RAG - runtimerevolution/labs GitHub Wiki
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an innovative approach in NLP (Natural Language Processing) that combines the strengths of information retrieval systems and generative language models. This hybrid model enhances the quality and relevance of generated content by incorporating relevant external information, rather than relying solely on pre-trained knowledge within the model. Traditional generative models like GPT (Generative Pre-Trained Transformers) are powerful in generating human-like text based on the patterns and data they were trained on. However, they have limitations, especially when dealing with specific, up-to-date, or rare information that wasn't included in their training data. On the other hand, information retrieval systems excel at fetching relevant documents or snippets from a large corpus of text, but they do not generate text or coherent responses on their own. RAG models leverage the retrieval component to fetch relevant information from a large corpus or knowledge base, and then use the generative component to integrate this information into coherent, contextually appropriate responses. This integration significantly enhances the accuracy and informativeness of the generated text, making RAG particularly useful for applications requiring up-to-date or highly specific information.
stateDiagram-v2
[*] --> Data
state Data {
Embedding --> Index
}
Index --> Vector_Storage
state Data {
Document_Loading --> Splitting
}
Splitting --> Vector_Storage
Vector_Storage --> Retrieval
Retrieval --> QA_Model
QA_Model --> Docs_Output_plus_Prompt
Docs_Output_plus_Prompt --> LLM
Context[System] --> LLM
Chain --> LLM
Memory --> LLM
LLM --> Memory
LLM --> Chain
LLM --> Output_Parser
Output_Parser --> Output
Output --> [*]
2. How RAG Differs from Standard LLMs
Standard LLMs (Large Language Models) generate text based solely on their training data and the prompts they receive. They do not have access to external databases or real-time information, which can lead to inaccuracies or outdated content. For instance, a standard LLM trained up until 2021 won't be able to provide information on events or developments that occurred after that time. In contrast, a RAG system dynamically incorporates relevant external information at the time of query. This means it can provide more accurate and current responses by pulling in real-time data or the latest information from a designated corpus. This retrieval step ensures that the generative process is informed by the most relevant and recent information available, thereby improving the quality and reliability of the output.
- Improved Accuracy: By accessing external sources, RAG systems can correct or update information that may be outdated or inaccurate in the generative model's training data.
- Enhanced Relevance: Retrieval mechanisms ensure that the generated responses are directly relevant to the user's query, drawing on specific, contextual information from a large corpus.
- Scalability: Instead of retraining a model to update its knowledge, a RAG system can dynamically access and use the latest data, making it easier to scale and keep up-to-date.
- Cost Efficiency: Fine-tuning large models can be resource-intensive. Using a retrieval component can reduce the need for constant retraining by leveraging existing, relevant datasets.
- Flexibility: RAG systems can be tailored to specific domains or applications by configuring the retrieval corpus accordingly, ensuring that the generative model is augmented with highly relevant information. In summary, RAG represents a significant advancement in NLP by marrying the strengths of retrieval and generation. This hybrid approach addresses many of the limitations of standalone generative models, resulting in outputs that are more accurate, relevant, and up-to-date. As we delve deeper into the components and architecture of RAG systems, we'll explore how these benefits are realized in practical implementations.
-
Loading
-
Indexing
-
Storing
-
Querying A retriever defines how to efficiently retrieve relevant context from an index when given a query.
Semantic Similarity Search: take the documents that are most similar to the query in the embedding space; you may miss out on diverse information.
Maximum Marginal Relevance (MMR): we send a query in, and then we initially get back a set of responses, with 'fetch_k' being a param that we can control in order to determine how many responses we get. This is based solely on semantic similarity. From there, we then work with that smaller set of docs and optimize for not only the most relevant ones, based on semantic similarity, but also ones that are diverse. And from that set of docs, we choose a final 'k' to return to the user.
