如何實作 unstack 函數? - tsungjung411/python-study GitHub Wiki
- 就是一個矩陣 A 的分解操作
- 沿著某個軸(維度),將 rank(A) = R 分解成 [R-1, R-1, ..., R-1] 清單
- 清單大小為 A.shape[axis]。
比如:
import numpy
a = numpy.array([
[[111,112],[121,122]],
[[211,212],[221,222]],
[[311,312],[321,322]],
])
print(a.shape)
print(a)(3, 2, 2)
[[[111 112]
[121 122]]
[[211 212]
[221 222]]
[[311 312]
[321 322]]]
unstack 前:
a[0][0][0] = 111
a[0][0][1] = 112
a[0][1][0] = 121
a[0][1][1] = 122
a[1][0][0] = 211
a[1][0][1] = 212
a[1][1][0] = 221
a[1][1][1] = 222
a[2][0][0] = 311
a[2][0][1] = 312
a[2][1][0] = 321
a[2][1][1] = 322根據 axis=1 進行 unstack 後:
# Step1: 把 axis=1 (第二個索引) 搬到最前面,形成新的矩陣
# Step2: 重新排序最前面的索引
a[0]<-[0]___[0] = 111 ---> a[0][0][0] = 111 ---> a[0][0][0] = 111
a[0]<-[0]___[1] = 112 ---> a[0][0][1] = 112 ---> a[0][0][1] = 112
a[1]<-[0]___[0] = 121 ---> a[1][0][0] = 121 ---> a[0][1][0] = 211
a[1]<-[0]___[1] = 122 ---> a[1][0][1] = 122 ---> a[0][1][1] = 212
a[0]<-[1]___[0] = 211 ---> a[0][1][0] = 211 ---> a[0][2][0] = 311
a[0]<-[1]___[1] = 212 ---> a[0][1][1] = 212 ---> a[0][2][1] = 312
a[1]<-[1]___[0] = 221 ---> a[1][1][0] = 221 ---> a[1][0][0] = 121
a[1]<-[1]___[1] = 222 ---> a[1][1][1] = 222 ---> a[1][0][1] = 122
a[0]<-[2]___[0] = 311 ---> a[0][2][0] = 311 ---> a[1][1][0] = 221
a[0]<-[2]___[1] = 312 ---> a[0][2][1] = 312 ---> a[1][1][1] = 222
a[1]<-[2]___[0] = 321 ---> a[1][2][0] = 321 ---> a[1][2][0] = 321
a[1]<-[2]___[1] = 322 ---> a[1][2][1] = 322 ---> a[1][2][1] = 322
print(unstack(a, axis=1))
[[[ 111. 112.]
[ 211. 212.]
[ 311. 312.]]
[[ 121. 122.]
[ 221. 222.]
[ 321. 322.]]]根據 axis=2 進行 unstack 後:
# Step1: 把 axis=1 (第三個索引) 搬到最前面,形成新的矩陣
# Step2: 重新排序最前面的索引
a[0]<-[0][0]___ = 111 ---> a[0][0][0] = 111 ---> a[0][0][0] = 111
a[1]<-[0][0]___ = 112 ---> a[1][0][0] = 112 ---> a[0][0][1] = 121
a[0]<-[0][1]___ = 121 ---> a[0][0][1] = 121 ---> a[0][1][0] = 211
a[1]<-[0][1]___ = 122 ---> a[1][0][1] = 122 ---> a[0][1][1] = 221
a[0]<-[1][0]___ = 211 ---> a[0][1][0] = 211 ---> a[0][2][0] = 311
a[1]<-[1][0]___ = 212 ---> a[1][1][0] = 212 ---> a[0][2][1] = 321
a[0]<-[1][1]___ = 221 ---> a[0][1][1] = 221 ---> a[1][0][0] = 112
a[1]<-[1][1]___ = 222 ---> a[1][1][1] = 222 ---> a[1][0][1] = 122
a[0]<-[2][0]___ = 311 ---> a[0][2][0] = 311 ---> a[1][1][0] = 212
a[1]<-[2][0]___ = 312 ---> a[1][2][0] = 312 ---> a[1][1][1] = 222
a[0]<-[2][1]___ = 321 ---> a[0][2][1] = 321 ---> a[1][2][0] = 312
a[1]<-[2][1]___ = 322 ---> a[1][2][1] = 322 ---> a[1][2][1] = 322
print(unstack(a, axis=2))
[[[ 111. 121.]
