GNSS timing - sujineie/BURSTT_ASIAA GitHub Wiki
Dual input to a bladeRF (dev6): rx1 = GPS 1, rx2 = GPS 2
* GPS 1 was originally connected to rx1 of dev6
* GPS 2 was originally connected to rx1 of dev13
From previous observations, dev13 signals are generally weaker (or unstable) than dev6 signals, so the two GPS antennas are connected to dev6.
- Receivers are aligned to E-W: E (GPS 1) -- W (GPS 2)





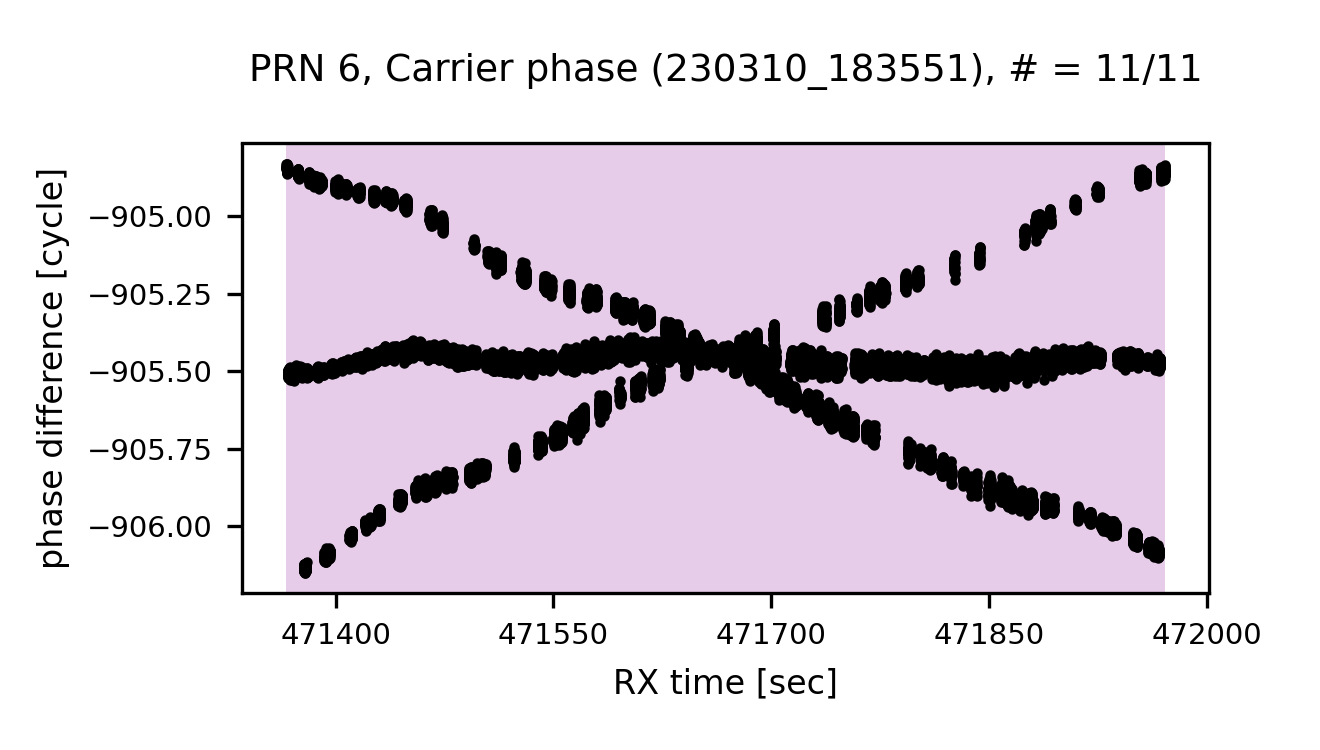
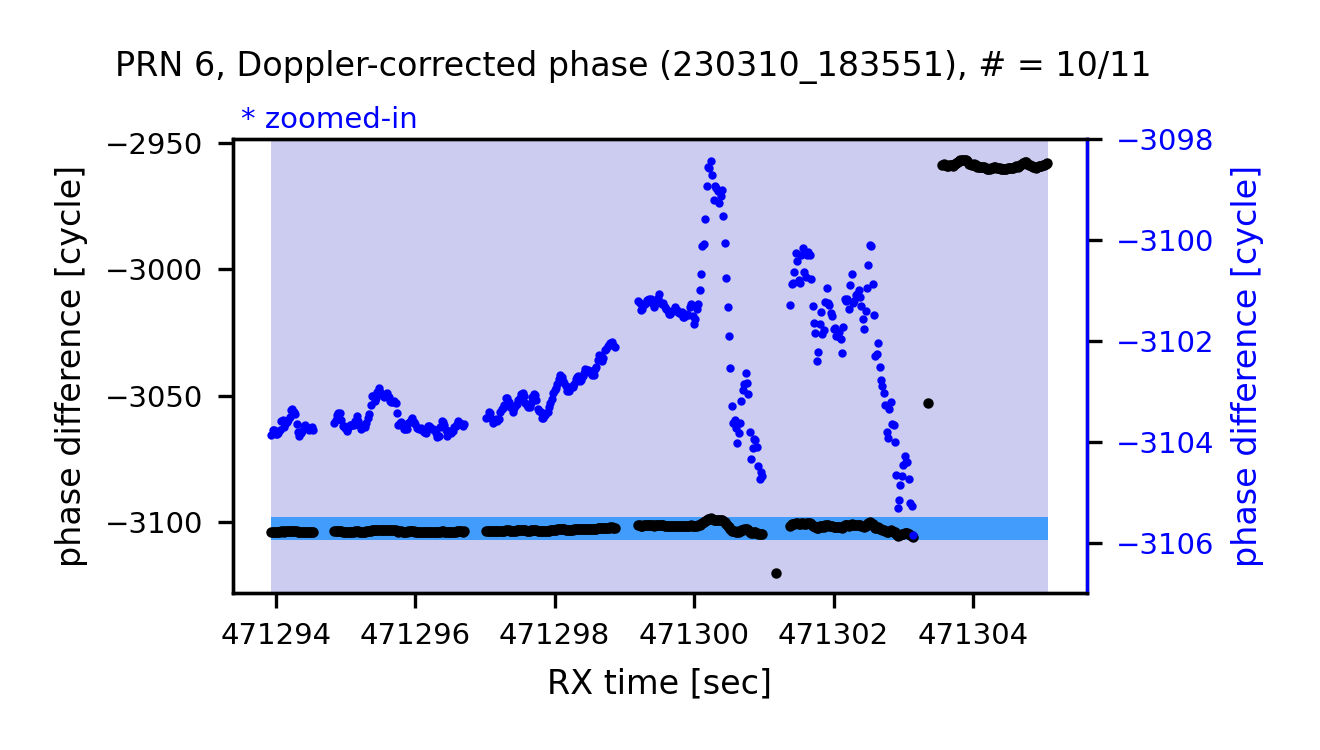
- doppler-corrected carrier phase
$=$ (carrier phase)$+$ cumulative sum(doppler shift)$\times \ dt$

zoom-in (Carrier phase)










zoom-in (Doppler-corrected)












zoom-in












Once the navigation solution is obtained, RINEX (Receiver Independent Exchange Format; a data format for raw satellite navigation system data) file can be saved.
The RINEX file includes
- time (the receiver time of the received signals)
- satellite IDs
- pseudo-range [meter], carrier phase [cycle], Doppler frequency [Hz], and signal strength of each satellite.




- cycle → second


| Difference in Carrier phase | Difference in Doppler-corrected carrier phase | |
|---|---|---|
| mean (deviation) | mean (deviation) | |
| G19 | -149.56 ns (110.76) | 112.51 |
| G06 | -150.76 ns (110.76) | 11.90 |
| G11 | -128.97 ns (110.76) | 113.52 |
Two antennas are connected to different bladeRF
* GPS 1 is connected to dev6 (both rx1 and rx2 were tested.)
* GPS 2 is connected to dev13 (both rx1 and rx2 were tested.)
Antenna settings are the same as Setting for dual inputs.




- doppler-corrected carrier phase
$=$ (carrier phase)$+$ cumulative sum(doppler shift)$\times \ dt$

zoom-in (Carrier phase)





zoom-in (Doppler-corrected phase)




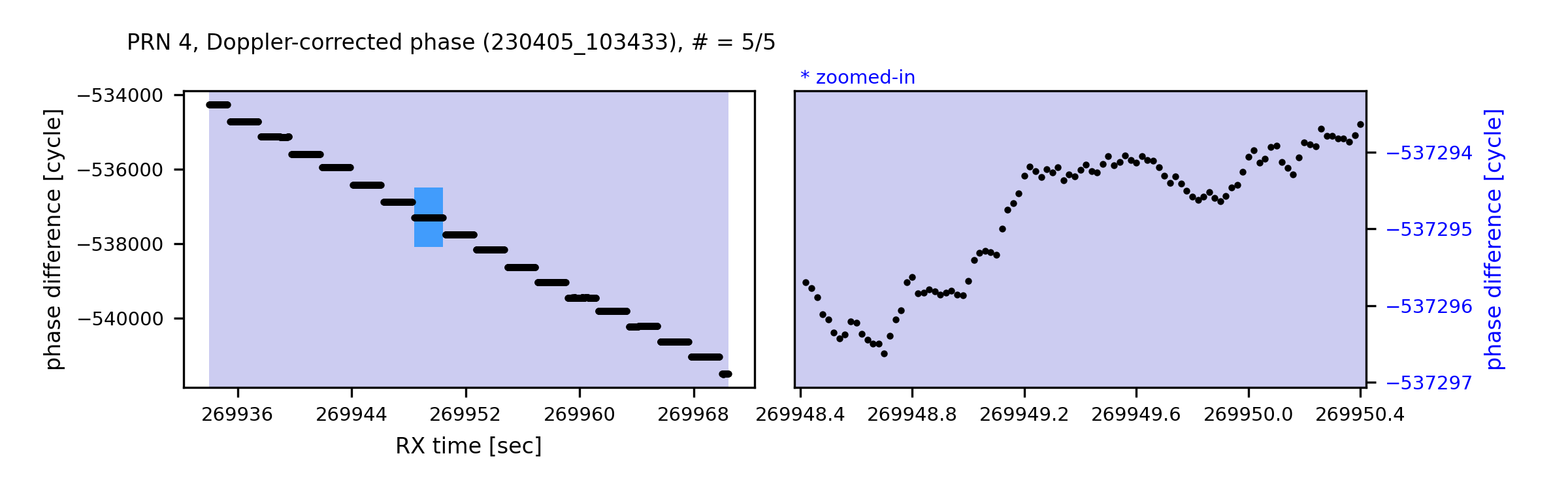


zoom-in (Carrier phase)

zoom-in (Doppler-corrected phase)



zoom-in (Carrier phase)



zoom-in (Doppler-corrected phase)





zoom-in (Carrier phase)

zoom-in (Doppler-corrected phase)



zoom-in (Carrier phase)

zoom-in (Doppler-corrected phase)






Once the navigation solution is obtained, RINEX (Receiver Independent Exchange Format; a data format for raw satellite navigation system data) file can be saved.
The RINEX file includes
- time (the receiver time of the received signals)
- satellite IDs
- pseudo-range [meter], carrier phase [cycle], Doppler frequency [Hz], and signal strength of each satellite.