SelfQuery: useful when you get questions that aren't solely about the content that you want to look up semantically, but also include some mention of some metadata that you want to do a filter on. we use the LLM itself to split that original question into two separate things, a filter and a search term. (Most vector stores support a metadata filter)
Compression: can be useful to really pull out only the most relevant bits of the retrieved passages. For example, when asking a question, you get back the whole document that was stored, even if only the first one or two sentences are the relevant parts. With compression, you can then run all those documents through a LLM and extract the most relevant segments and then pass only the most relevant segments into a final LLM call. This comes at the cost of making more calls to the LLM, but it's also really good for focusing the final answer on only the most important things.
-
Evaluation
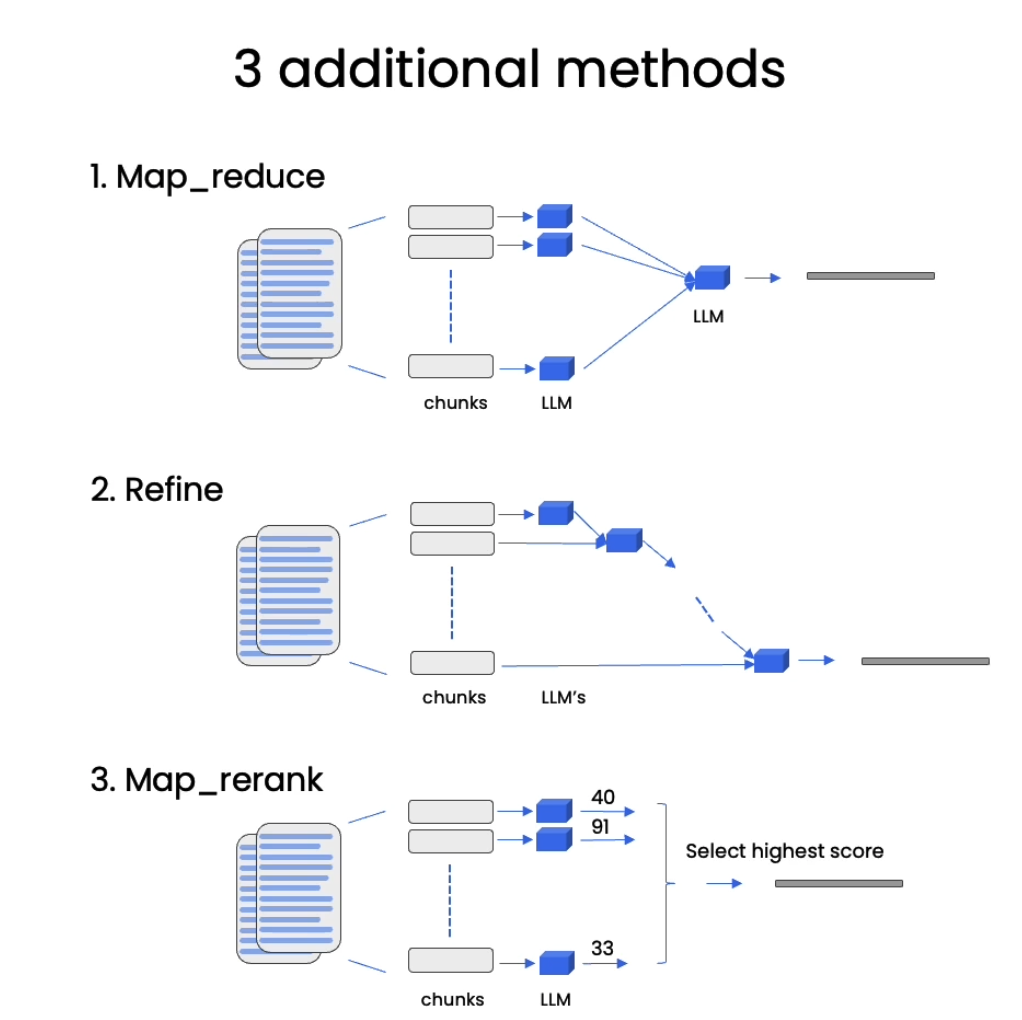
- Stuff method
- All of the retrieved documents are passed to the LLM at the same time.
 |
|---|
| Methods for Q&A over Documents29 |
- Each of the retrieved documents is passed to the LLM, then all the results are stuffed and passed to the final LLM.
