Security - sufiyan63/SAP-Hana-Cloud GitHub Wiki
-
CREATE USER AND ROLE WITH DBADMIN
-
DBADMIN
- Admin user used for creating another user, roles and other super admin activities
- One user cannot assign privileges to the same user even admin cannot assign own privilages
- One way of creating a new user is going to the SAP Hana Central ⇒ select the Hana instance ⇒ open sap Hana cockpit ⇒ Select security and user management tab ⇒ user management
- //creating a new user
CREATE USER FASHION_ADMIN PASSWORD <> NO FORCE_FIRST_PASSWORD_CHANGE SET USERGROUP DEFAULT;
//creating a role
CREATE ROLE "<>"
// the user having this role can grant access to schema EFASHION to other users
GRANT SELECT, SELECT METADATA ON SCHEMA EFASHION TO "rolename" WITH GRANT OPTION
GRANT "rolename" to FASHION_ADMIN with ADMIN OPTION
-
DBADMIN
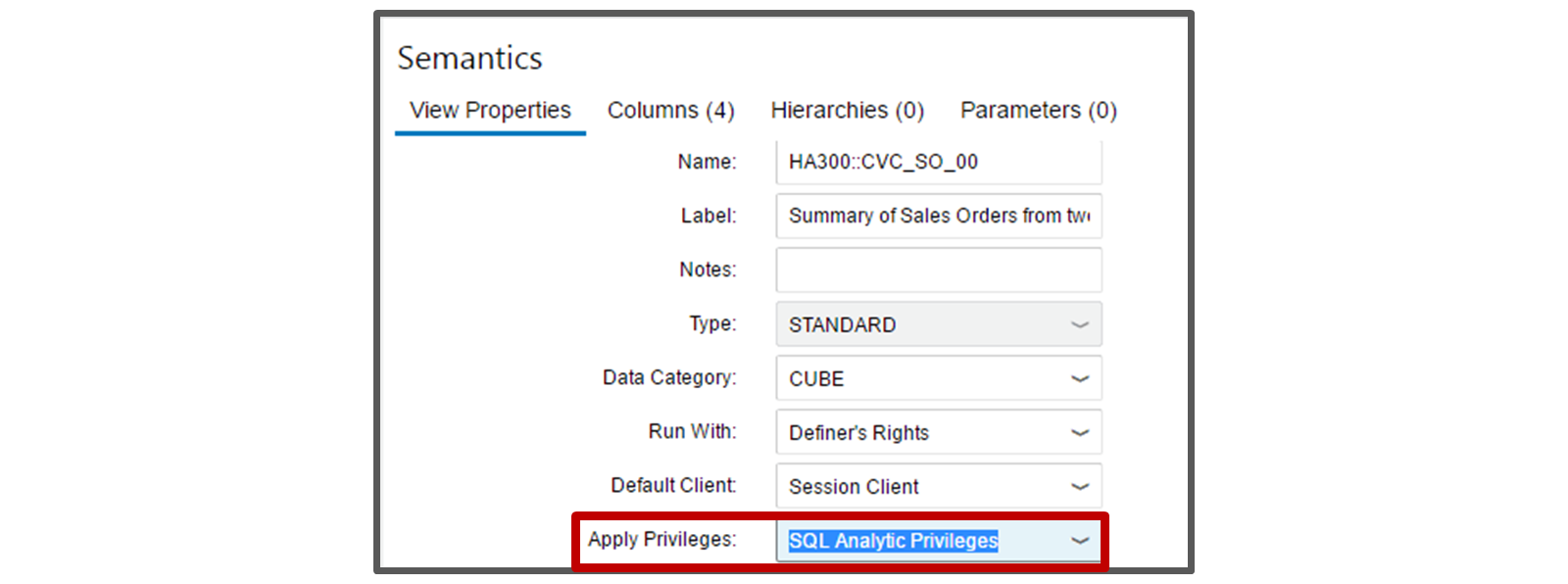
- Make calculation view a secured view
- Select semantics node ⇒ view properties ⇒ general ⇒ [Property] Apply privileges ⇒ SQL analytical privileges
- Deploy the enabled calculation view
- Create analytical privilege (.hdbanalyticalprivilege)
- In SAP BAS, Create a new SAP Hana DB artifact
- Click on Add Secured Models
- Choose the calculation view
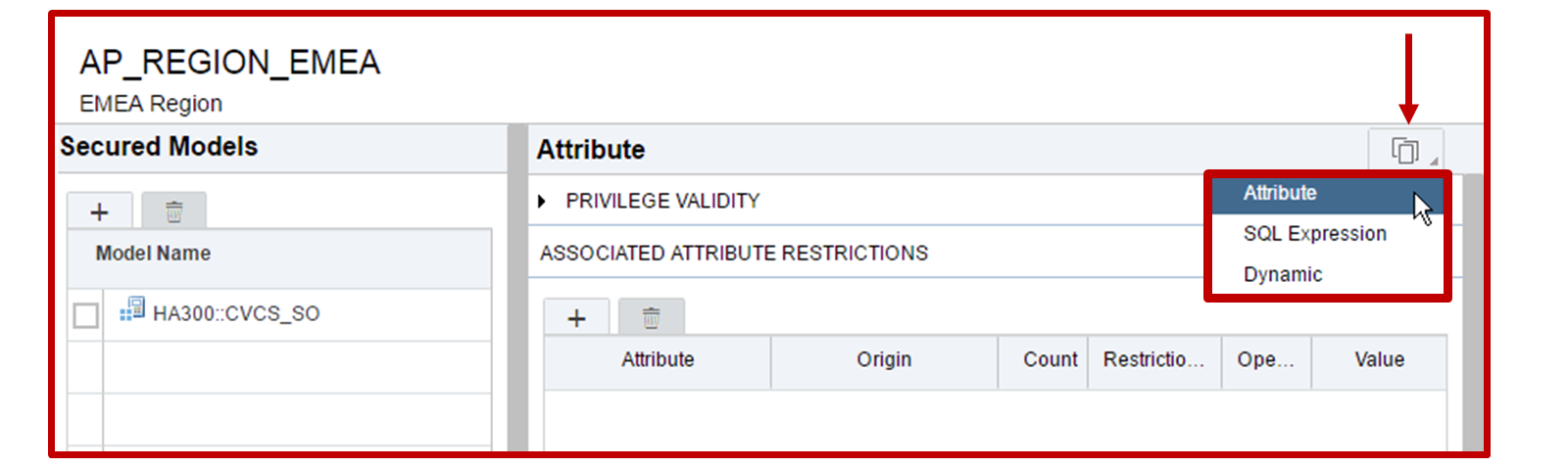
- Click on add in ASSOCIATED ATTRIBUTE RESTRICTIONS
- Select Attribute, Which is Field of calculation view
- Click on Add Restriction
- Give Fixed Value = US
- Create Role (.hdbrole)
- Create a new SAP Hana Database Artifact
- Click object privilege tab
- Select Object name ⇒ calculation view
- Select Object type ⇒ VIEW
- Select Privileges ⇒ SELECT
- Select privilege with grant option if you want that user to grant privilege to other users
- Click analytical privilege tab
- Select privilege name ⇒ Analytical privilege name
- Click on define schema reference
- Deploy the entire project
- Object Privileges ⇒ Control the access to the database objects defined in your container such as tables views procedures
- Schema Privileges ⇒ Control the access to the entire schema usually granted by the technical user configured in the user provided service ( for external schema access )
- System Privileges ⇒ Privileges related to the database operations such as user management and backups
- User Groups
- Allow related users to be managed together supporting efficient user management
- Each user group can have one or more dedicated group administrators
- Group administrators can be assigned specific tasks for managing users within the respective user groups
