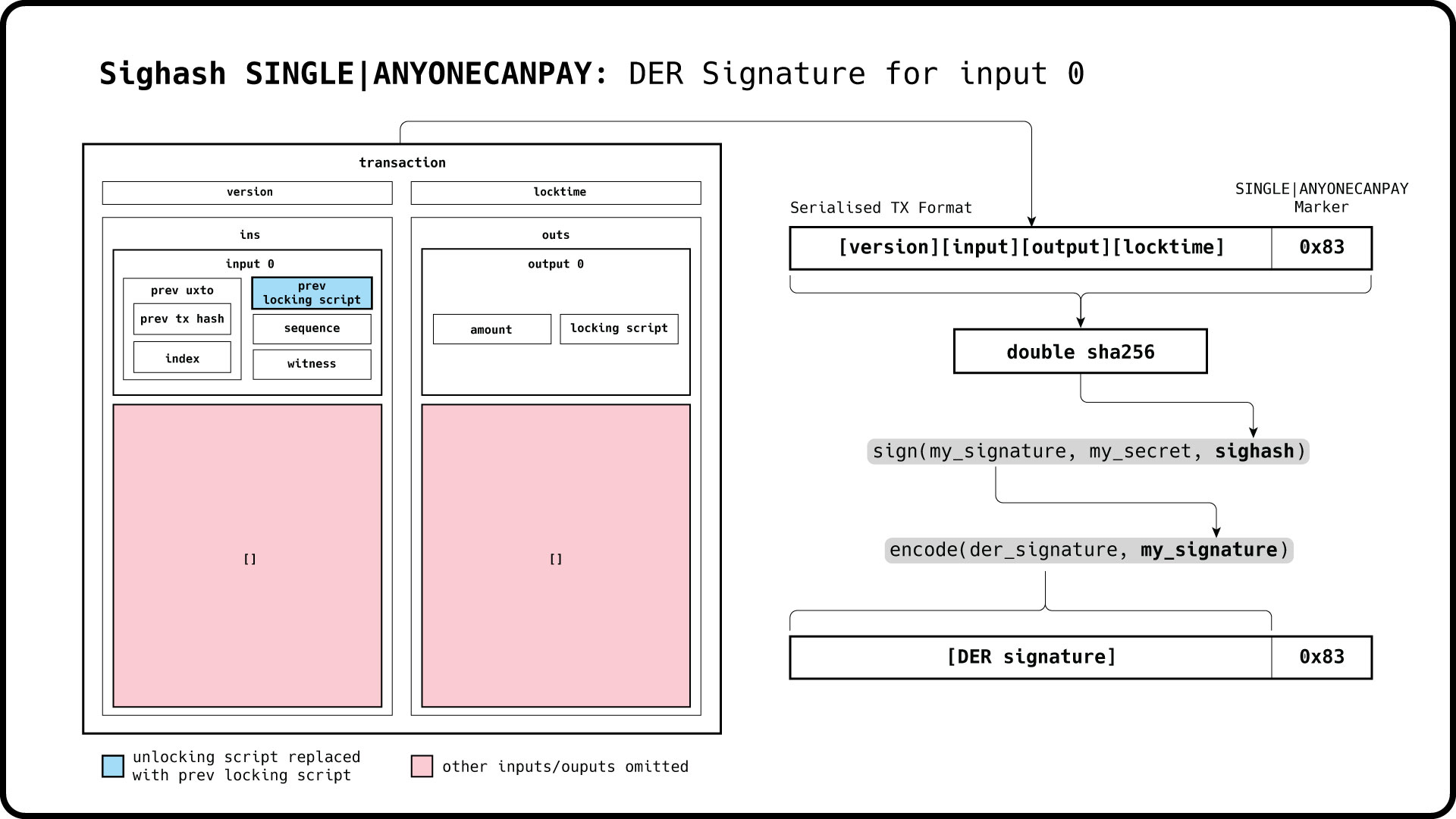
The following image illustrates the signature derivation for an input set to SINGLE|ANYONECANPAY
Sighash Example: NONE|ANYONECANPAY
We construct a transaction with a NONE|ANYONECANPAY input signature below:
// Not shown:
// Construction of inputs and outputs.
// We only sign a single input.
tx.inputs().push_back(input_0);
// Construct previous output script of input_0.
script prevout_script0 = script::to_pay_key_hash_pattern(my_address0.hash());
// TX signature for input_0.
endorsement sig_0;
uint8_t input0_index(0u);
script::create_endorsement(sig_0, my_secret0, prevout_script0, tx,
input0_index, none_anyone_can_pay);
// Construct input script_0.
operation::list sig_script_0;
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(sig_0));
sig_script_0.push_back(operation(to_chunk(pubkey0)));
script input_script0(sig_script_0);
// Add unlockingscript to TX.
tx.inputs()[input0_index].set_script(input_script0);
// ANYONECANPAY: We can modify other inputs after signing.