[ 211. 221.]
[ 311. 321.]]
[[ 112. 122.]
[ 212. 222.]
[ 312. 322.]]]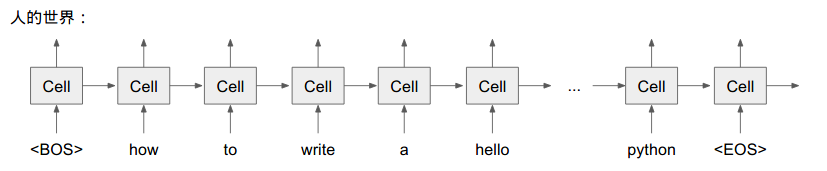
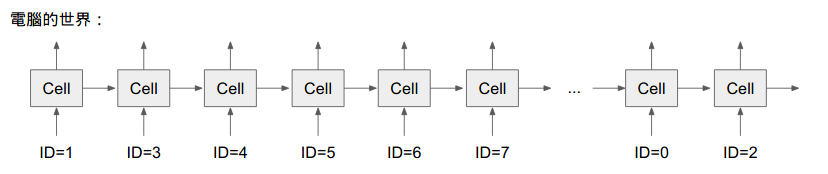
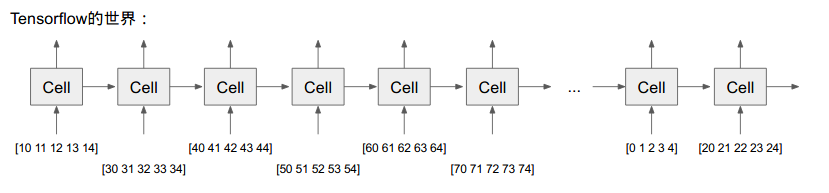
假設有一個句子,需要將句子轉成序列供 ML 分析:
# 原始序列,其中
# '^' 表示序列開始(BOS, Begin Of Sentence)
# '$' 表示序列結束(EOS, End Of Sentence)
^How To Write a Hello World Program in Python$將序列轉成 ID:
# UNK 未知詞定義為 0, BOS = 1, EOS = 2, python 是未知詞
# ^How To Write a Hello World Program in Python$
token[0] = <BOS> = 1
token[1] = "how" = 3
token[2] = "to" = 4
token[3] = "write" = 5
token[4] = "a" = 6
token[5] = "hello" = 7
token[6] = "world" = 8
token[7] = "program" = 9
token[8] = "in" = 10
token[9] = "python" = 0
token[10] = <EOS> = 2
# 將序列轉成 ID 後,得到
[1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 0, 2]但如果想要再繫結 「詞向量(word imbedding)」 (假設有 100 個維度),期望得到:
# 矩陣大小:(句子長度+2)x100
[[ID=1的詞向量], [ID=3的詞向量], [ID=4的詞向量], ..., [ID=2的詞向量]]
#也就是
# 矩陣大小:(句子長度+2)x100
[[<BOS>的詞向量], ["how" 的詞向量], ["to" 的詞向量], ..., [<EOS>的詞向量]]那該如何把 [1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 0, 2] 矩陣
轉成 [[<BOS>的詞向量], ["how" 的詞向量], ..., [<EOS>的詞向量]] 矩陣?
再如何將矩陣打散成 [<BOS>的詞向量], ["how" 的詞向量], ..., [<EOS>的詞向量] 清單?
