basics testing and injecting transactions - SkycoinWikis/CXChains GitHub Wiki
 HOME » CX » CX CHAINS » TESTING AND INJECTING TRANSACTIONS
HOME » CX » CX CHAINS » TESTING AND INJECTING TRANSACTIONS
Testing and Injecting Transactions
Once a CX chain has been initialized, transactions can be run against the program state stored on the blockchain. There are two flags that can be used for this purpose: --transaction and --broadcast, where the first flag is used to only retrieve the current program state of a CX chain and run the transaction code against it locally, and the latter is used to additionally broadcast the transaction. For example, consider the following blockchain and transaction codes:
package number
var Num i32
func main() {
Num = 10
}
package main
import "number"
func main() {
number.Num = 11
}
If the transaction code in the second snippet is run using the --transaction flag, the program state of the CX chain represented by the first code snippet will still be holding 10 as the value of the global variable Num. In contrast, if the second code snippet is run using the --broadcast flag, the program state of the CX chain will be mutated, and the value of the global variable Num will now be changed to 11.
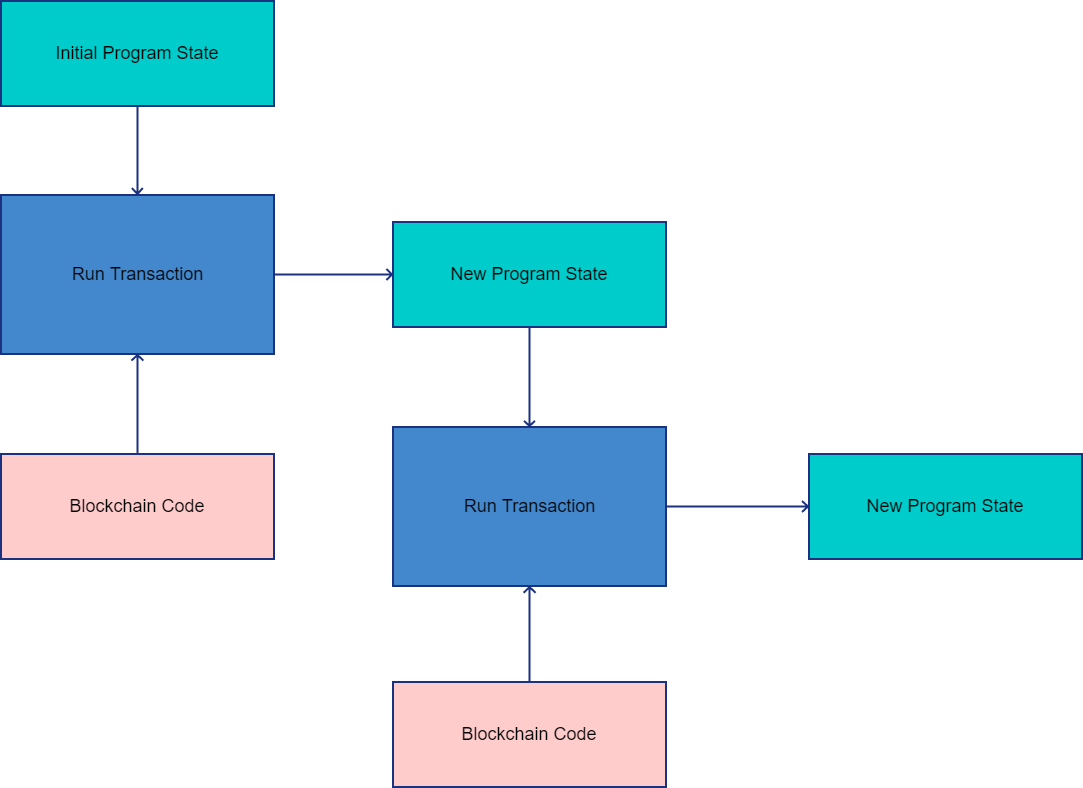
The diagram below depicts the workflow of a CX chain after its initialization. It can be seen how blockchain codes are used to form a transaction that will be changing the current program state in order to generate a new program state to be used by future transactions.