mwp in Windows 11 WSL G - stronnag/mwptools GitHub Wiki
As a result of user interest in running mwp on Windows 11 / WSL-G, here's an experiment to see if it's possible. By a Windows neophyte, so if I can install mwp on WSL, anyone can.
There is also an excellent, but sadly obsolete, you-tube video tutorial from Marc Hoffmann (in English and German).
It is also possible to run mwp on Windows 10 (and 7) using WSL-1 (win10) and / or Cygwin (win7 - win10). This is documented in the mwp wiki.
Tested with Windows 11 VM hosted on Arch Linux by the developer.
- Installed default Ubuntu
- Note that serial ports remain difficult (workarounds described below)
None other than the serial port issue, Wayland (GUI) and sound just work.
The serial port problem can be mitigated by a "serial to IP" solution; mwptools provides ser2udp for this purpose or using usbipd / usbip (Microsoft's recommended method).
Use one of the following:
(a) Install the current release from GitHub.
- Down load the
.debfile -
cdto where ever you saved the.debfile - In the WSL terminal
sudo apt install ./mwptools_x.y.z_amd64.deb
Example: using curl to download ...
$ curl -LO https://github.com/stronnag/mwptools/releases/download/x.y.z/mwptools_x.y.z_amd64.deb
$ sudo apt install ./mwptools_x.y.z_amd64.deb
Where x.y.z represents the build tag.
For the initial installation, there is a unified / simplified install / build / install script: Instructions
This installs mwptools to $HOME/.local/bin.
If you want more control over build options.
If git is not pre-installed in WSL, then it will be necessary to install it.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
sudo apt install git
Note: /etc/sudoers (via visudo) was edited to allows the WSL user to run commands as root without asking for a password.
Then it was just a case of cloning the mwp repository and following mwp's instructions (mwptools/docs/debian-ubuntu-dependencies.txt), to install the dependencies, this is available as an executable script thusly:
sudo mwptools/docs/debinstall.sh -y # "-y" bypasses interactive query / responses
Then build and install mwp and optionally the blackbox tools (as mwptools/docs/debian-ubuntu-dependencies.txt). Build documentation.
For blackbox replay, install the flightlog2x tools; build from source in Linux/WSL or install the release binaries.
Note that the normative build reference is the INSTALL file in the source tree.
Compared to Win10/WSL or Cygwin, there is no longer any need to mess around the DISPLAY or udev settings. No 3rd party X-server, Windows 11 / WSL-G handles all the GUI.
-
WSL installs a very cut down icon theme that does not provide the all the system / standard icons used by mwp. Fix this by:
sudo apt install adwaita-icon-theme-full -
If you wish to replay blackbox / OTX / BulletGCSS logs, it may be necessary to have an IPv6 definition of
localhost; WSL's/etc/hostsdoes not provide this:# updated in /etc/hosts for ipv6 ::1 localhost ip6-localhost ip6-loopbackNote: This was caused by an unnecessary assumption in flightlog2x's
fl2ltmwhich is corrected in flightlog2x release (> 0.11.0), so you might not need it anymore. -
Then tell WSL to please not break your
hostsfile again### Add the following entry to /etc/wsl.conf: [network] generateHosts = false -
ser2udp.exe. mwp can start and stop the Windowsser2udp.exeon demand. This is quite a neat trick by Microsoft's enabling extra-VM process management. In the example below, we have installedser2udp.exeasc:\Users\win11\ser2udp.exe:# Start command gsettings set org.mwptools.planner atstart '/mnt/c/Users/win11/ser2udp.exe' # Shutdown command gsettings set org.mwptools.planner atexit 'pkill ser2udp.exe'
Then you are ready to run mwp.
mwp
In order to use a serial device, it is necessary to run a "serial to IP" bridge on the Windows side. There are two solutions to this, both involve some effort on both the Windows and Linux sides.
-
usbip, a long-standing Linux feature that has recently been introduced to Windows - Standalone "serial-to-IP" bridge, such as mwp's
ser2udptool. This application will need to be white-listed in the Windows firewall.
