| Binary |
A base 2 number system that uses 1s and 0s; computing language that computers use to operate and store data  |
|
| Hexadecimal |
A base 16 number system that is used to simplify binary; symbols include 0-9 and A-F; used for color  |
Color |
| Bit |
A binary digit, either holding a value of 0 or 1 |
|
| Nibble |
Unit of digital data consisting of 4 bits; sometimes used to describe amount of memory used |
|
| Byte |
Unit of digital data consisting of 8 bits; computers process data in bytes of information |
|
| Lossless Compression |
A process which reduces a file's size without losing the file's quality; original data file rewritten in a more compressed, efficient way (lossless compression algorithms include JPEG 2000 and Apple Lossless compression)  |
|
| Lossy Compression |
A Process which reduces a file's size while also losing data and quality from the original data file; typically applies to image (JPEG) and audio files (MP3) |
|
| Metadata |
data that describes other data  |
Metadata |
| Library |
Collections of prewritten code that programmers can implement and use in their projects to optimize and enhance tasks (ex: numpy, pillow)  |
|
| Dependencies |
Software that another piece of software relies on; essential for a different part of the code to work |
|
| Import |
Command in python used to allow a python file access to another python file; uploads data from external sources |
Import |
| Computer Network |
Multiple computers are linked and allow for the sharing of data 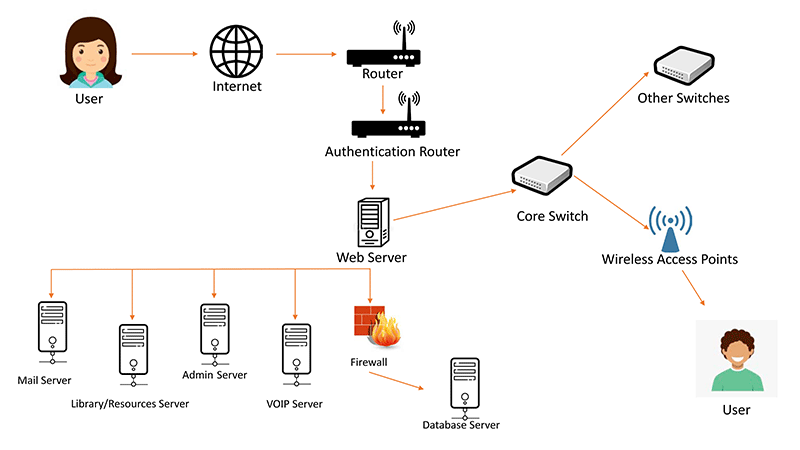 |
|
| Parallel computing |
A large problem is broken into smaller calculations tackled by multiple processors |
|
| Distributed computing |
When there are multiple software pieces tackling a problem but they run as a single system |
|
| Blueprints |
Connection between Python and HTML files that together enable users to have data and fetch it |
Blueprints |
| Sort |
Sorting algorithms put the elements of an array in order depending on the sorting requirements (low to high, high to low, alphabetical order) |
|
| Search |
Search algorithms traverse along an array to look for an element that means a certain requirement and returns the location(s) of the number(s) |
|
| Linear search |
In this algorithm, one checks each element in the array from left to right. Once a match is made, the position is returned. If the match isn’t made at the end of the array, then the algorithm usually returns -1 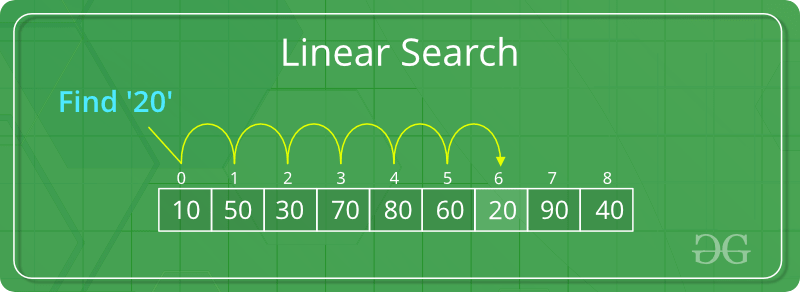 |
|
| Binary search |
In this algorithm, the search interval is repeatedly divided in half for every iteration. In the first iteration, the array elements are split and then there is a check to see which interval has the intended value. This process is repeated until the intended value is found 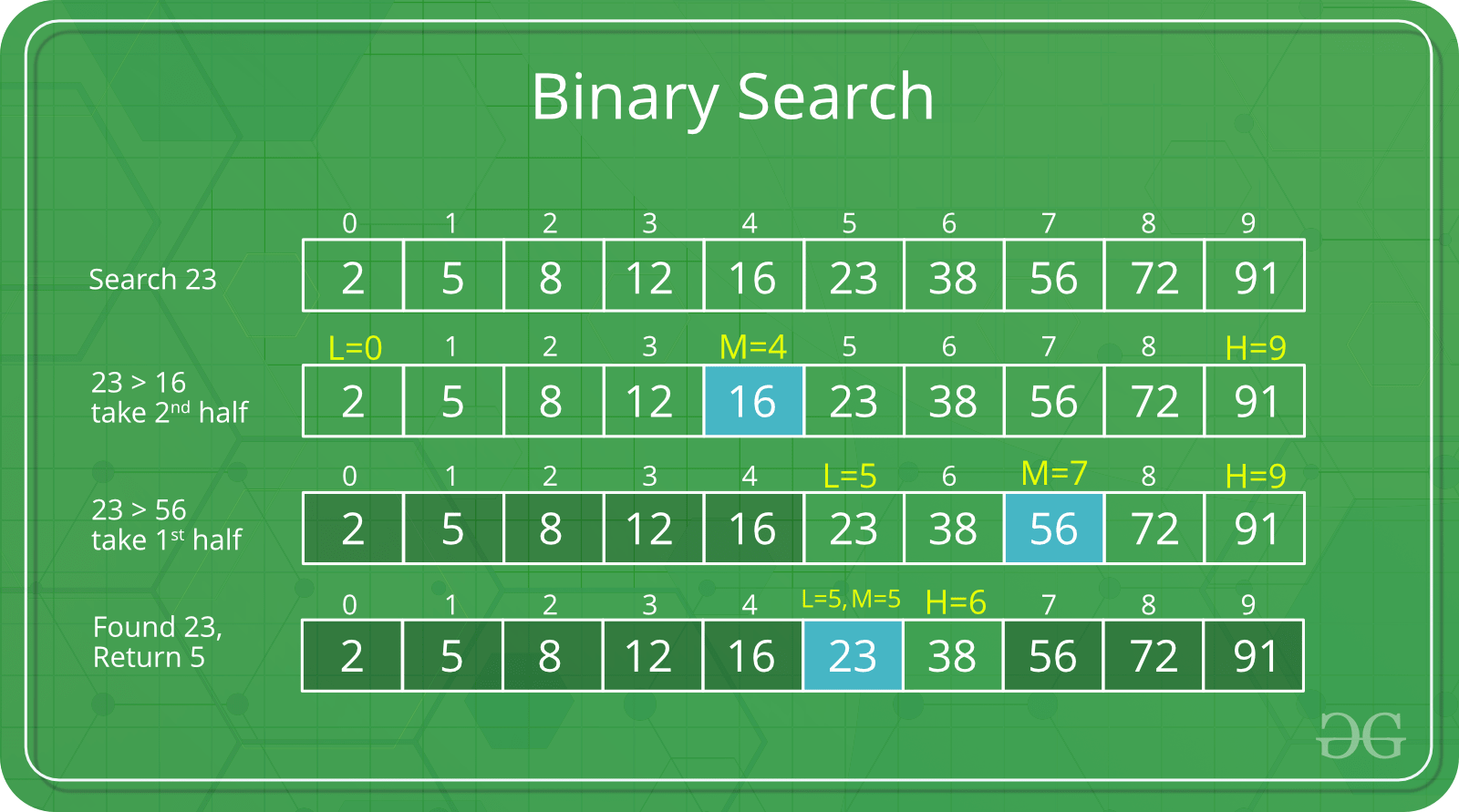 |
