| Binary |
Binary is a term that describes a base 2 numbering system that only has two possible values for each digit which include 0 and 1. The highest number you can represent with bits can be represented by the formula 2^n-1 |
|
| Hexadecimal |
Hexadecimal is a term that describes a base 16 numbering system that uses numbers 0-9 and letters A-F. It used used to describe colors as well  |
Color |
| Bit |
A digit of binary that either has a value of 1 or 0 |
|
| Nibble |
It is a digital data unit that has 4 bits and is usually used to describe the amount of memory that has been used |
|
| Byte |
It is a digital data unit that has 8 bits and is usually used to describe how computers process data in 'bytes' of information |
|
| Lossless Compression |
This is a process that reduces a size of a file without compromising the file's quality. The original data is written again except is more compressed to make it more efficient  |
|
| Lossy Compression |
This is a process that reduces a size of a file while also compromising the file's quality. This usually applies to images or audio files. |
|
| Metadata |
It is essentially data that describes other data. It makes finding and working with different instances of data easier. Does not affect the file but it describes it. Also seen in images |
Metadata |
| Library |
An area of prewritten code that programmers can use to help benefit and make their tasks easier. Examples: NUMPY & PILLOW |
--- |
| Dependencies |
This is when a piece of software relies on another piece in order to work. It is needed for a different part of the code to work |
--- |
| Import |
This is a command that is used in python to allow a file to have access to another python file. It uploads data from external sources. A command to import data from a separate file.  |
Import |
| Computer Network |
A place where many computers are linked to allow the sharing of data |
--- |
| Parallel Computing |
This is where a big problem is broken up into smaller pieces so that it can be tackled by multiple processors |
--- |
| Distributed Computing |
This is when there are multiple software pieces that tackle a single problem but they are run as the same system |
--- |
| Blueprints |
This is the connection between HTML files and Python files that allow users to have data and to fetch it. A sense of organization. Each person has their own file that you link smaller files to so that they all follow similar pattern |
Blueprints |
| Sort |
Algorithms that sort put the elements of an array in order based on sorting requirements. These can be from low to high, high to low, or in alphabetical order. |
--- |
| Search |
Algorithms that search look for elements that meet a certain requirement and returns the locations of numbers. If you go through a list of elements in a list, it will return the location of that element |
--- |
| Linear Search |
In a linear search algorithm, one checks each element in the array from left to right. Once there is a match, the position is returned. If there is no match, the algorithm will usually return a -1  |
--- |
| Binary Search |
The search interval will be divided in half repeatedly for each iteration. In the first iteration, the elements of the array are split and then there is a check to see which interval has the intended value. This is repeated until the intended value is found.  |
--- |
| Code Sequence |
A code sequence is the order of execution. If the code is line by line then it executes linearly |
--- |
| Procedures/Functions |
Each code does specific tasks based on the code sequence. A block of code that is called to perform a certain task. The function will return one or more values based on the code that is called. |
--- |
| Procedural Abstraction |
This is when we know what we want to do with the code but now how it happens. The complex code is simplified with different methods and functions. |
--- |
| Object Oriented Programming |
This is a style of programming that uses objects and classes. The main goal is to have related functions work together in a single unit 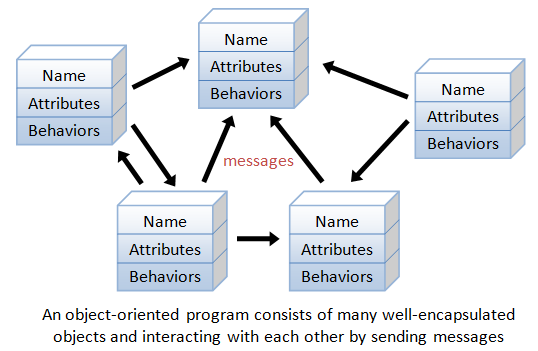 |
--- |
| Class |
A class is an environment to initialize objects, methods, and attributes |
--- |
| Attribute |
A characteristic of a component of a program that is usually changeable |
--- |
| Method |
This determines the action that an object does |
--- |
| Object |
These are instances of classes that perform different procedures and have certain characteristics |
--- |
| Protocol |
This is a set of rules for sending data on the internet and how computers communicate with one another |
--- |
| TCP/IP |
IP is addresses that data is sent to (kind of like home addresses) and TCP is how the information is delivered (mail being sent to said addresses)  |
--- |
| HTTP |
Hyper Text Transfer Protocol. This is used for accessing the web and interacting with files between servers. Clients send file requests to web servers that handle requests through a HTTP service. |
--- |
| GET |
This is a specific HTML request for data from a specific resource. This is only used for getting data not changing it |
--- |
| POST |
The HTML request to accept data and make changes |
Post |
| Data |
Any type of information that is stored by a computer |
--- |
| Data Abstraction |
This simplifies representations of data from the end user such as databases and data structures. An example of this is when you drive a car, you only need to know how to steer and brake and what gears to use. You don't need to know how the engine works/runs. Likewise, data abstraction simplifies code to make it easier to read or learn.  |
--- |
| Web API |
This is a set of functions that allow users to access data and interact with the application. Allows you to access live data from the internet in your website. Get information from JSON |
Web API |
| REST |
This stands for REPRESENTATIONAL STATE TRANSFER which means that there is a set of guidelines to build a Web API. It uses HTTP requests to access and use data |
--- |
| FETCH |
This allows developers to make HTTP requests from web browsers and to fetch resources from across networks. Retrieves data from a separate server and puts it in alternate location  |
Fetch |
| Async |
This is responses to API. Calls are immediately returned without refreshing URLs |
--- |
| Request |
The request is sent by the client to trigger action on the server |
--- |
| Response |
This is sent as an answer back from the server to the client |
--- |
| MVC |
This stands for Model View Controller. Model is the database where info is stored. View is what the consumer sees. Controller is how model and view communicate. This is a software design pattern that are commonly used for developing user interfaces that divide logic into three elements  |
--- |
| CRUD |
Stands for create, read, update, and delete operations in traditional database systems |
--- |