- This method is slower than the stuff method.
- Because each retrieved document has little information and context, the end result may be worse than the stuff method.
- In this method, the first retrieved document is passed to the LLM. Then the result is joined together with the second document and passed again, and so on, until we have the result of the final document.
- In other words, this method generates a response to the first retrieved document and then improves that answer iteratively based on the subsequent documents.
- This method generally produces a better result than the map reduce method, since it keeps adding new information to the response.
- With map rerank, all the retrieved documents are passed to the LLM, but in this case we ask the LLM to rank the passed documents according to their relevance compared to the question asked. Only the most relevant documents will be passed to the final LLM.
- This method may produce good results because it gets rid of noise introduced by irrelevant retrieved documents and produces an answer based only on relevant content.
- Clean Your Data
- Ensure data clarity and consistency for enhanced retrieval accuracy.
- Combine documents logically and remove conflicting or redundant information.
- Use LLM to create summaries for easier retrieval.
- Index Types
- Use keyword-based search alongside embedding-based retrieval.
- Consider hybrid approaches for different use cases.
- Fine-Tune Embedding Model
- Customize embedding models for domain-specific relevance.
- Fine-tune embeddings to improve retrieval performance.
- Updating Chunk Size
- Adjust chunk size and overlap for better retrieval of relevant information.
- Increase the number of top retrieved chunks to enhance comprehensiveness.
- Base Prompt
- Customize base prompts to guide LLM behavior.
- Experiment with different prompt formats for specific query types.
- Metadata Filtering
- Add metadata to context chunks to aid in filtering and prioritizing results.
- Utilize metadata like date for relevance sorting.
- Extract critical metadata fields (e.g., tags, author ID) using an LLM.
- Consider few-shot learning for optimising the extraction of multiple metadata types.
- Query Routing
- Employ multiple indexes and route queries accordingly.
- Optimize indexes for specific query types or behaviors.
- Query Transformations
- Alter user queries for better matching.
- Explore techniques like rephrasing, and sub-queries.
- Use multi-step query transformations for effective processing of complex questions.
- Query Expansion
- Utilize an LLM to generate multiple queries from the initial query for different perspectives.
- Employ zero-shot prompt engineering for query expansion.

- Reranking
- Rerank retrieved chunks based on relevance to the initial question.
- Combine reranking with query expansion for comprehensive context retrieval.
- Use LLMs or Bi-Encoders for reranking to capture semantic information efficiently.
- Consider specific reranking models like FlagEmbeddingReranker, RankGPTRerank, and Cohere Reranker.

- Improving RAG Performance with HyDE
- Create hypothetical answers to user queries and transform them with the query into embeddings for retrieval.
- Focus on origins rather than relationships to improve retrieval accuracy.
- Use LLM Dev Tools
- Leverage debugging tools in frameworks like LlamaIndex and LangChain.
- Explore external tools for deeper insights into RAG system workings.
