DDA X Brasenham's line algorithms - sarahmss/Cub3d GitHub Wiki
In any 2D plan, if we connect two points (x0, y0) and (x1, y1) we get a line segment. In computer graphics, we can't draw a line without the coordinate of each point who composes it.
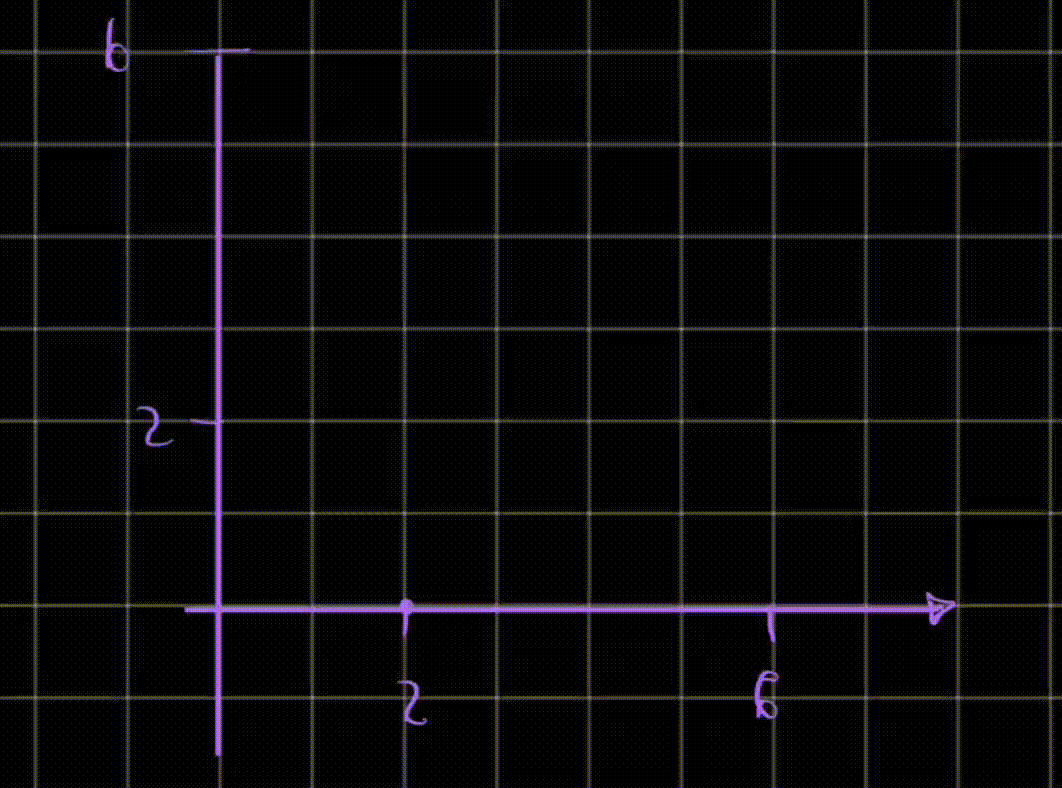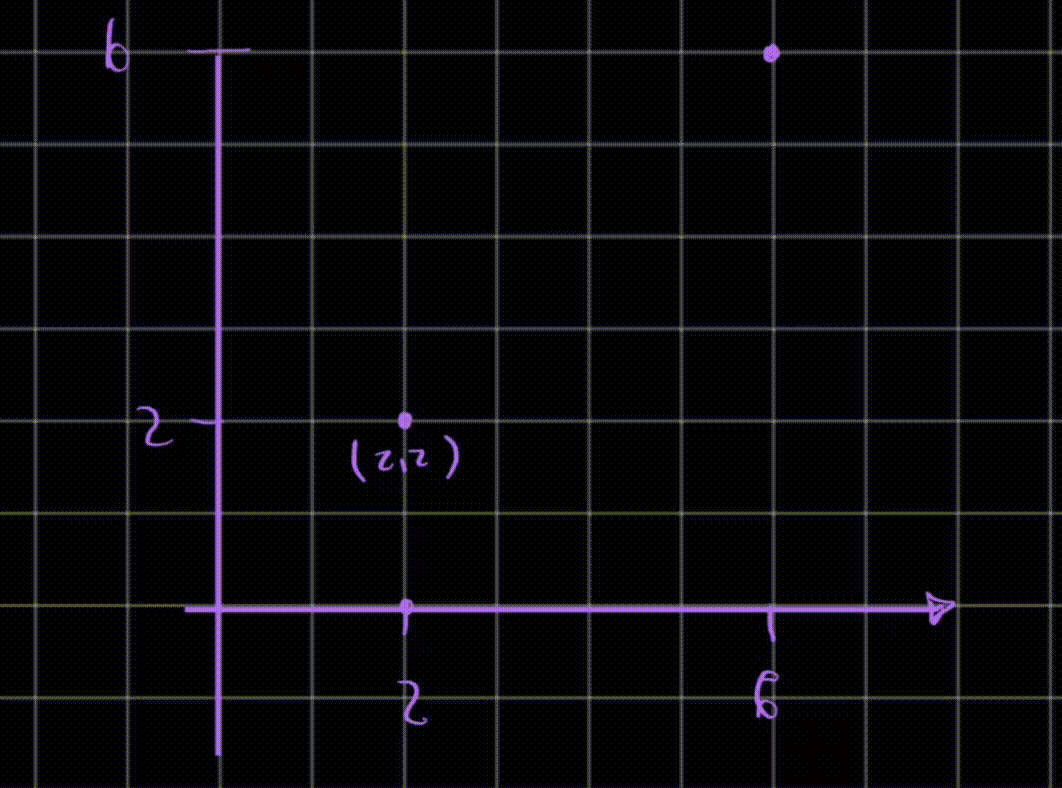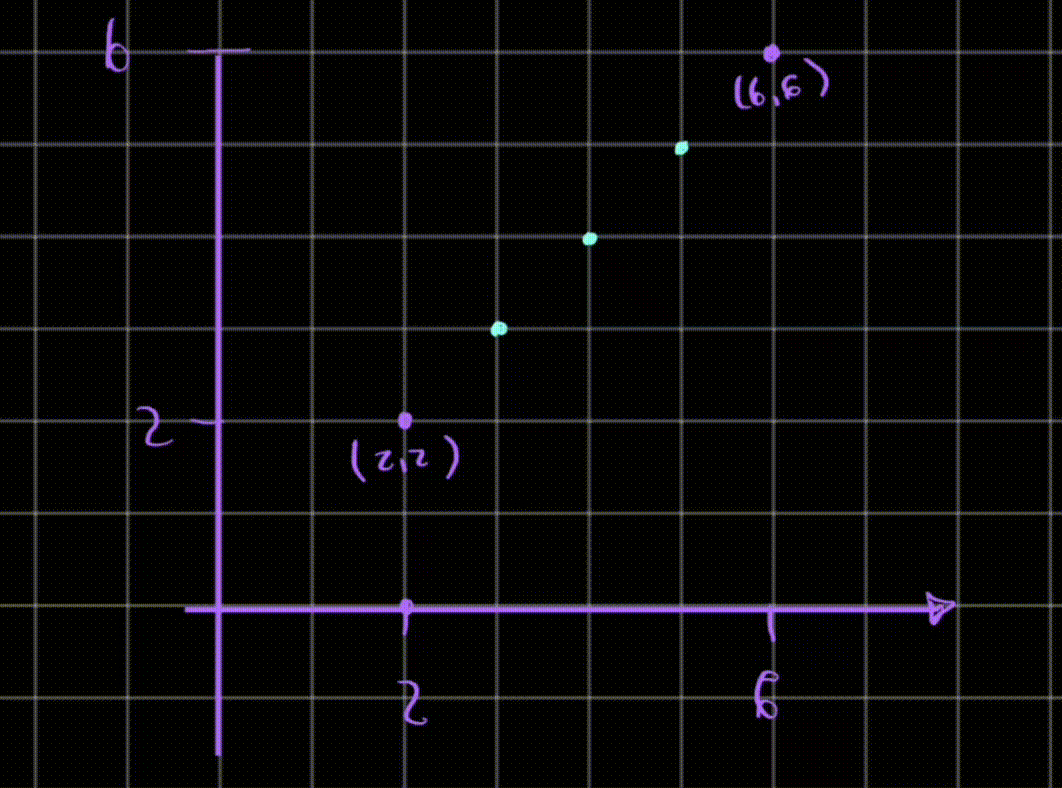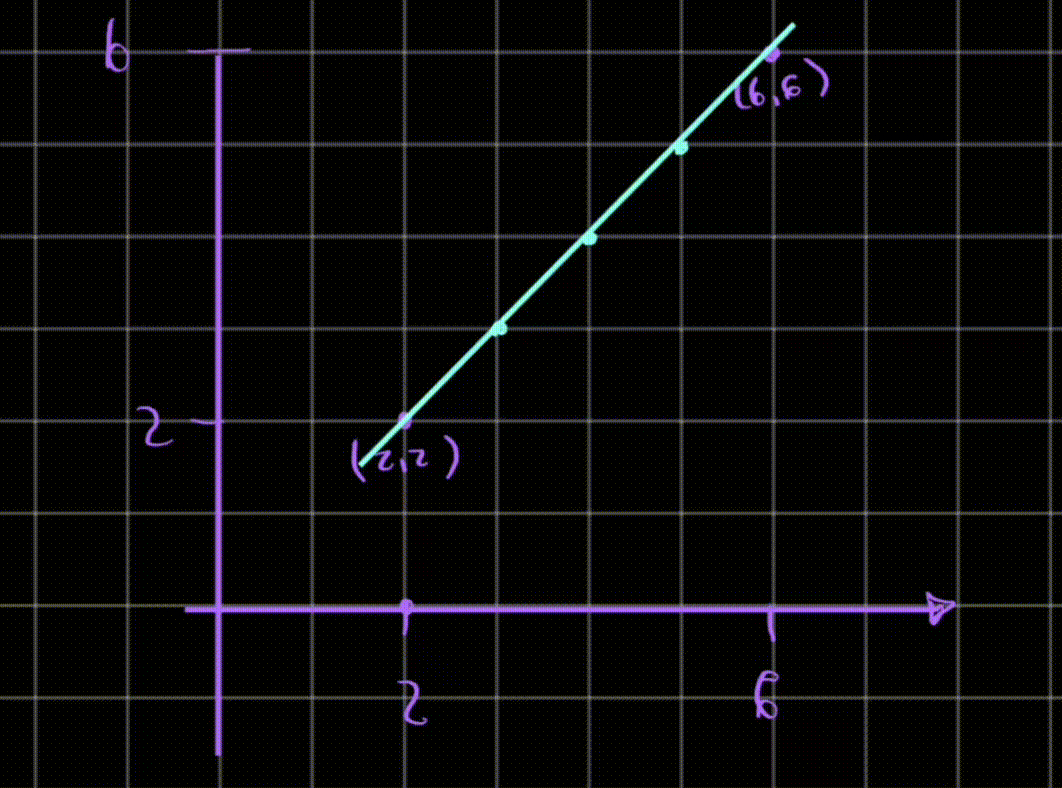 To calculate the intermediate points we can use an algorithime.
