01.Association13.Decomposition methods - sporedata/researchdesigneR GitHub Wiki
1. Use cases: in which situations should I use this method?
-
Healthcare disparity (inequality) studies where there is interest in distinguishing (decomposing) the contribution of individual variables to the inequality versus factors that can be attributed to all other, unmeasured factors, which will often include discrimination. See A Decomposition Method to Assess the Contributions of Geographic and Nongeographic Factors to White-Black Disparities in Health Care
-
Decomposition methoods are used to understand the factors contributing to differences or disparities, such as wage gaps between different groups (like men and women, or different racial or ethnic groups). The most common methods used for this purpose are the Oaxaca-Blinder decomposition and the Mincer wage equation.
2. Input: what kind of data does the method require?
- Continuous outcome and multiple risk factors (continuous or categorical, although the latter needs some special algorithms to avoid estimate errors)
- Count outcomes, which can be achieved by aggregating boolean variables within a geographic or temporal unit, such as counting the number of deaths for hospitals within a given time interval.
3. Algorithm: how does the method work?
Model mechanics
Describing in words
The most common methods used for decomposition are the Oaxaca-Blinder decomposition and the Mincer wage equation. Both methods are extensively used in labor economics to study wage disparities although their application is not limited to this field. They can be applied to any situation where there is a need to understand the differences in outcomes between two groups and what factors contribute to these differences, including disparities in health outcomes, educational attainment, or employment opportunities, among others.
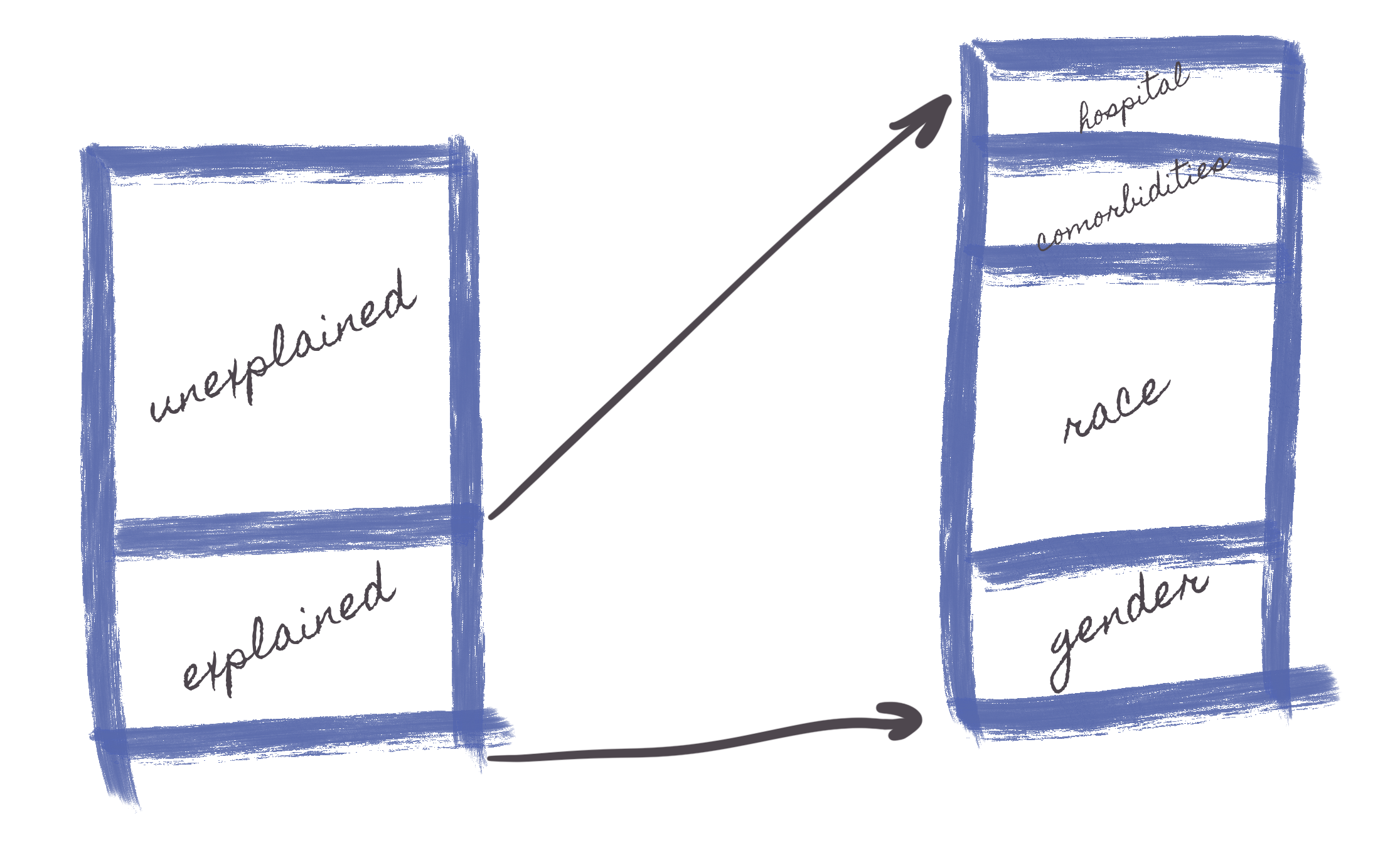
- The Oaxaca-Blinder Decomposition method is widely used to analyze differences in wages (or other outcomes) between two groups. The decomposition is typically done using linear regression models where wages are regressed on a set of explanatory variables for each group. The difference in the regression coefficients and the means of the explanatory variables between both groups helps in understanding the wage gap. The basic idea is to decompose the observed wage gap into two parts:
1.1. The Explained Part which is a result of differences in the characteristics or 'endowments' (like education, experience, occupation, etc.) between the groups. For example, if one group tends to have higher education, part of the wage gap could be explained by this.
1.2. The Unexplained Part which includes all the wage gap that cannot be accounted for by observable characteristics. It often includes factors like discrimination, differences in unmeasured abilities or skills, or labor market structures.
- Mincer Wage Equation is not a decomposition method per se, but is often used in conjunction with decomposition analysis. It is a regression model where the dependent variable is the natural logarithm of wages, and the independent variables typically include education, work experience, and other relevant factors. The Mincer equation helps in understanding how different factors contribute to wage levels.
By decomposing these differences, researchers and policymakers can better understand the underlying causes of disparities and design more effective interventions to address them.
Describing in images
Data science packages
Suggested companion methods
Learning materials
4. Output: how do I interpret this method's results?
Metaphors
Decomposition models help sifting the contribution of disparities on a specific health outcome.