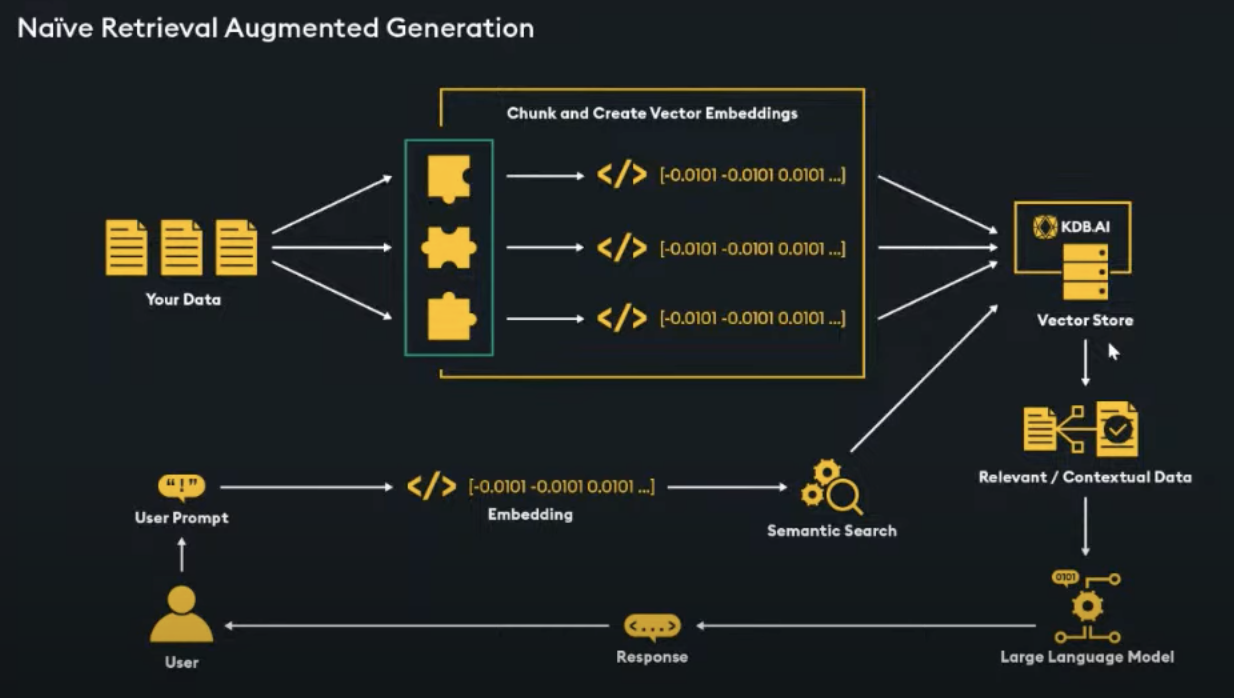
Naive approach
 |
|---|
| Naive approach 30 |
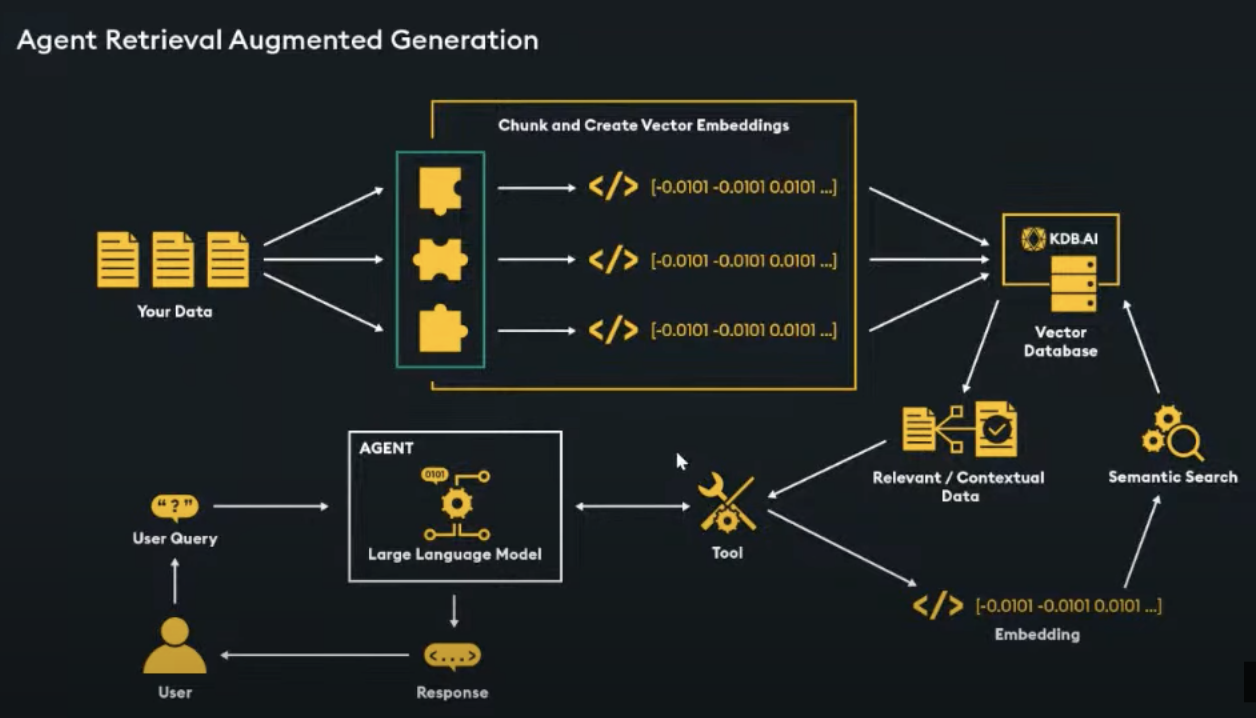
Agent approach
 |
|---|
| Agent approach 30 |
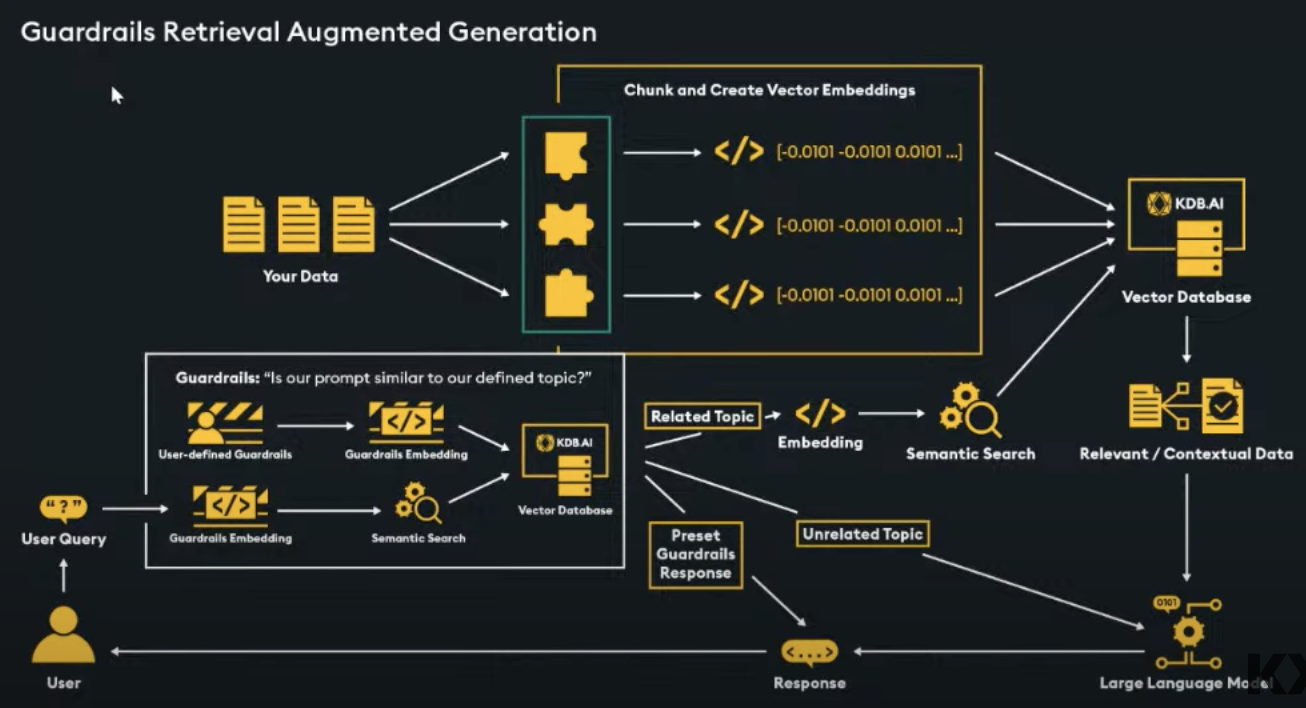
Guardrails approach
 |
|---|
| Guardrails approach 30 |
Knowledge graph approach
 |
|---|
| Guardrails approach 30 |
-
Advantages of Graph Databases in RAG:
- Context-Rich Data Storage: Graph databases store information in nodes and edges, capturing relationships and links between data points. This additional context is valuable for RAG.