- User groups can have groups specific configurations such as password policy settings or client connection restrictions
- Users with a system privilege CREATE USERGROUP can create user groups
- Initially the database administrator (DBADMIN) has the privilege and can enable other users to create user groups by granting them the CREATE USERGROUP privilege
- User group administrators can designate dedicated administrators for specific user groups by granting the object privilege USERGROUP OPERATOR on the user group
- Group administrators can add new users to a user group using the CREATE USER statement or the cloud cockpit
- To move a user from one group to another a user authorized for both user groups can use the ALTER USER statement to set the user's user group to the new user group automatically removing the user from the original user group you can also use cloud cockpit
- Authorizations
-
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access protocol)
- Serves as the external authentication provider responsible for handling user authentication
- Users can authenticate themselves in sap Hana directly from ODBC or JDBC database clients using a password stored in an LDAP directory server
- This authentication method is applicable when the local sap Hana authentication for users has been disabled
- Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML)
-
JWT
- A JSON web token can be utilized for user authentication when accessing sap Hana directly from ODBC or JDBC database clients
- SAP Hana database validates the JWT to verify its authenticity and extracts user identity details
- They extracted user identity is then mapped to the identity of an internal database user for access authorization
- External authentication provider must still have a known database user in sap Hana, And the external identity is linked to an internal database user for authentication purpose
- SSO capable
- X.509
- User accessing sap Hana directly from ODBC or JDBC clients can be authenticated using client certificates signed by a trusted certification authority
- During authentication, the client presents a digital certificate, which contains the user's identity and is signed by a trusted CA
- SAP Hana verifies the certificate authenticity by validating the CA signature
- Upon successful validation, the users identity is extracted from the certificate and mapped to the identity of an internal database user for authorization purpose
- SSO Capable
-
LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access protocol)
- Privileges
