Generative Adversarial Networks - rugbyprof/5443-Data-Mining GitHub Wiki
Generative Adversarial Network
A generative adversarial network an artificial intelligence algorithm that pits two neural networks, a generative model and a discriminative model, against each other to create data that is similar to data provided to the network.
Discriminative Model
A discriminative model learns a function that maps the input data to some desired output class label. The discriminative model in an adversarial net is a convolutional neural network. The discriminative model receives samples from both the generative model and real training data.
Convolutional Neural Network
A convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of deep, feed-forward artificial neural networks that has successfully been applied to analyzing visual imagery. CNNs use a variation of multilayer perceptrons designed to require minimal preprocessing. They are also known as shift invariant or space invariant artificial neural networks (SIANN), based on their shared-weights architecture and translation invariance characteristics.
Generative model
A generative model tries to learn the joint probability of the input data and labels simultaneously, then creates new samples. In an adversarial net, the generative model generates samples by passing random noise through a multilayer perceptron.
Multilayer Perceptron
A multilayer perceptron (MLP) is a class of feedforward artificial neural network. An MLP consists of at least three layers of nodes. Except for the input nodes, each node is a neuron that uses a nonlinear activation function. MLP utilizes a supervised learning technique called backpropagation for training.
Backpropagation
Backpropagation is a method used in artificial neural networks to calculate the error contribution of each neuron after a batch of data (in image recognition, multiple images) is processed. In the context of learning, backpropagation is commonly used by the gradient descent optimization algorithm to adjust the weight of neurons by calculating the gradient of the loss function.
Both models are trained using backpropagation and dropout algorithms. The generative model then creates data based on information from the trained discriminative model.
GAN Model:
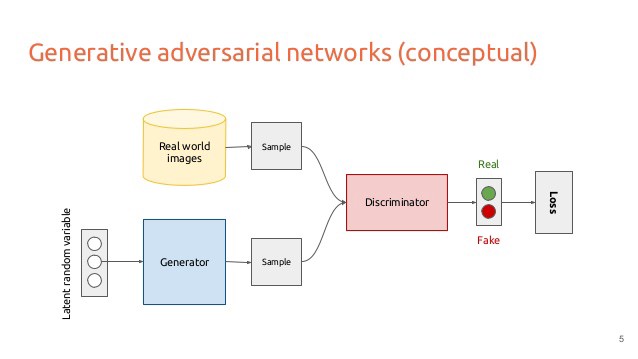
Training the model
Let D be the discriminative model, and G be the generative model. Then:
- Optimize D (without training G) to predict real data as real
- Create fake data with G and train D to predict them as fake
- Use predictions from D to train G to fool D
- Repeat steps 1-3 for several epochs
- Stop once generated data converges to real data
Advantages:
- No need for Markov chains
- No inference needed during learning
- Wide variety of functions can be incorporated in to the model
- Very sharp looking results
Disadvantages:
- No explicit representation of how good data is
- Training of D and G must be closely synchronized
Importance:
- No longer get “false positive” from the discriminative model when fed random noise
- Model has learned that not everything fits into the real data distribution
- Can be used as a feature extractor
- Can predict future (such as next frame in a video)