LDAP - yolmant/LDAP GitHub Wiki
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) is a software protocol for enabling anyone to locate organizations, individuals, and other resources such as files and devices in a network, whether on the public Internet or on a corporate intranet. LDAP is a "lightweight" (smaller amount of code) version of Directory Access Protocol (DAP), which is part of X.500, a standard for directory services in a network. LDAP is lighter because in its initial version it did not include security features. LDAP originated at the University of Michigan and has been endorsed by at least 40 companies. Netscape includes it in its latest Communicator suite of products. Microsoft includes it as part of what it calls Active Directory in a number of products including Outlook Express. Cisco also supports it in its networking products.
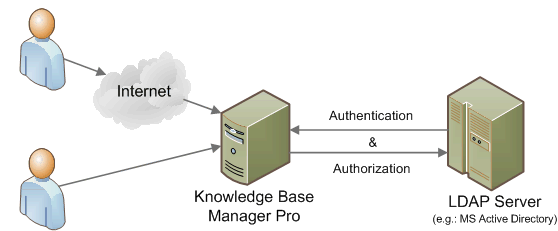
Protocol:
A client starts an LDAP session by connecting to an LDAP server, called a Directory System Agent (DSA), by default on TCP and UDP port 389, or on port 636 for LDAPS.[9] Global Catalog is available by default on ports 3268, and 3269 for LDAPS.[10] The client then sends an operation request to the server, and the server sends responses in return. With some exceptions, the client does not need to wait for a response before sending the next request, and the server may send the responses in any order. All information is transmitted using Basic Encoding Rules (BER).
operations:#
StartTLS — use the LDAPv3 Transport Layer Security (TLS) extension for a secure connection Bind — authenticate and specify LDAP protocol version Search — search for and/or retrieve directory entries Compare — test if a named entry contains a given attribute value Add a new entry Delete an entry Modify an entry Modify Distinguished Name (DN) — move or rename an entry Abandon — abort a previous request Extended Operation — generic operation used to define other operations Unbind — close the connection (not the inverse of Bind)