- System privileges
- In SAP Hana central ⇒ General system settings. They are primarily used for administrative purpose such as
- Creating schemas
- Creating and changing users and roles
- Monitoring and tracing system activities
- Essential for performing administrative tasks and managing the Sap Hana database
- Object privileges
- Depending on the object type different actions can be authorized such as select, create any, alter, and drop
- You can select Tables and Views as object
- Schema privileges are object privileges granting access to and modification of schemas and contained objects
- Source privileges are object privileges used to control access to and modification of remote data sources connected through sap hana smart data access
- Object, schema, source privileges are essential for controlling access to specific data and database objects ensuring data security and integrity in SAP Hanna
- Analytical Privilege
- Analytic privileges are used to enable data access in calculation views by filtering the data based on the values of one or more attributes.
- They are based on certain values or combination of values and are evaluated during query processing
- Enabling fine-grained data access permissions based on user roles or attributes
- Hierarchy Node in an Attribute Restriction
- If a DIMENSION calculation view contains a parent-child hierarchy and the hierarchy is enabled for SQL access, it's also possible to define the restriction on a hierarchy node.
- Add the calculation view
- Create an Attribute restriction type.
- From the section Hierarchical Privilege select one of the available hierarchies..
- Choose a hierarchy node value.
- If two analytic privileges (or more) are defined to apply to the same view, SAP HANA combines the corresponding conditions with a logical OR.
- Steps
- Create a source file with the extension .hdbanalyticprivilege.
- Assign the calculation views that you want to secure with this analytic privilege.
- Choose the type of restrictions that you want to use and define the restrictions.
- Attribute : With the restriction editor, select one or several attributes from the secured views. For each of them, define restrictions.
- SQL Expression : ("REGION"=’EMEA’ AND "YEAR"=’2015’)
- Dynamic Restriction Type
- Use a procedure to derive a dynamic SQL expression to restrict the data set. This expression must be similar to a WHERE clause in a select statement.
- For example, a procedure could return ("COUNTRY"='US') for User1 and ("COUNTRY"='UK' OR "COUNTRY"='FR') for User2.
- When a user executes a calculation view that has an analytic privilege referencing a procedure, SAP HANA automatically runs that procedure in the context of the logged-in user built-in functions CURRENT_USER
- lv_user := CURRENT_USER;
- Procedure must be read-only
- Security mode must be DEFINER
- No input parameters
- Only one scalar output parameter of type VARCHAR or NVARCHAR
- Set the secured calculation views to check analytic privileges.
- Deploy the analytic privilege.
- create a design-time role – Create Role (.hdbrole) and grant the new analytic privilege to this role.
- Assign the role to a user
- grant "SIMPLE_PROJECT_HDI_DB_1"."HC::ROLE_US_MANAGERS" TO username
- Nested Calculation Views – Data Access Security Principles
- The key rules that govern the access to data are as follows:
- Object privileges
- There's no need to grant SELECT privileges on the underlying views or tables. The end user only needs to be granted SELECT privileges on the top column view of the view hierarchy.
- Analytic Privileges
- The analytic privileges logic is applied through all the view hierarchy.
- Whenever the view hierarchy contains at least one view that is checked for analytic privileges but for which the end user has no analytic privilege, no data is retrieved (not authorized).
- Note that the end user always needs an explicit SELECT privilege on a calculation view to be able to query its data. That is, granting an Analytic Privilege to this user doesn't also grant an implicit SELECT authorization on the views that this Analytic Privilege secures.
- System privileges
-
SQL Security
-
DEFINER
- The procedure executes with the privileges of the user who created the procedure.
- Use Case: Useful for enforcing consistent permissions, as the invoker's permissions do not affect execution.
- Default Behavior: If not specified, SQL procedures default to DEFINER mode.
- Scenario 1: DEFINER Mode
-- Create a procedure in DEFINER mode CREATE PROCEDURE FetchEmployees() SQL SECURITY DEFINER AS BEGIN SELECT * FROM Employees; -- Requires SELECT permission END;- If
user_definer
hasSELECT
permission on theEmployees
table, any user can invoke this procedure without havingSELECT
permission themselves.
-
INVOKER
- The procedure executes with the privileges of the user who invokes (runs) the procedure.
- Use Case: Useful for granting flexibility, especially when different users have varying permissions on underlying tables or resources.
CREATE PROCEDURE procedure_name SQL SECURITY {DEFINER | INVOKER} AS BEGIN -- Procedure logic END;- Scenario 2: INVOKER Mode
-- Create a procedure in INVOKER mode CREATE PROCEDURE FetchEmployees() SQL SECURITY INVOKER AS BEGIN SELECT * FROM Employees; END;- The permissions of the invoking user (
user_invoker
) are used to execute the procedure. Ifuser_invoker
lacksSELECT
permission on theEmployees
table, the procedure will fail.
