Sequencing Technologies - NBISweden/workshop-genome_assembly GitHub Wiki
A description of common sequencing technologies used in De novo sequence assembly, including diagrams and videos:
- Illumina
- Pacific Biosciences
- Oxford Nanopore
- 10X Genomics
- Hi-C
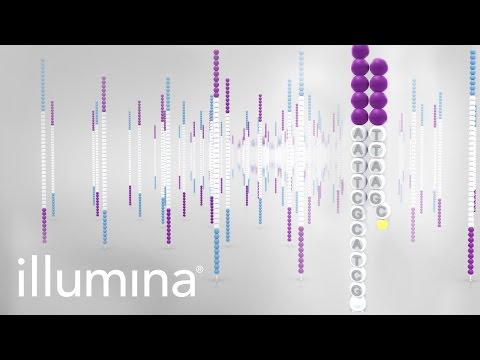
Illumina
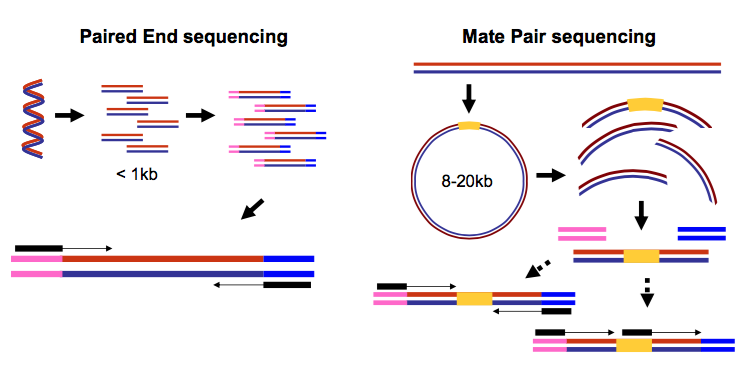
Illumina produces different types of libraries. The two most common for genomic data are Paired-end (PE) and Mate-pair (MP) libraries.
Paired End Library
Description:
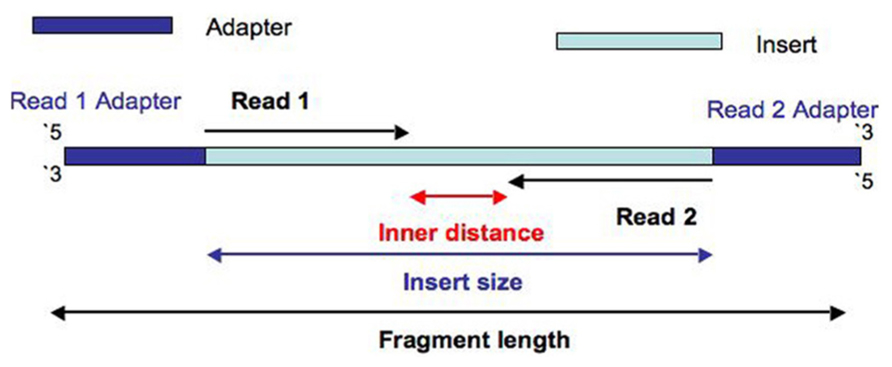
Illumina data is created by taking DNA and fragmenting it down to an approximate size, e.g 500bp. After ligating adapters and barcodes, the fragments are amplified on a flowcell in a process called Bridge-Amplification. Flourescently barcoded nucleotides are incorporated in cycles, and images are taken of the flowcell at each cycle to determine the incorporated nucleotide. The number of cycles determines the read length. The process is first applied to the forward strand, then the barcode, and finally the reverse strand. After processing, this results in two data files containing the forward and reverse ends of the DNA fragment, annotated with the barcode.
Diagram of the data:
Video of the sequencing process:
Mate pair Library
Description:
To produce Mate pair libraries, size selected long DNA fragments are labelled with biotin on both ends, and circularized using a linker. These DNA circles are then fragmented down to a size suitable for paired end sequencing. DNA fragments containing the biotin marker are then selected, and loaded onto the Illumina flowcell where it is sequenced using the method above.
Diagram of the data:
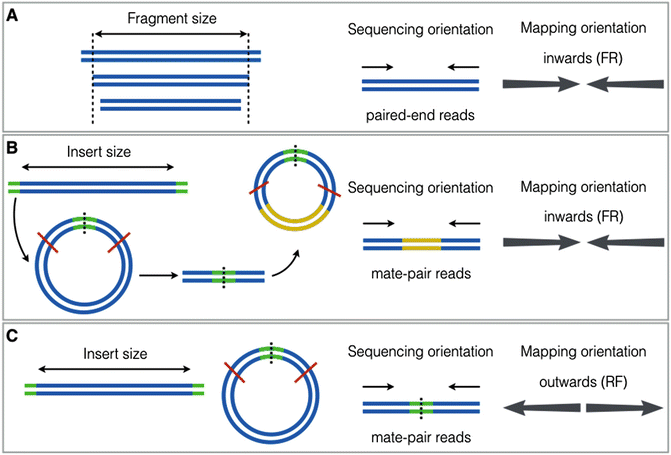
A primary difference between Mate pair and Paired end data, besides the insert size, is the orientation of the reads. This depends on the library preparation kit used to make the library. In the figure below, mate pairs are prepared using different kits in B and C, changing the orientation of the reads in the resulting data.
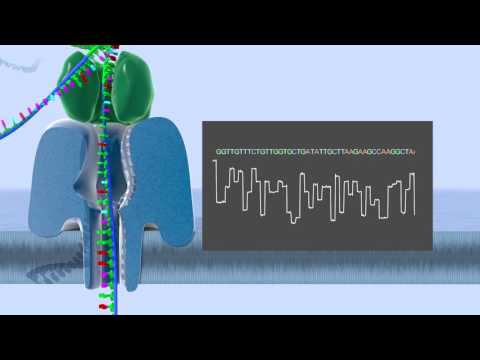
Pacific Biosciences
Description:
The Pacific Biosciences platform (PacBio) is a single molecule sequencing platform, meaning the DNA is not amplified. Long fragments of double-stranded DNA are ligated to hairpin adapters at both ends of the DNA molecule. This construct is then loaded into a zero-mode waveguide on a SMRT chip, where the molecule is denatured and sequenced. A polymerase attaches itself to the single stranded DNA circle, and light signals are captured at each phospholinked nucleotide incorporation in the zero-mode waveguide. The sequences of light signals are then translated into nucleotides. These sequences are known as polymerase reads, and potentially contain multiple copies of the DNA molecule in both the forward and reverse directions, and the hairpin adapter sequence. After processing the polymerase reads to remove adapter sequence, subreads are left. If these subreads are processed further, the result are Circular consensus reads (CCS), alternatively known as Reads of Insert (RoI). De novo assemblies typically use PacBio subread data as input.
Diagram of the data:

Video of the sequencing process:
Oxford Nanopore
Description:
Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) is another single molecule sequencing technology, that is quickly rising in popularity. DNA is mixed with processive enzymes, that upon approaching a nanopore, feed single strands through the nanopore apertures. An electrical current is passed through each nanopore and the disruption measured as each base is fed through. These electrical signals are then translated into nucleotide sequences.
Diagram of the data:

Video of the sequencing process:
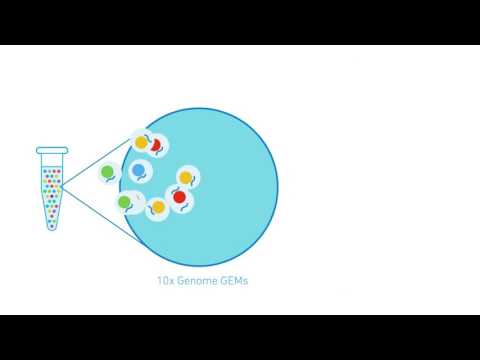
10X Genomics
Description:
10X Genomics genome sequencing takes advantage of both long reads and short read sequencing. Molecules from high molecular weight genomic DNA are partitioned into GEMs using the Chromium Controller device. GEMs are gel-emlusion droplets that each contain approximately 10 HMW gDNA molecules mixed with barcoded primers and incubation enzymes. GEMs undergo isothermal incubation which generates 10X barcoded amplicons, such that every fragment from the same GEM has a common 10X barcode. These amplicons are then suitable for Paired End sequencing using the Illumina platform. Although there are approximately 10 molecules per GEM, it's highly unlikely that two molecules from the same locus from opposing haplotypes will have the same 10X barcode.
Diagram of the data:

The amplicons are sequenced on the Illumina platform, where the first 16bp of read 1 contain the 10X barcode.

Video of the sequencing process:
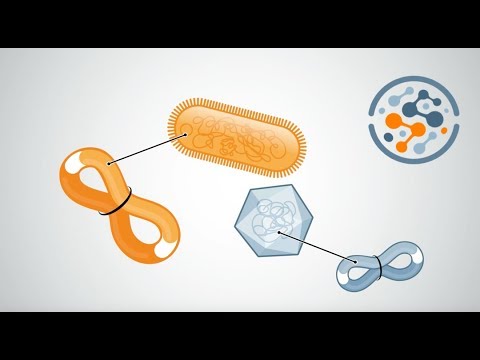
Hi-C
There are many flavours of Hi-C available for scaffolding, such as from Phase Genomics, or Dovetail Genomics.
Description:
Within cells, DNA is cross-linked to physically close DNA. The DNA is then fragmented using endonucleases, and the fragmented loci are biotinylated and ligated in a step called proximity ligation. Biotinylated loci are then purified and sequenced using a paired end sequencing platform, such as Illumina.
Diagram of the data:

Video of the sequencing process:
Phase Genomics:
Dovetail Genomics: