Non Blocking I O - vinhtbkit/bkit-kb GitHub Wiki
Introduction to Java I/O
Traditional Java I/O:
- InputStream and OutputStream classes.
- Blocking nature.
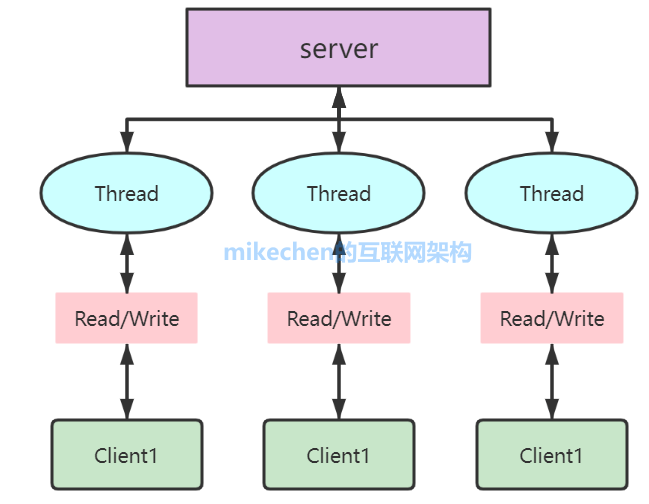
Limitations:
- Scalability issues in high concurrency environments.
- Thread per connection model.
- Introduction to Java NIO
Why NIO?

- Address limitations of traditional I/O.
- Scalability needs for modern applications.
Key Difference:
Behavior
- Blocking I/O blocks a thread until operation completes.
- NIO doesn't block the thread, it can still do other tasks
Resource Utilization
- Blocking I/O: inefficient resource usage with high concurrency, including memory size ( ~2Mb per thread) and CPU for context switching between threads
- NIO: better concurrency since one thread can handle many concurrent I/O operations
Complexity
- Blocking I/O is more simple to work with
- NIO is more complex (selectors, callback) to check or notified when an I/O operation completes.
Core components

- Under the hood, NIO leverages much of the underlying OS to provide non-blocking capabilities
Buffers
- Data container for I/O operations
- Types:
ByteBuffer, CharBuffer, IntBuffer ...
Direct vs Non-direct buffer
- Direct buffers allocate memory in OS-level memory outside the usual JVM heap. They can be more expensive to allocate but can be passed directly to native code without copying.
- Non-direct buffers are stored inside the JVM heap and might need copying when passed to native code.
Structure
- Capacity: The number of elements a buffer can contain.
- Limit: The first element that shouldn't be read or written. You can't read or write data at positions greater than this limit.
- Position: The next element to be read or written. After reading/writing n elements, the position increases by n.
Operations
- flip
- rewind
- clear
- compact
Channels
- Represent open connections to I/O devices.
Sample
FileChannel: to work with filesSocketChannel, ServerSocketChannel: working with network connections
Properties
- Bidirectional: unlike streams (should be either input stream or output stream)
- Support asynchronous operations
Operations
- open / close
- read / write
- configureBlocking
Selectors
- Allows a single thread to handle multiple channels
Selection key
- A channel register with a selector for specific SelectionKey
SelectionKey key = channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
- 4 types: READ, WRITE, CONNECT, ACCEPT
Operations
- select(): blocks until at least one channel is ready
- select(long timeout): blocks until timeout
- selectNow(): non-blocking
Non-blocking IO vs Asynchronous vs Reactive