-
DEFINER
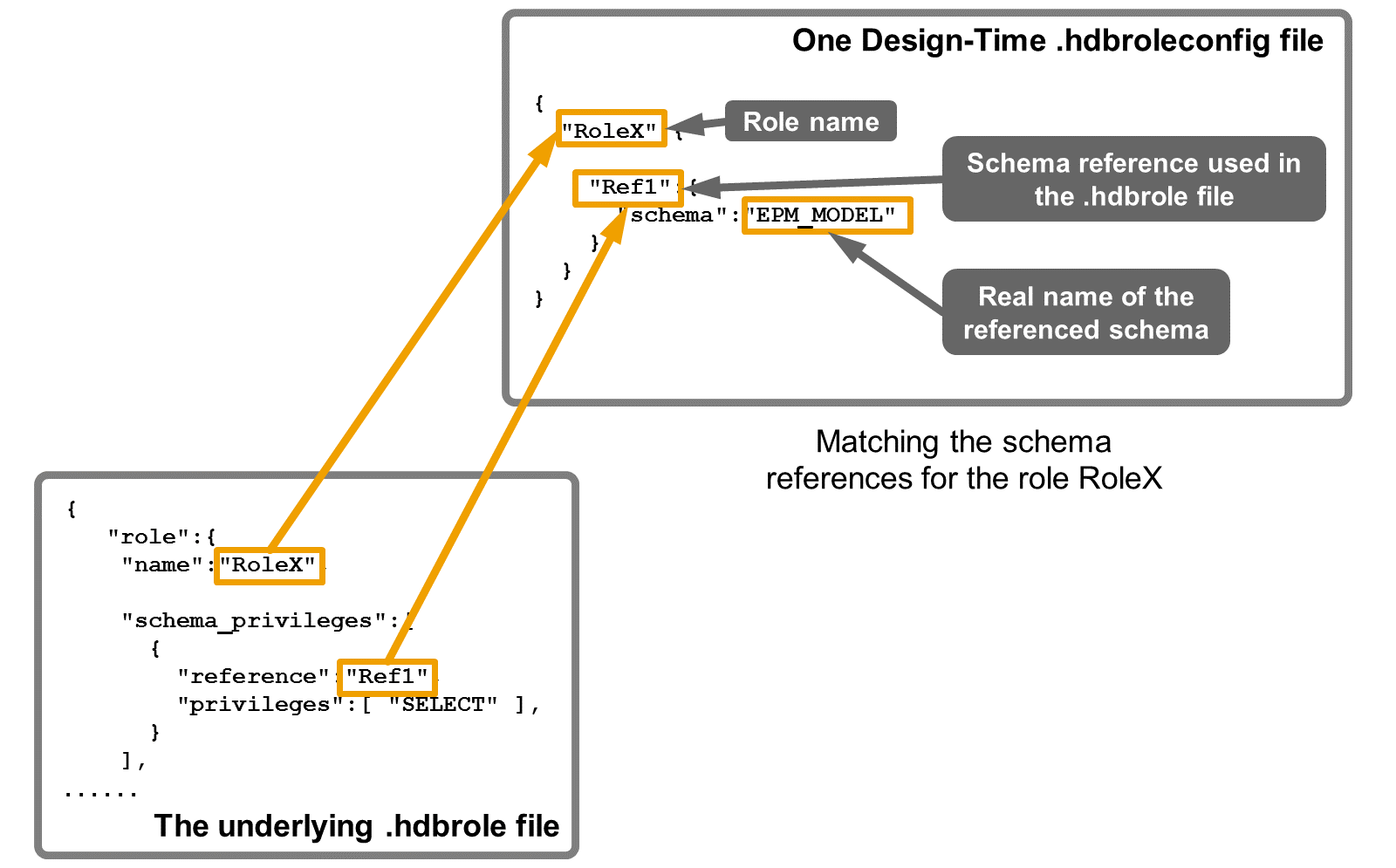
- The .hdbroleconfig File
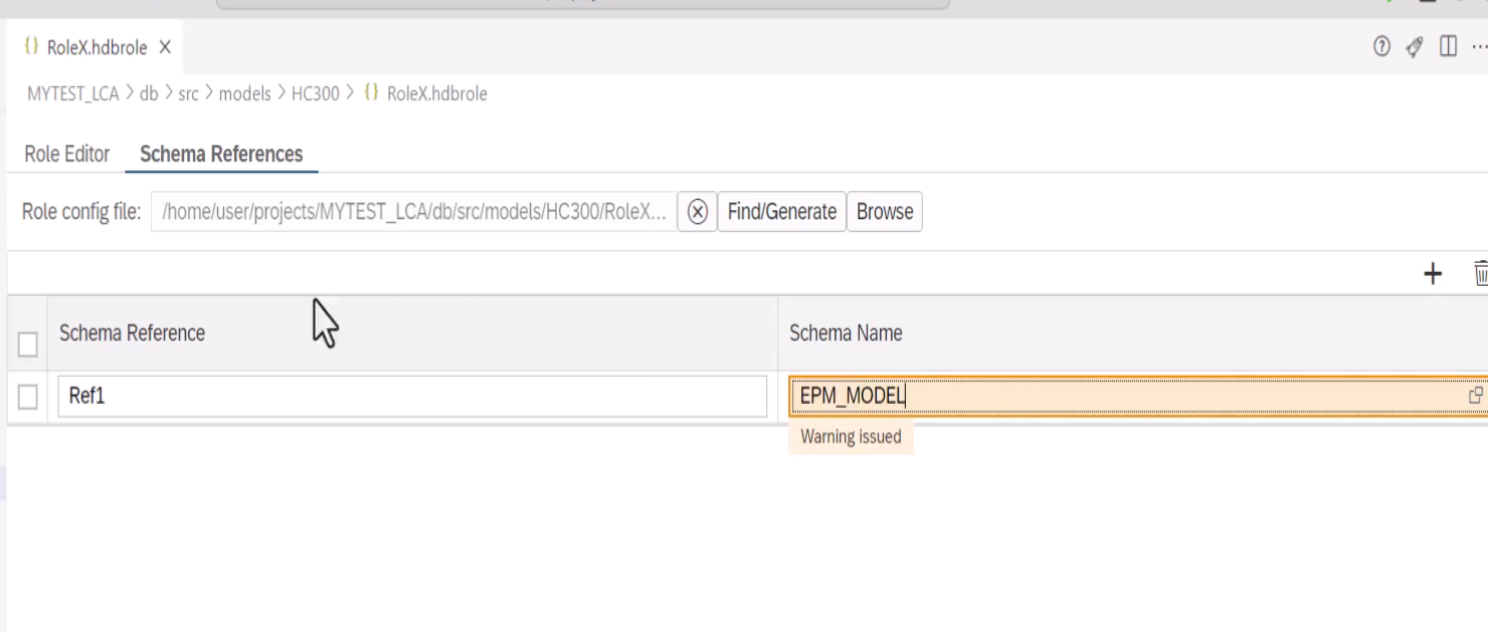
- The .hdbrole file can't contain references to real schema names, but only logical references to schemas that are resolved in another type of design-time file: the .hdbroleconfig file.
- You can create the .hdbroleconfig file manually and then specify this file when you create your .hdbrole file. Or you can generate the .hdbroleconfig file automatically from within the .hdbrole editor and then optionally adjust the generated file if necessary.
- Defining a Mask Expression
- A mask expression is defined in a calculation view as follows:
- In the Semantics node, choose the Columns tab.
- Select a column, and choose the Data Masking icon in the toolbar
- Define the masking expression using SQL
- Only columns of certain data types can be masked in a calculation view: VARCHAR, NVARCHAR. CHAR, SHORTTEXT
- For example, you can mask the middle part of a credit card number stored in column credit_card with the following mask expression:
- LEFT || '-XXXX-XXXX-' || RIGHT
- Nested calculation views with mask mode
- when two calculation views are nested, A column asking define in an underlying calculation view with mask mode default does not affect the calculation view that consumes it as a consequence you must make sure that the calculation views that you expose to the end users contain the relevant mass definition
- Calculated Columns Use Unmasked Data
- When the expression of a calculated column refers to the column that has a column mask assigned the calculation uses unmasked data regardless of whether the user has the unmasked privilege for the view or not
- Authorizing Access to a Masked Column
- At the schema level:
- {
"role":
{
"name":"db::UNMASK_ENTIRE_SCHEMA",
"schema_privileges":[{
"privileges":["UNMASKED"]}]
}
} - At the object level:
- {
"role":
{
"name":"db::UNMASK_EMPLOYEES_PAYMENT",
"object_privileges":[{
"type":"VIEW",
"name":"db::CVD_EMPLOYEES_PAYMENT",
"privileges":["UNMASKED"]}]
}
}