|
| Code Sequence |
The order of execution, if line by line then code executes linearly |
|
| Procedures/Functions |
These are specific tasks that the code does, the code calls functions based on code sequence |
Procedures/Functions |
| Procedural Abstraction |
When we know what we want the code to do but not how it does it; When complex code is simplified with methods/functions |
??? |
| Object oriented programming |
A style of programming which uses objects and classes; Main goal is to have related functions work as a single unit |
|
| Class |
It is an environment to initialize objects, methods, and attributes |
Class |
| Attribute |
Property or characteristic of a component of the program (usually changeable) |
|
| Method |
Determines what an object does; action that object does |
|
| Object |
Instances of classes, entities that performs procedures and have certain characteristics |
|
| Protocol |
Set of rules for sending data on the internet; how computers can communicate with one another |
|
| TCP/IP |
Suite of communication protocols; IP is addresses that data is sent to (you can think of it as home addresses) and TCP is how the data is delivered (you can think of it as the mail delivery service in the analogy) |
|
| HTTP |
Used for accessing web browsers and interacting with HTML files between clients and servers, application layer protocol |
HTTP |
| GET |
HTML request to get/request data from a specific resource; only used for receiving data not changing it |
Parse GET request in search |
| POST |
HTML request to accept data in the request and make a change to a web form |
GET/POST |
| Data |
Any information stored or processed by a computer |
|
| Data abstraction |
Simplifying representation of data from the end user; for example, databases and data structures |
|
| Web API |
Set of functions that allows developers to access data and interact with a web application |
Weather API |
| REST |
Stands for representational state transfer; set of guidelines to build a web API, uses HTTP requests to access and use data |
|
| FETCH |
Allows developers to make HTTP requests to servers from web browsers; fetch resources async across network |
Fetch API |
| Async |
Responses to API call is returned immediately without refreshing the URL |
Crud Async |
| Request |
Request is sent by client to trigger action on server |
Get requests from form |
| Response |
Sent as answer back from the server to the client |
HTML Responses |
| MVC |
Model-View-Controller: model is the data, view is the user interface, and controller is processing the input |
|
| CRUD |
Create, read, update, and delete operations in traditional database systems |
Crud |