Section 1 ROS Bags - ika-rwth-aachen/acdc GitHub Wiki
This subsection shows how to record and play back data from ROS topics such that you can store them.
In this exercise you will learn
- how to use rosbag record to save data from ROS topics
- to analysis rosbags with rosbag info and the rqt logging feature
- how to play back data from a robag with to hands-on examples
- Contents
- Prerequisites
- ROS bag command line tool
- RQT bag GUI
- CARLA Application: Combination of ROS Bag, RViz, ROS Launch
- Wrap-up
Start multiple terminals in an acdc docker container and start:
roscoreFrom official ROS documentation: A bag is a file format in ROS for storing ROS message data. Bags - so named because of their .bag extension - have an important role in ROS, and a variety of tools have been written to allow you to store, process, analyze, and visualize them.
The command line tool for dealing with bags is rosbag. Check out its functionalities:
rosbagWe will use rosbag record, info, and play.
In the following, we will record all messages from the /vehicle/actuator_commands topic. Therefore, first start the flatland simulation:
roslaunch racing flatland_simulation.launchIn another terminal, find out how to use rosbag record:
rosbag record --helpWe see that the command expects topic names to be recorded as arguments. Besides that, there are many useful options which are not important now. rosbag record stores the recorded .bag file in the current directory of the terminal in which it is executed. Therefore, navigate into the racing package:
roscd racingRecord all messages that are published to the /vehicle/actuator_commands topic from now on:
rosbag record /vehicle/actuator_commandsSo far, nobody publishes to this topic yet. Therefore, open a new terminal window and execute the vehicle controller so actual messages are available for recording:
roslaunch racing racing_controller.launchOnce the cart is stuck, stop the recording by hitting Ctrl+C in the "rosbag record" terminal. Also terminate the controller and the flatland simulation for now.
In your "rosbag record" terminal, you can now see the recorded .bag file with a time stamp in its name:
ls
In a real-world project, bag files usually become too large (multiple GB) for tracking them inside a git repository. Therefore, the *.bag extension has been added to the so-called .gitignore file of this branch. This means that even though you now have a new file in your git repository, its status is still "clean":
git statusNow, we analyze the newly recorded file:
rosbag info 20<<< HIT TAB FOR AUTO-COMPLETION >>>Useful information are especially "topics" and "types". Note that "duration" is probably shorter than the time span during which rosbag record was just running because the initial interval without available messages has been automatically truncated.
We will now steer the cart from the bag file without a running controller node. Therefore, start the simulation again:
roslaunch racing flatland_simulation.launchFind out how to use rosbag play:
rosbag play --helpIt expects the bag file name (or path) as an argument and accepts a number of further options. Make sure you are in the recorded bag file's directory and execute:
rosbag play -l 20<<< HIT TAB FOR AUTO-COMPLETION >>>The -l option means "loop", so we have the messages available for more than just a few seconds. You should see the cart moving just like before. Pause and resume the playback using Space.
You can record, analyze, and play back bag files also in the rqt plugin rqt_bag.
rqtSelect Plugins --> Logging --> Bag. If there are other open plugins from a config you may have used before, close them, e.g. using Running --> Close [...].
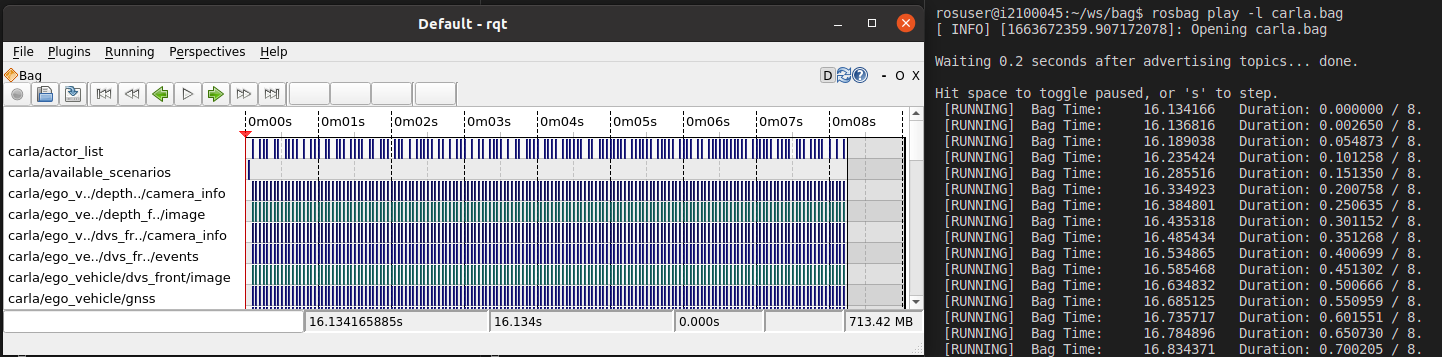
Use  to open the bag file you have just recorded, which brings something like this:
to open the bag file you have just recorded, which brings something like this:

Similar to rosbag play, you can right-click on the topic name and check "publish". Only then, the play symbol  will actually publish this recorded topic.
will actually publish this recorded topic.
If you only want to analyze the bag file within rqt_bag, you can unselect the "Publish" option and instead:
- Right-click the topic name --> View --> Raw (similar to "Topic Monitor")
- Right-click the topic name --> View --> Plot (similar to "Plot")
The main advantage of these rqt_bag plugins over the similar general rqt plugins is the possibility to easily stop and go forward or back in time.
Select linear.x for plotting and play back the file:

In a last step, we observe the provided bag file carla.bag, which was recorded within the CARLA simulator environment. CARLA is a well known, widely used, open-source simulation software, based on Unreal Engine. It comes with a built in ROS bridge, allowing the usage and visualization within ROS. In this Unit, we will visualize some simulation results, contained in the provided carla.bag file.
Download the bag file from the Sciebo project folder and save the file to the local directory ${REPOSITORY}/bag on your host.
wget -O ${REPOSITORY}/bag/carla.bag https://rwth-aachen.sciebo.de/s/LJoX6lL8gdvO2e2/downloadAlternatively, you can download the bag file for this Unit here Link (approx. 700 MB). (In case you have not done yet)
We can use the provided launch file carla.launch in the workshops/section_1/carla/ folder to play the rosbag together with the provided carla_ad_demo.rviz configuration in Rviz.
cd src/workshops/section_1/carla
roslaunch carla.launchNote: Using roslaunch is possible outside of a defined ROS package, but we have to launch it from the corresponding folder.
The launch file replays all recorded topics from the bag file and visualizes them inside of RViz.
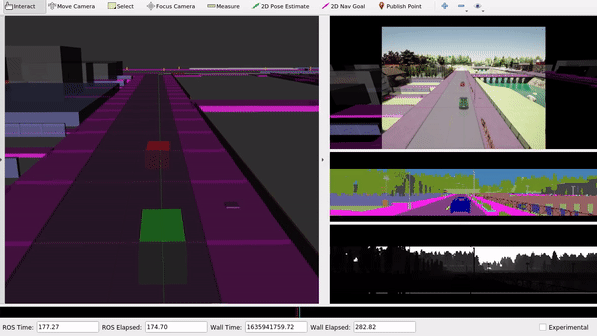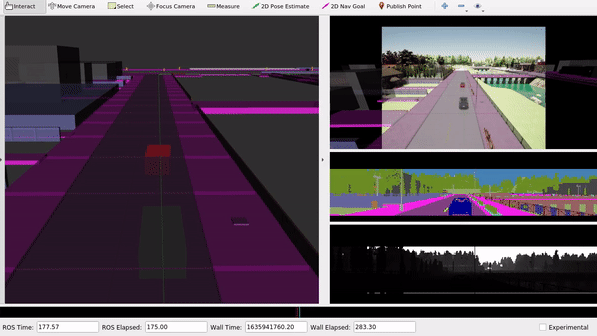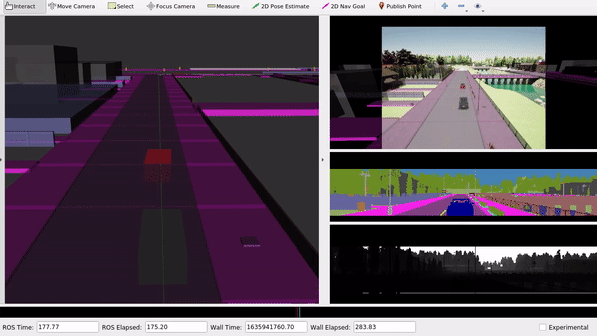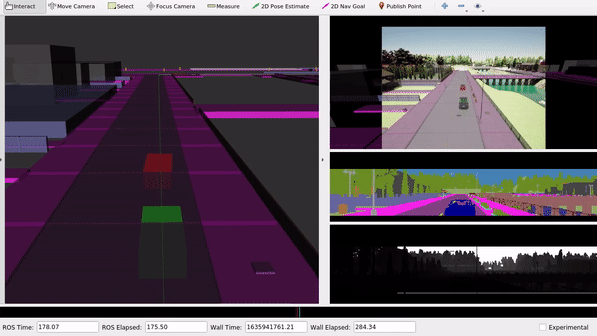
We can observe the different sensor data which are captured for the simulated scene in CARLA. Within ROS, we could use those sensor topics for further data processing.
- You learned to use the
rosbagcommand to record, analyze, or play data within rosbags - You learned how to analyze rosbag data in more detail with rqt