tensorflow + python 的程式碼:
import tensorflow as tf
# 避免將 GPU 記憶體整個吃滿,先配置基本的,若有需要在增加
config = tf.ConfigProto()
config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
word_id_list = tf.constant([1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 0, 2])
print('word_id_list: type:', word_id_list)
print('word_id_list: value:')
print(word_id_list.eval())
print('------------------------------------\n')
# 透過 tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_matrix, word_id_list)
# 將 word_id_list 轉成 word_embedding_list
# 假設每個 word 有 5個維度 (5個特徵值)
embedding_matrix = tf.constant([
[0,1,2,3,4],
[10,11,12,13,14],
[20,21,22,23,24],
[30,31,32,33,34],
[40,41,42,43,44],
[50,51,52,53,54],
[60,61,62,63,64],
[70,71,72,73,74],
[80,81,82,83,84],
[90,91,92,93,94],
[100,101,102,103,103]
])
word_emb_list = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding_matrix, word_id_list)
print('word_emb_list: type:', word_emb_list)
print('word_emb_list: value:')
print(word_emb_list.eval())
print('------------------------------------\n')
# 將 shape=(11,5) 的 tensor,拆成 11 個 shape=(5) 的 tensor 之清單
rnn_input = tf.unstack(word_emb_list, axis=0)
print(rnn_input)
for idx, item in enumerate(rnn_input):
print('[' + str(idx) + ']', item)tensorflow 執行結果:
word_id_list: type: Tensor("Const:0", shape=(11,), dtype=int32)
word_id_list: value:
[ 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 0 2]
------------------------------------
word_emb_list: type: Tensor("embedding_lookup:0", shape=(11, 5), dtype=int32)
word_emb_list: value:
[[ 10 11 12 13 14]
[ 30 31 32 33 34]
[ 40 41 42 43 44]
[ 50 51 52 53 54]
[ 60 61 62 63 64]
[ 70 71 72 73 74]
[ 80 81 82 83 84]
[ 90 91 92 93 94]
[100 101 102 103 103]
[ 0 1 2 3 4]
[ 20 21 22 23 24]]
------------------------------------
[<tf.Tensor 'unstack:0' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:1' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:2' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:3' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:4' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:5' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:6' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:7' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:8' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:9' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>, <tf.Tensor 'unstack:10' shape=(5,) dtype=int32>]
[0] Tensor("unstack:0", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[1] Tensor("unstack:1", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[2] Tensor("unstack:2", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[3] Tensor("unstack:3", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[4] Tensor("unstack:4", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[5] Tensor("unstack:5", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[6] Tensor("unstack:6", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[7] Tensor("unstack:7", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[8] Tensor("unstack:8", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[9] Tensor("unstack:9", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
[10] Tensor("unstack:10", shape=(5,), dtype=int32)
- 需具備 列舉多維度陣列索引 的概念
'''
unpacks the given dimension (axis) of a rank-R array into rank-(R-1) array
input:
in_array: input a given array
axis: an int; the axis to unstack along
output:
out_array: output an unpacked array
'''
def unstack(in_array, axis):
# checks the arguments
if axis < 0 or axis >= len(in_array.shape):
raise Exception('axis should be located in [0,' + str(len(in_array.shape)) + ')')
# end-of-if
# allocates the unstacked array
out_array_shape = __get_unstack_shape(in_array.shape, axis)
out_array = numpy.zeros(out_array_shape)
# iterates the index of the given input array
in_index0 = tuple(numpy.zeros(len(a.shape), dtype=numpy.int32)) # start index
in_index = in_index0
out_index = in_index0
while True:
out_index = __get_unstack_shape(in_index, axis)
out_array[out_index] = in_array[in_index]
#print(in_index, '=', '->', out_index)
# moves to the next index
in_index = __get_next_index(in_array, in_index)
if in_index == in_index0:
break
# end-of-if
# end-of-while
return out_array
# end-of-def
'''
creates an unstacked shape
input:
index: a tuple consists of each dimension's index, e.g. (1,2,3)
axis: an int; the axis to unstack along
output:
axis=0, ('1',2,3)-> ('1',2,3)
axis=1, (1,'2',3)-> ('2',1,3)
axis=2, (1,2,'3')-> ('3',1,2)
'''
def __get_unstack_shape(index, axis):
new_shape = list()
# moves the axis-th dimention to the 1st
new_shape.append(index[axis])
# splits the index by axis
for n in range(0, axis):
new_shape.append(index[n])
# end-of-for
for n in range(axis + 1, len(index)):
new_shape.append(index[n])
# end-of-for
return tuple(new_shape)
# end-of-def
'''
moves to the next index from 'current_index'
input:
array: n-dim array
current_index: the tuple of the current index for each dimension, e.g. (1,2,3)
'''
def __get_next_index(array, current_index):
shape = array.shape
# copies 'current_index', and moves to the next index
next_index = list(current_index)
next_index[array.shape[-1]] += 1
carry = 0
for idx in reversed(range(len(shape))):
next_index[idx] = next_index[idx] + carry
if next_index[idx] < shape[idx]:
break;
else:
carry = int(next_index[idx] / shape[idx])
next_index[idx] = next_index[idx] % shape[idx]
# end-of-if
# end-of-for
return tuple(next_index)
# end-of-def