See this Microsoft developer blog article for installation / usage information.
There are a number of existing solutions that may work; mwp provides a simple, dedicated ser2udp tool that works well, and once set up is transparent in usage.
Build on the Linux/WSL side:
cd mwptools/src/samples/s2nmake ser2udp.exe- copy
ser2udp.exeto the d̶a̶r̶k̶ Windows side
See above for automating starting and stopping ser2udp.exe.
On the Windows side:
-
Use the Windows firewall settings to allow
ser2udp.exeto accept UDP traffic. -
Either automate in mwp (recommended) or run
ser2udp.exe; it will autodetect your serial port. By default this listens on UDP port 17071, you can change this by supplying a second parameter, e.g., to use port 34567. In this case, either define the serial port or useauto(auto-detect).> ser2udp.exe auto :34567 ## or just let ser2udp autodetect > ser2udp.exe External address: fe80::1439:d6de:efcb:97e1%7 External address: 172.29.32.1The colon is required to define an alternative port.
-
ser2udpwill survive removal of USB devices and attempt to re-connect (e.g. if the FC is rebooted). -
ser2udpwill only attempt to automatically acquire STM32 USB devices (0483:5740vid:pid) -
You need to terminate
ser2udpwhen you're done with it (e.g. to use the INAV configurator in Windows).
- On the Linux side, we need to know the IP address (or have a hostname for) the Windows WSL endpoint. Fortunately this happens to be Linux's default gateway, so we can handle it fairly transparently.
It is easily automated by using the magic __MWP_SERIAL_HOST name in the serial device.
mwp -d udp://__MWP_SERIAL_HOST:17071
# recognised by other tools as well ...
cliterm udp://__MWP_SERIAL_HOST:17071
__MWP_SERIAL_HOST is resolved as:
- If an environment variable
$MWP_SERIAL_HOSTexists, it is used; else - The default gateway (which on WSL is the Windows host IP) is used; else
- It will fail, as the literal name is unlikely to exist as a resolvable host name (not even a RFC legal host name).
Thus:
- For WSL and
ser2udp, in mwp preferences, set the serial device toudp://__MWP_SERIAL_HOST:17071 - Or in the shell, for some other scenario,
export MWP_SERIAL_HOST=foobox.orgin the event that you have a valid use case
-
Automate
ser2udp.exein mwp's settings -
Create a new
txtfile in the same folder whereser2udp.exeis located and copy the following lines into that file:@echo off echo Launching MWP Mission Planner start wslg.exe -d Ubuntu mwp exit -
rename the file with any name and change the extension to
.cmd -
Create a shortcut anywhere on your PC or in
C:\Users\<username>\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programsto pin it to your Start Menu -
Replace the shortcut symbol with the MWP icon from here
ser2udp expects that the UDP side (mwp, Linux/WSL) "speaks" first; this enables ser2udp to evince the remote UDP address to which data received from the serial side (Windows) is sent.
If you are only receiving unsolicited telemetry on the serial / Windows side (e.g. CRSF, Smartport, LTM), then it is necessary to tell ser2udp the address of the remote, using the -remote option. In this case, you can set the device name in mwp to udp://:17071 (for port 17071) to listen unconditionally.
- To replay blackbox logs, you need (mandatory):
- INAV blackbox tools, and
- flightlog2x / bbl2kml. Provides a much better blackbox replayer than the old ruby script shipped with mwp (and you can generate really pretty Google Earth files from blackbox / EdgeTX/OpenTX / bulletgcss logs).
- Terrain Analysis
- Gnuplot. Check the installer script that it's enabled.
You see in the console:
(org.stronnag.mwp:462): dconf-WARNING **: 21:57:12.806: failed to commit changes to dconf: Could not connect: No such file or directory
This is a known WSL "feature". See the Official WSL Issue. Most likely, adding export $(dbus-launch) to ~/.bashrc will fix it.
Note also that enabling systemd in WSL may also break dconf (or not).
- Much, much better than the prior WSL instances, pity about the difficulty in using serial ports (still) and general display flakyness.