// Important: input added here must include valid input script!
// ...and previously be signed with tx index = 1
tx.inputs().push_back(input_1); //second input
//...nth input
// NONE: We can modify all outputs after signing.
tx.outputs().push_back(output_0); //first output
tx.outputs().push_back(output_1); //second output
//...nth output
witness empty_witness; // Only verified in a p2w tx.
uint64_t prevout_amount(1); // Only verified in a p2w endorsement.
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 0.
auto ec_input0 = script::verify(tx, input0_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script0, empty_witness, prevout_script0,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input0.message() << std::endl;
// Verify input script (and endorsement) for input 1.
auto ec_input1 = script::verify(tx, input1_index,rule_fork::all_rules,
input_script1, empty_witness, prevout_script1,
prevout_amount);
// Success.
std::cout << ec_input1.message() << std::endl;You can find the entire chapter example code here.
Users | Developers | License | Copyright © 2011-2024 libbitcoin developers
- Home
- manifesto
- libbitcoin.info
- Libbitcoin Institute
- Freenode (IRC)
- Mailing List
- Slack Channel
- Build Libbitcoin
- Comprehensive Overview
- Developer Documentation
- Tutorials (aaronjaramillo)
- Bitcoin Unraveled
-
Cryptoeconomics
- Foreword by Amir Taaki
- Value Proposition
- Axiom of Resistance
- Money Taxonomy
- Pure Bank
- Production and Consumption
- Labor and Leisure
- Custodial Risk Principle
- Dedicated Cost Principle
- Depreciation Principle
- Expression Principle
- Inflation Principle
- Other Means Principle
- Patent Resistance Principle
- Risk Sharing Principle
- Reservation Principle
- Scalability Principle
- Subjective Inflation Principle
- Consolidation Principle
- Fragmentation Principle
- Permissionless Principle
- Public Data Principle
- Social Network Principle
- State Banking Principle
- Substitution Principle
- Cryptodynamic Principles
- Censorship Resistance Property
- Consensus Property
- Stability Property
- Utility Threshold Property
- Zero Sum Property
- Threat Level Paradox
- Miner Business Model
- Qualitative Security Model
- Proximity Premium Flaw
- Variance Discount Flaw
- Centralization Risk
- Pooling Pressure Risk
- ASIC Monopoly Fallacy
- Auditability Fallacy
- Balance of Power Fallacy
- Blockchain Fallacy
- Byproduct Mining Fallacy
- Causation Fallacy
- Cockroach Fallacy
- Credit Expansion Fallacy
- Debt Loop Fallacy
- Decoupled Mining Fallacy
- Dumping Fallacy
- Empty Block Fallacy
- Energy Exhaustion Fallacy
- Energy Store Fallacy
- Energy Waste Fallacy
- Fee Recovery Fallacy
- Genetic Purity Fallacy
- Full Reserve Fallacy
- Halving Fallacy
- Hoarding Fallacy
- Hybrid Mining Fallacy
- Ideal Money Fallacy
- Impotent Mining Fallacy
- Inflation Fallacy
- Inflationary Quality Fallacy
- Jurisdictional Arbitrage Fallacy
- Lunar Fallacy
- Network Effect Fallacy
- Prisoner's Dilemma Fallacy
- Private Key Fallacy
- Proof of Cost Fallacy
- Proof of Memory Façade
- Proof of Stake Fallacy
- Proof of Work Fallacy
- Regression Fallacy
- Relay Fallacy
- Replay Protection Fallacy
- Reserve Currency Fallacy
- Risk Free Return Fallacy
- Scarcity Fallacy
- Selfish Mining Fallacy
- Side Fee Fallacy
- Split Credit Expansion Fallacy
- Stock to Flow Fallacy
- Thin Air Fallacy
- Time Preference Fallacy
- Unlendable Money Fallacy
- Fedcoin Objectives
- Hearn Error
- Collectible Tautology
- Price Estimation
- Savings Relation
- Speculative Consumption
- Spam Misnomer
- Efficiency Paradox
- Split Speculator Dilemma
- Bitcoin Labels
- Brand Arrogation
- Reserve Definition
- Maximalism Definition
- Shitcoin Definition
- Glossary
- Console Applications
- Development Libraries
- Maintainer Information
- Miscellaneous Articles