- Navigating Hierarchies: Graph databases excel at representing hierarchical structures, making them suitable for scenarios where deep hierarchies need to be navigated.
- Hidden Connections: Graph Database reveal hidden connections between items, which can enhance the quality of generated responses.
- Discovering Relationships: Graph Databases facilitate the discovery of relationships between items, aiding in generating relevant content.
-
Use Cases for RAG with Graph Databases:
-
Recommendation Chatbot:
- Graph databases can power recommendation systems by modeling user-item interactions and capturing preferences.
- The chatbot can provide personalized recommendations based on user queries.
- Example: Suggesting relevant products to users based on their preferences15.
-
AI-Augmented CRM (Customer Relationship Management):
- Graph databases allow modeling complex customer relationships.
- The chatbot can assist sales or support teams by providing context-aware responses about customer interactions.
- Example: Understanding the history of interactions with a specific customer15.
-
Behavior Analysis with Natural Language:
- Graph databases enable analyzing correlations between data points.
- The chatbot can analyze customer behavior patterns using natural language queries.
- Example: Identifying trends or anomalies in customer behavior based on textual descriptions15.
-
Recommendation Chatbot:
-
Knowledge Expansion:
- Scenario: When you want to augment a large language model (LLM) with external data to improve contextuality and accuracy.
- Why?: Vector databases allow efficient access to vast information, expanding the LLM's knowledge base19,22.
-
Customer Support Chatbots:
-
Research Literature Review:
- Scenario: Analyzing research papers to summarize developments in a field.
- Why?: RAG can extract key themes from a literature database using vector search23.
-
Text Summarization and Classification:
- Scenario: When summarizing or classifying text data.
- Why?: Vector databases aid in retrieving relevant content for summarization or classification tasks24.
-
Sentiment Analysis:
- Scenario: Analyzing sentiment in user-generated content.
- Why?: Vector databases help retrieve relevant examples for sentiment analysis24.
In the evolving landscape of large language models (LLMs) and retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), the choice of database technology—vector databases or knowledge graphs—plays a critical role in shaping the performance and scalability of these systems. This detailed explanation combines insights from three articles to provide a clear understanding of when to use vector databases and when to opt for knowledge graphs.
Vector Databases: Unleashing the Power of Embeddings
Characteristics and Strengths:
- Unstructured Data Handling: Vector databases are designed to manage large volumes of unstructured data, such as text, images, and audio, by storing them as high-dimensional vector embeddings. These embeddings capture the semantic relationships between data points.
- Efficient Similarity Search: They excel in scenarios where similarity search is a primary concern. Optimised indexing structures enable swift identification of vectors with similar semantic meanings, facilitating faster and more accurate responses.
- Scalability: Vector databases are highly scalable, making them suitable for handling the massive datasets often associated with LLMs. Horizontal scaling allows seamless expansion to meet growing data requirements.
- Versatility: Capable of handling diverse data types, vector databases provide a unified approach to data representation and retrieval, making them versatile in various applications.
- Cost and Speed: Generally, vector databases offer lower costs and faster retrieval times compared to knowledge graphs, making them efficient for large-scale operations.
Use Cases:
- Customer Service Applications: Ideal for RAG systems designed to assist customer service representatives by dynamically fetching relevant answers from a structured knowledge base. This reduces wait times and ensures consistent information delivery.
- Procedural Queries: Suitable for scenarios requiring quick retrieval of information from standard operating procedures or other structured knowledge bases, enhancing user satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Knowledge Graphs: Navigating the Web of Relationships
Characteristics and Strengths:
- Structured Data and Relationships: Knowledge graphs represent data as networks of nodes (entities) and edges (relationships), making them excellent for managing and exploiting complex relationships between structured data entities.