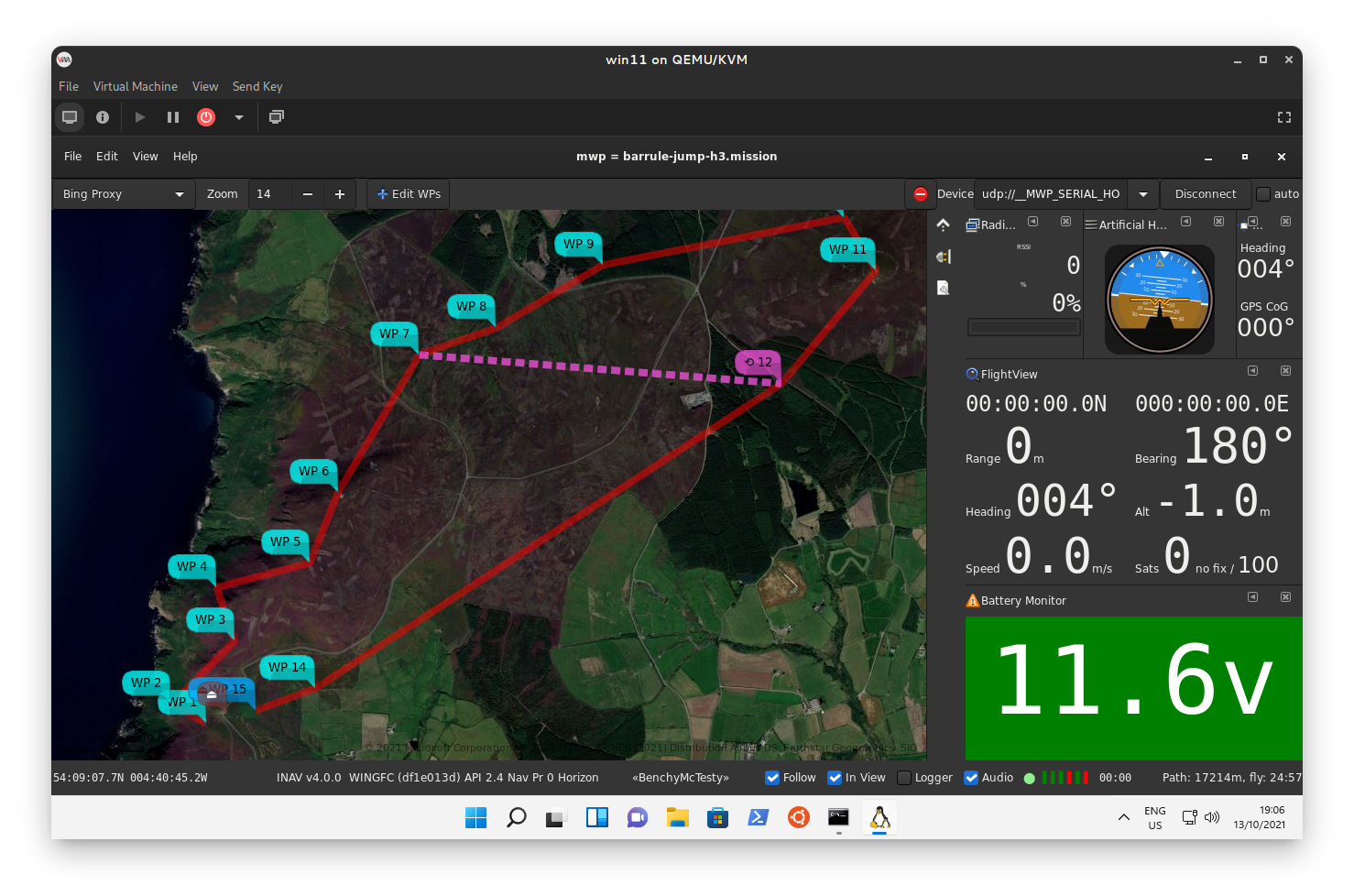 {: width="80%" }
Dark theme, correct system icons installed, connected to FC via
{: width="80%" }
Dark theme, correct system icons installed, connected to FC via ser2udp.
