01. Home - senthilpazhani/ReactJS GitHub Wiki
React
React is a javascript library used to build the user interface for web applications. React is the "View" in MVC architecture.
React Fiber and ReactVR.
React Fiber is a complete rewrite of the previous release focusing on incremental rendering and quick responsiveness, React Fiber is backward compatible with all previous versions. ReactVR is built on top of React Native frameworks, it enables developing UI with the addition of 3D models to replicate 360-degree environment resulting in fully immersive VR content.

Key terms:
JSX (JavaScript Extension) JSX Allows us to include ‘HTML’ in the same file along with ‘JavaScript’ (HTML+JS=JSX). Each component in React generates some HTML which is rendered by the DOM.
ES6 (ES2015) The sixth version of JavaScript is standardized by ECMA International in 2015. Hence the language is referred to as ECMAScript. ES6 is not completely supported by all modern browsers.
ES5(ES2009) This is the fifth JavaScript version and is widely accepted by all modern browsers, it is based on the 2009 ECMA specification standard. Tools are used to convert ES6 to ES5 during runtime.
Webpack A module bundler which generates a build file joining all the dependencies.
Babel This is the tool used to convert ES6 to ES5. This is done because not all web browsers can render React (ES6+JSX) directly.
DOM (Document Object Model) DOM is an object that is created by the browser each time a web page is loaded which can dynamically add or remove the data at the back end. But each time any modifications were done a new DOM is created for the same page. This repeated creation of DOM results in unnecessary memory wastage and decrease in applications performance.
Component In ReactJS, everything is a component. The biggest advantage of using components is that, you can change any component at any point of time without affecting the rest of the applications. This feature is most effective when implemented with larger and real time applications where data changes frequently. Each time any data is added or updated, ReactJS automatically updates the specific component whose state has actually changed. This saves the browser from the task of reloading the whole application to reflect the changes.
Features Of React
Now that you have understood what is React and why it is used, lets now uncover few of its intriguing features.
JSX: JSX stands for JavaScript XML. Its an XML/ HTML like syntax used by React. It extends the ECMAScript so that XML/ HTML like text can co-exist along with JavaScript react code. This syntax is used by the pre-processors like Babel to transform HTML like text found in JavaScript files into standard JavaScript objects. With JSX, we can go a step further by again embedding the HTML code inside the JavaScript. This makes HTML codes easy to understand and boosts JavaScript’s performance while making our application robust.
Virtual DOM: Like an actual DOM, virtual DOM is also a node tree that lists the elements and their attributes and content as Objects and their properties. React’s render function creates a node tree out of the react components. Then, it updates this tree in response to the mutations in data model caused by various actions done either by the user or by the system.

This virtual DOM works in three simple steps.
- Whenever any underlying data changes, the entire UI is re-rendered in Virtual DOM representation.

- Then the difference between the previous DOM representation and the new one is calculated.
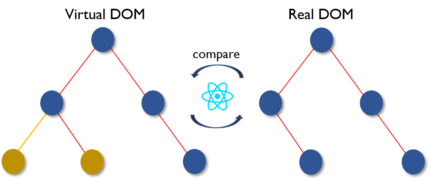
- Once the calculations are done, the real DOM will be updated with only the things that have actually changed. You can think of it as a patch. As patches are applied only to the affected area, similarly, the virtual DOM acts as patches and are applied to the elements which are updated or changed, in the real DOM.
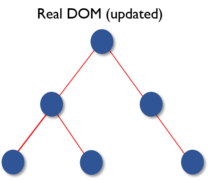
This makes our application faster and there is no memory wastage.
Testability: React views can be used as functions of the state (state is an object which determines how component will render and behave). Thus, we can easily manipulate with state of the components which we pass to the ReactJS view and take a look at the output and triggered actions, events, functions, etc. This makes React applications quite easy to test and debug.
Server-Side Rendering(SSR): Server-Side rendering allows you to pre-render the initial state of your react components at the server side only. With SSR, the server’s response to the browser becomes only the HTML of the page which is now ready to be rendered. Thus, the browser can now start rendering without having to wait for all the JavaScript to be loaded and executed. As a result, the webpage loads faster. Here the user will be able to see the web page inspite of React still downloading the JavaScript, creating the virtual DOM, linking events, etc. at the back end.
One-Way Data Binding: Unlike other frameworks, ReactJS follows unidirectional data flow or one way data binding. Major advantage of One-Way-Data binding is that, throughout the application the data flows in a single direction which gives you better control over it. Because of this, application’s state is contained in specific stores and as a result, rest of the components remains loosely coupled. This makes our application more flexible leading to increased efficiency.

Simplicity: Use of JSX files makes the application really simple and easy to code as well as understand. Even though we can use plain JavaScript here, using JSX is easier. React’s component-based approach along with distinct life cycle methods also make it simple to learn.
Debugging There will be a point when a developer goes through a roadblock. It could be as simple as a ‘missing bracket’ or as tricky as a ‘segmentation fault’. In any case, the earlier the exception is caught the lesser is the cost overhead. React uses compile time debugging and detects errors at an early stage. This ensures that errors don’t silently turn up at run-time. Facebook’s unidirectional data flow allows clean and smooth debugging, fewer stack traces, lesser clutter and an organized Flux architecture for bigger applications.
Note: Webpack offers several plugins which further minimize (minify) the size during production, The React + Redux bundle minified constitutes around 200 kb whereas its rival Angular is almost four times bigger (Angular + RxJS bundle).