- Relationship Exploration: They excel at traversing and understanding intricate relationships within data, which enhances contextual understanding by navigating semantic connections between words and phrases.
- Flexible Schema: Adaptable to evolving data structures and relationships, knowledge graphs are suitable for dynamic language modelling tasks.
- Query Expressiveness: Offer expressive query languages (e.g., Cypher for Neo4j) that allow sophisticated queries to uncover nuanced relationships within the data, contributing to improved language model performance.
- Explainability and Traceability: Provide transparent reasoning paths, making it easier to understand how conclusions are reached, which is crucial for applications requiring high explainability.
- Data Integrity and Consistency: Maintain high data integrity and consistency, ensuring reliable data representation.
Use Cases:
- Complex Insurance Claims: Ideal for roles demanding deep understanding of relationships and interdependencies among various entities, such as policies, claims, and customers. Knowledge graphs provide a structured representation of these relationships, aiding in complex decision-making processes.
- Domain-Specific Applications: Particularly useful in fields requiring deep, domain-specific knowledge representation, such as medicine, law, or engineering, where structured, interconnected data is essential for accurate and reliable outputs.
Key Considerations for Choosing Between Vector Databases and Knowledge Graphs
Nature of Data:
- Vector Databases: Best suited for applications dealing primarily with unstructured data where semantic similarities are key.
- Knowledge Graphs: More appropriate for structured data where understanding and exploring complex relationships are crucial.
Scalability Requirements:
- Vector Databases: Excel in handling massive datasets and are highly scalable, making them suitable for applications with significant data growth.
- Knowledge Graphs: Excel in scenarios where efficient traversal and understanding of relationships are critical, though they may come at a higher cost.
Query Complexity:
- Vector Databases: Suitable for less complex queries focused on similarity search and fast retrieval.
- Knowledge Graphs: Advantageous for applications requiring complex, relationship-based queries and sophisticated data exploration.
Explainability Needs:
- Knowledge Graphs: Provide greater explainability and traceability, making them suitable for applications where understanding the reasoning behind outputs is important.
Cost and Performance:
- Vector Databases: Typically offer lower cost and higher speed, making them efficient for large-scale, fast retrieval tasks.
- Knowledge Graphs: May be more expensive but provide accurate and context-rich outputs essential for intricate problem-solving.
Combining Both Approaches
In some scenarios, a hybrid approach that leverages the strengths of both vector databases and knowledge graphs can be beneficial. For example:
- Hybrid Solutions: Use a knowledge graph to maintain structured, domain-specific knowledge and a vector database to handle unstructured data and leverage machine learning models. This combination can provide both the deep, structured understanding of a knowledge graph and the flexibility and scalability of a vector database.
Conclusion
The decision to use a vector database or a knowledge graph for RAG with LLMs depends on several factors:
- Data Nature and Complexity: Structured vs. unstructured data and the complexity of relationships.
- Scalability and Speed Requirements: The need for handling massive datasets efficiently.
- Query and Explainability Needs: The complexity of queries and the need for transparent reasoning.
- Cost Considerations: Balancing cost against the benefits of accuracy and explainability.
Understanding these factors will help IT leaders and CIOs make informed decisions to enhance the performance, scalability, and effectiveness of their RAG systems with LLMs, ultimately driving innovation, productivity, and enhanced user experiences.
1: "Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks" Original paper on RAG by Facebook AI
2: "Retrieval-augmented Generation (RAG): A Comprehensive Guide" - This guide provides an in-depth look at RAG systems, explaining how they combine information retrieval with text generation. Datastax Guide on RAG
3: "RAG: How Retrieval Augmented Generation Systems Work" - This article discusses how RAG enhances generative AI and the key considerations for implementing RAG systems. Willowtree on RAG
4: "Evaluation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation: A Survey" - This survey paper provides a comprehensive evaluation of RAG systems and their impact on natural language processing. Arxiv Survey on RAG
5: "What is RAG? - Retrieval-Augmented Generation Explained" - AWS explains the process of optimizing large language models with RAG by referencing an authoritative knowledge base. AWS Explanation of RAG
6: "The Ultimate Guide to Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)" - This guide explores how RAG combines retrieval-based and generation-based models to revolutionize natural language processing. Pareto AI on RAG
7: "A Survey on Retrieval-Augmented Text Generation for Large Language Models" - This paper offers a detailed perspective on RAG from the retrieval viewpoint. Read more.