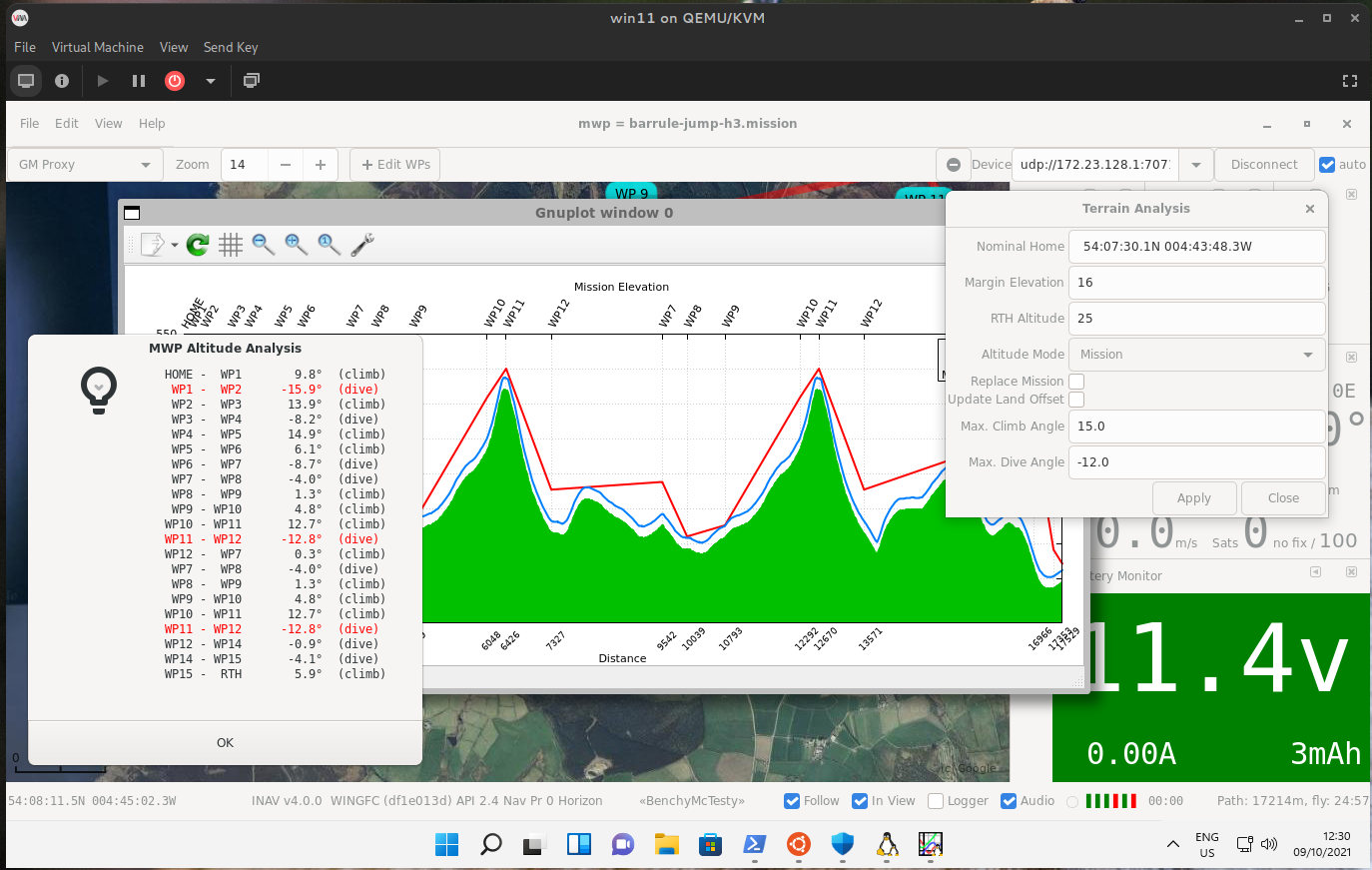 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
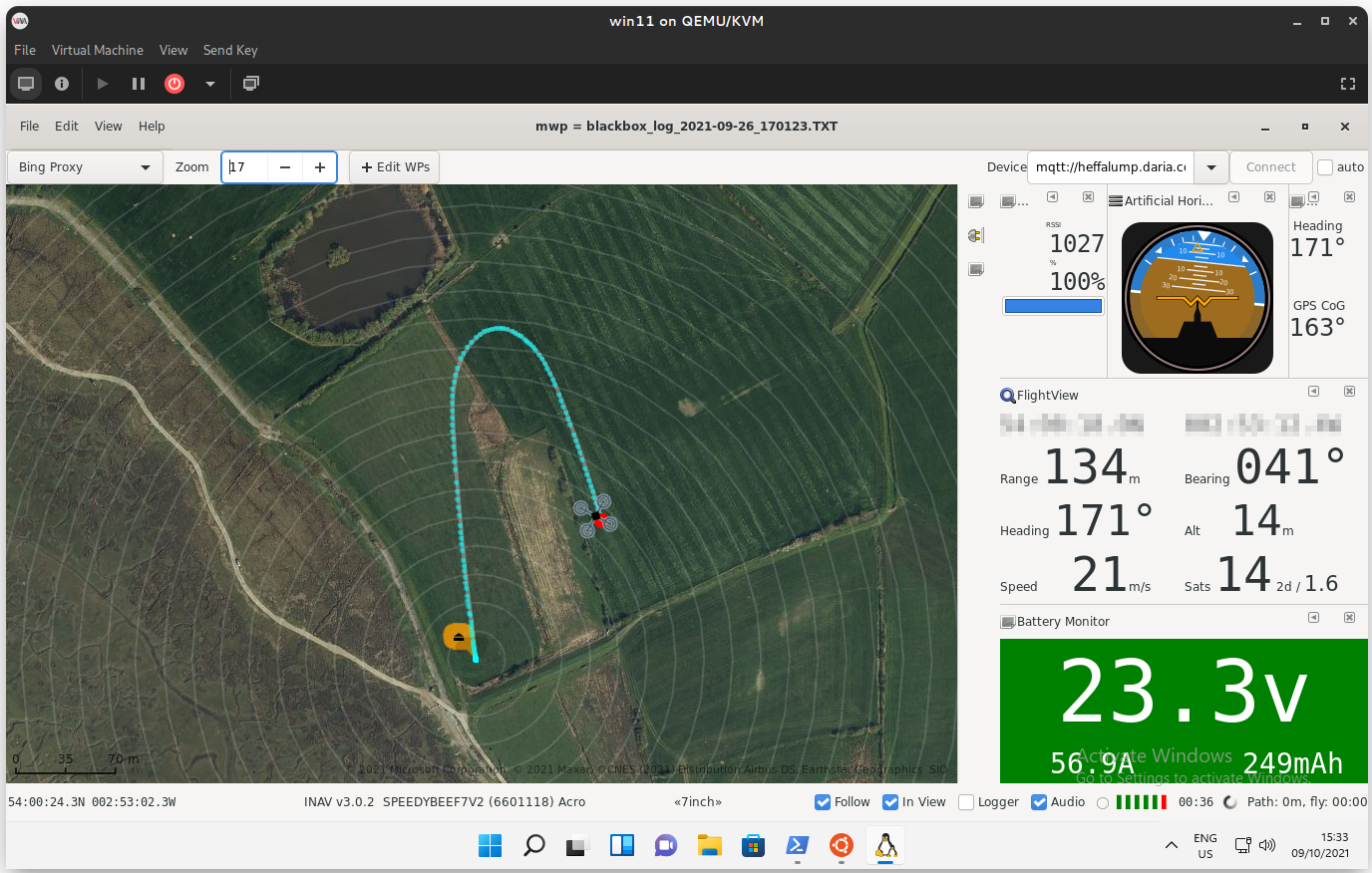 {: width="80%" }
{: width="80%" }
!!! Note "Good enough!" The user's compass seems good enough for navigation functions (top right widget comparing GPS CoG v. compass heading).