Some assumptions to keep algorithm simple:
To calculate the intermediate points we can use an algorithime.
Some assumptions to keep algorithm simple:
- Lines are drwaned left --to--> right
- xi < xf and yi < yf
- 0 < m < 1 ; f(x) = mx + b
Digital Differential Analyzer
-
given (xi, yi) and (xf, yf) define dx and dy
dx = xf - xi;dy = yf - yi; -
choose the number of steps to put pixel
steps = max(abs(dx), abs(dy)); -
Calculate increment for each step
x_inc = dx / (float)stepsy_inc = dy / (float)steps -
Use a function to put pixels
for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++) { putpixel (round(X),round(Y),WHITE); X += Xinc; Y += Yinc; }
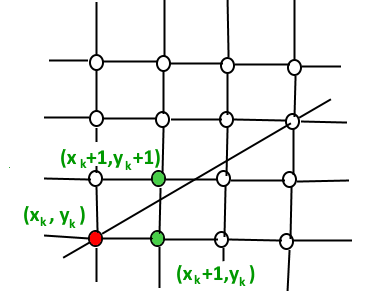
Brasenham's line algorithm
- Always increase x by 1 and choose if keep in y or go to y + 1 this means
from any position (Xk, Yk) we need to choose (based in point that is closer to the original line) between (Xk + 1, Yk) and (Xk + 1, Yk + 1)