Transfer existing data from Postgres - v22-appfactory/appfactory-wiki GitHub Wiki
Port existing data
Challenges:
All the tables, schemas, and data need to be brought into Oracle.
There are some differences between Postgres and Oracle in how databases are structured. One of the biggest differences is in how schemas are created and used.
A schema in Postgres is an independent collection of objects, tables, functions, etc. Permissions are granted to users to determine what they are allowed to do in the schema, such as read or write data.
In Oracle, a schema is not independent of a user but one is created for every user, who is the schema owner. This means the data will need to be organized differently than how it is now in Postgres. It is not clear what the best way to organize the data in Oracle is.
Another challenge, to a lesser degree, will be in using different data types than what is available in Postgres. For example, Oracle does not have an integer array type by default. It must be created as a custom type. This may be true for other types that are available in Postgres.
To use the JSON type for a column, when creating a table make the column type CLOB and then add a constraint AS JSON in Oracle.
Currently there are 37 tables under the app schema, and 23 tables under the metadata schema.
Moving the data:
The process of copying the tables will be made easier by using a tools in the Datagrip IDE.
When viewing tables, a user can right click on a Postgres table, and select Copy Table to... to open the dialog.
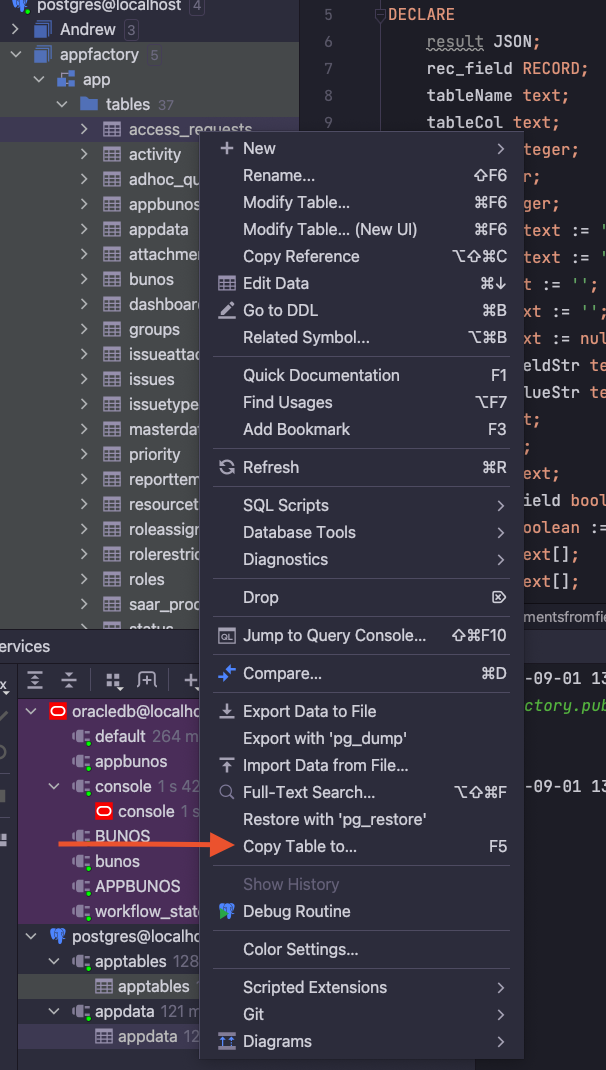
The following menu will appear.
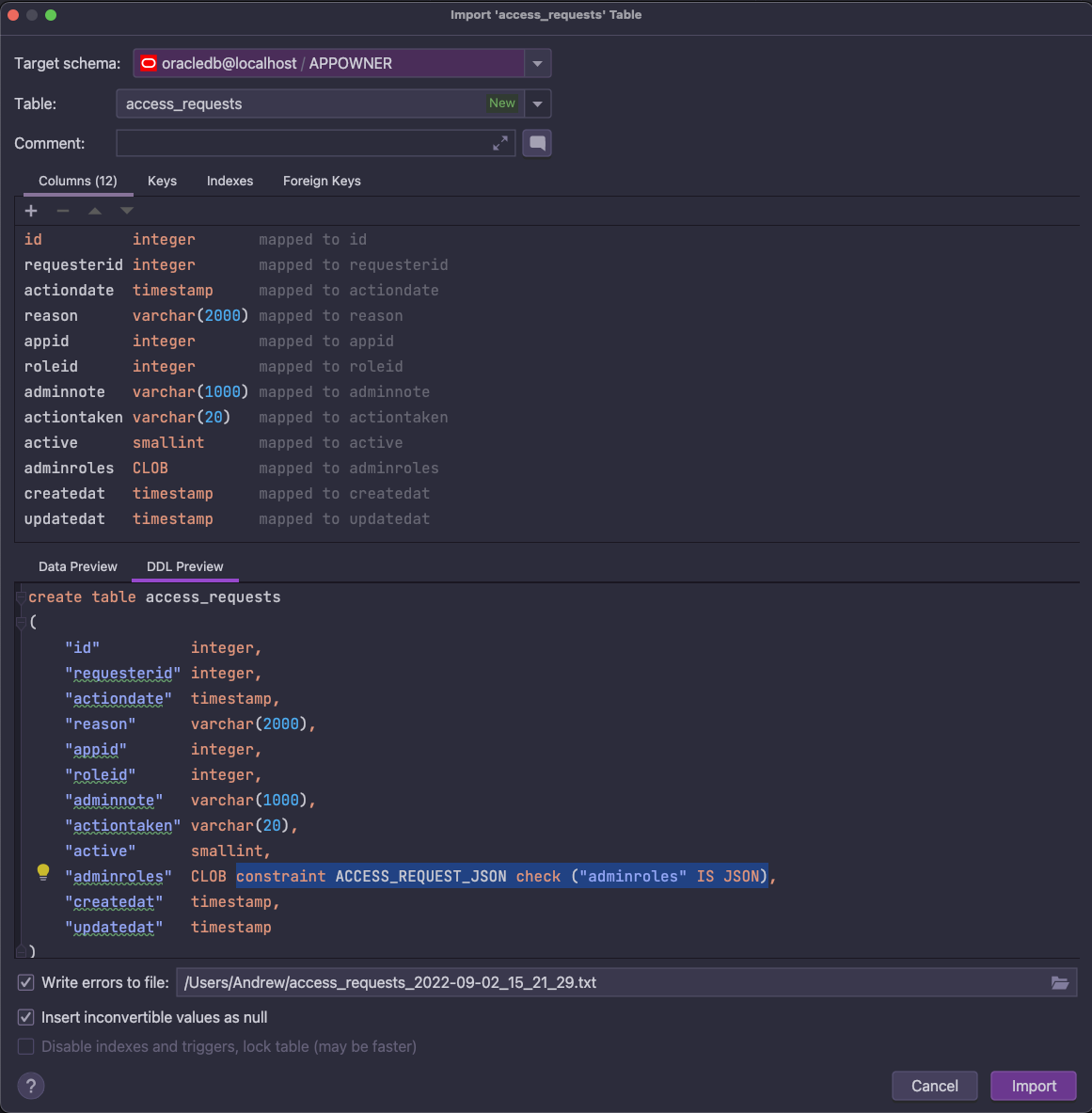
After selecting Import, the table and data will be imported into the Oracle database.
This process could be repeated for all 60 tables.