8: IBM Research Blog - An article explaining what RAG is and how it improves LLM-generated responses. Read more.
9: Azure AI Search | Microsoft Learn - An overview of RAG and its integration with generative AI in the Azure platform. Read more.
10: High-Level Concepts (RAG). (https://docs.llamaindex.ai/en/stable/getting_started/concepts/)
11: Advanced RAG Algorithms to Optimize Retrieval https://www.comet.com/site/blog/advanced-rag-algorithms-optimize-retrieval/
12: 10 Ways to Improve the Performance of Retrieval Augmented Generation Systems https://towardsdatascience.com/10-ways-to-improve-the-performance-of-retrieval-augmented-generation-systems-5fa2cee7cd5c
13: How to Improve RAG Performance: 5 Key Techniques with Examples https://www.datacamp.com/tutorial/how-to-improve-rag-performance-5-key-techniques-with-examples
14: RAG Value Chain: Retrieval Strategies in Information Augmentation for Large Language Models https://medium.com/@abhinavkimothi/rag-value-chain-retrieval-strategies-in-information-augmentation-for-large-language-models-3a44845e1e26#:~:text=According%20to%20LangChain's%202023%20State,Multi%2Dquery%20and%20time%20weighted.
15: RAG with a Graph database | OpenAI Cookbook.(https://cookbook.openai.com/examples/rag_with_graph_db)
16: Improving RAG performance: Introducing GraphRAG - Lettria. (https://www.lettria.com/blogpost/improving-rag-performance-introducing-graphrag)
17: Graph Data Models for RAG Applications - Graph Database & Analytics. (https://neo4j.com/developer-blog/graph-data-models-rag-applications/)
18: Implementing Graph RAG with NebulaGraph. (https://www.nebula-graph.io/posts/implement_graph_rag_with_nebulagraph)
19: Overview of RAG Approaches with Vector Databases. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=twM_9CM_3RY.
20: Optimizing RAG: A Guide to Choosing the Right Vector Database. https://medium.com/@mutahar789/optimizing-rag-a-guide-to-choosing-the-right-vector-database-480f71a33139.
21: RAG and Vector Search: Better Together for AI. https://www.capellasolutions.com/blog/rag-and-vector-search-better-together-for-ai.
22: Building a RAG Application using LLM and Vector Database. https://medium.com/@niren.p.pai/building-a-rag-application-using-llm-and-vector-database-555db9a8fbe5.
23: The Secret Sauce of RAG: Vector Search and Embeddings. https://www.thecloudgirl.dev/blog/the-secret-sauce-of-rag-vector-search-and-embeddings.
24: Vector Search RAG Tutorial – Combine Your Data with LLMs with Advanced Search. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JEBDfGqrAUA.
25: Evaluating RAG Performance with Vector Databases | BLEU, ROUGE, and RAGAS. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yO7-VhtWWno.
26: Vector Databases vs Graph Databases for Large Language Models https://medium.com/@vkrntkmrsngh/vector-databases-vs-graph-databases-for-large-language-models-33f795f4eda2
27: Vector Database vs. Knowledge Graph: Making the Right Choice When Implementing RAG https://www.cio.com/article/1308631/vector-database-vs-knowledge-graph-making-the-right-choice-when-implementing-rag.html
28: RAG: Vector Databases vs Knowledge Graphs? https://medium.com/@ahmedbehairy/rag-vector-databases-vs-knowledge-graphs-f22697b1a940
29: Question Answering https://learn.deeplearning.ai/courses/langchain-chat-with-your-data/lesson/6/question-answering
30: Overview of RAG Approaches with Vector Databases https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=twM_9CM_3RY