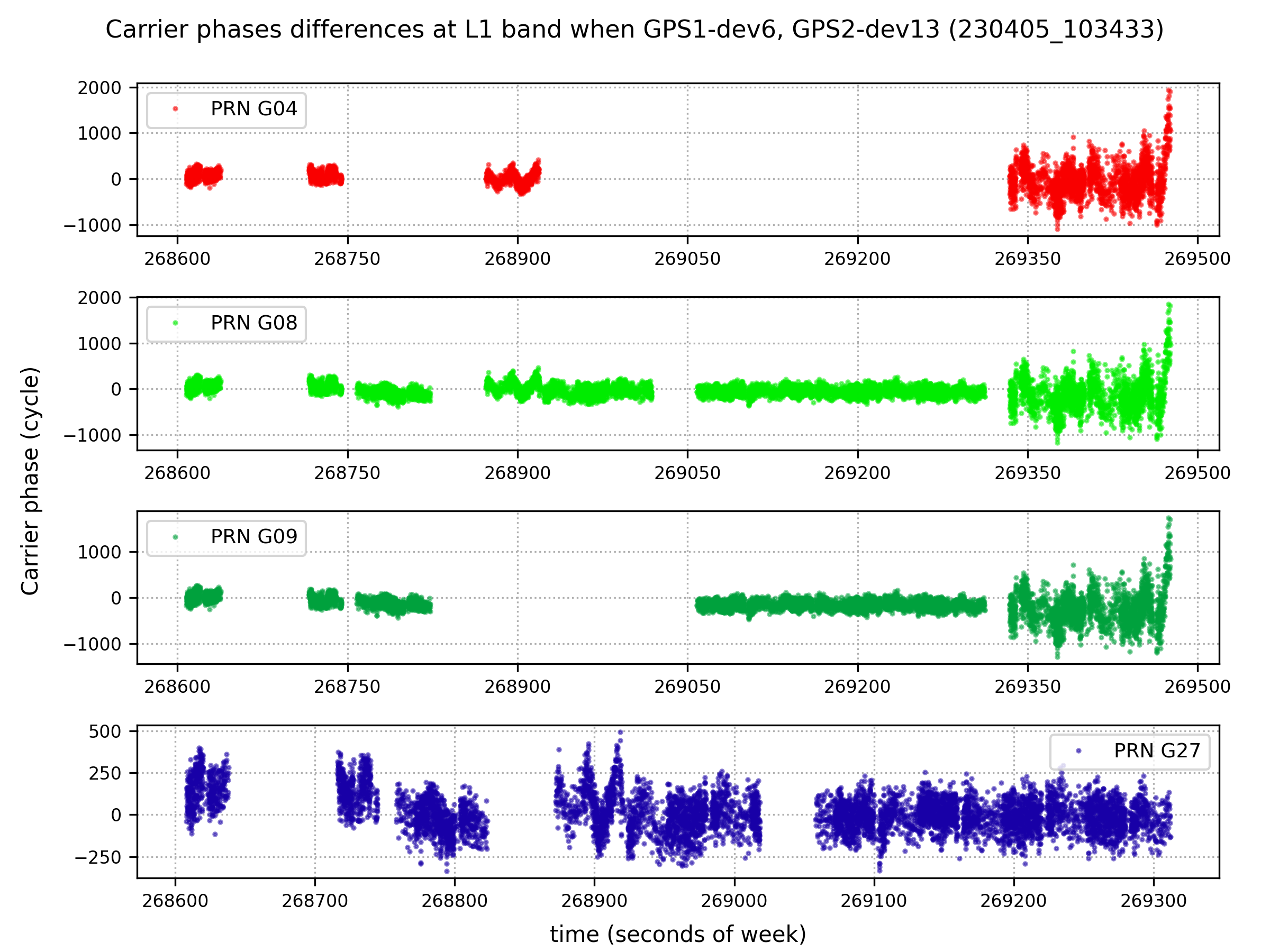

- cycle → second


| Difference in Carrier phase | Difference in Doppler-corrected carrier phase | |
|---|---|---|
| mean (deviation) | mean (deviation) | |
| G04 | -3.57 ns (184.75) | |
| G08 | -31.55 ns (126.84) | |
| G09 | -98.49 ns (138.45) | |
| G27 | 8.88 ns (71.76) |
- GNSS-SDR: https://gnss-sdr.org/docs/
- Live Map of Satellite Positions: https://in-the-sky.org/satmap_radar.php
- NAVSTAR GPS: https://www.n2yo.com/satellites/?c=20
- RINEX ver.2: https://files.igs.org/pub/data/format/rinex211.txt
- RINEX ver.3: https://files.igs.org/pub/data/format/rinex303.pdf