slides - wrongbaud/ghidra-utils GitHub Wiki
Godzilla Vs. Kong Vs. Ghidra
Exercises in Ghidra scripting and emulation Matthew Alt / wrongbaud
Outline
- Intro
- Problem Description
- Ghidra Scripting
- Example demo
- PCode Emulation
- Example demo
- Conclusion
- Maybe more emulation?
Intro / whoami
- Twitter: @wrongbaud / @voidstarsec
- Embedded systems reverse engineer
- Started in automotive performance industry
- Currently work as a security researcher for CCSW / VoidStar Security
- I write musings about RE / training at wrongbaud.github.io / voidstarsec.com
Problem Description / Goals
-
Ghidra's API is extremely powerful when attempting to automate reverse engineering tasks
- There aren't many examples online
- Let's fix this!
-
Target ROM: Kong: King of Atlantis
-
RE Goal: Determine what passwords are valid
Next Steps
- Step 1: Load the ROM into Ghidra
- Step 2: Perform Initial Analysis
- Step 3: Locate subroutines responsible for parsing the passwords
- Step 4: ???
- Step 5: Profit!
Initial Analysis Results

Initial Analysis Results
If we take a cursory look through all of these functions, we can see that most of them have a similar function prologue:

Initial Analysis Results
From this, we can infer a couple of things about this codebase:
- A large amount of this code seems to be operating in ARM's Thumb mode
- Most of these functions seem to begin with the same function prologue
Initial Analysis Results

Initial Analysis Results
If we attempt to disassemble this data as THUMB code, we see the following appear:
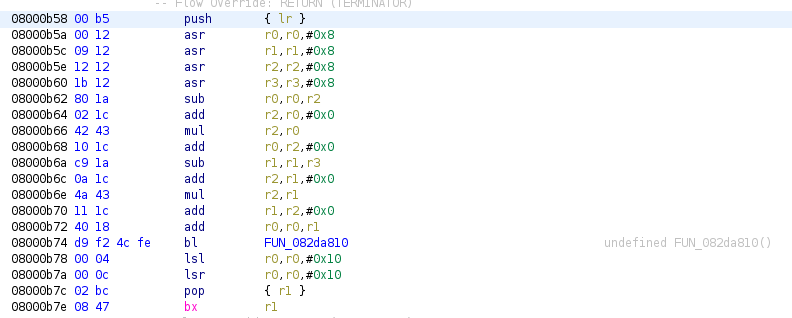
Initial Analysis Results
- We have two options going forward:
- Search for byte sequences / undefined code regions and create them manually
- Search for byte/instruction sequences that match the
pushinstruction and attempt to automate function discovery
- We can utilize Ghidra's API for the second option!
Ghidra Scripting
- We can utilize Ghidra's API to automate some of this analysis for us!
- Ghidra's script manager is an excellent place to start
- Using the examples from the script manager, we can find the building blocks of what we need
- The next few examples will be ... live
Ghidra Scripting - Useful API Calls
currentProgram.getMemory()- Returns the memory space of the program being analyzedmemory.findBytes(start, end, functionBytes, null, true, monitor)- Searches the memory space for the provided byte sequencegetFunctionContaining(found)- Returns the function that contains the addressfounddisassemble(found)- Attempts to disassemble code at the provided addressfound
Ghidra Scripting
- Our ghidra script was able to locate and define a large amount of functions for us
- Disclaimer: This doesn't mean we found all of them!
- This script can be found in the ghidra-utils github repository
Examining Functions of Interest
- What can we use about our knowledge of the password system to help us discover what functions are interesting?
- They are 7 characters long
- A "wrong password" message is generated when an incorrect password is entered
- Let's take a closer look
PCode
- PCode is a language defined within Ghidra that is used to model processor behavior.
- This language describes what instructions do and how they affect the CPU and its memory space.
- PCode is used to define how instructions work via a predetermined set of operators.
PCode Emulation
- Using Ghidra's API, PCode can be emulated
- Requires knowledge of the following (typically)
- Memory layout
- Memory contents
- Register contents
- The emulation is only as powerful as the information you provide it!
- We can gather this information with
gdb
- We can gather this information with
- Let's emulate!
PCode Emulation - Useful API Calls
emuHelper.setBreakpoint(returnAddress): Sets a breakpoint on our return addressemuHelper.run(mainFunctionEntry, entryInstr, monitor);: Launches the emulation, this blocks until execution stops (i.e our breakpoint is hit!)emuHelper.readRegister("r0"): Allows for the reading of register values during PCode emulationemuHelper.getExecutionAddress(): Returns the current execution address of the emulator
Emulation Results
- After running, our script generated over 800 passwords!
- These can be found on the github repository
- All passwords seem to be valid!
- I've not worked through all 800+ yet
Conclusion
- Ghidra's API / PCode Emulation capabalities can be extremely powerful!
- They can also enable laziness ;)
- Example scripts contained within Ghidra can be a treasure trove of information
- Thank you for listening!
- Please reach out with any questions via twitter/email!