Projection Data HDF5 File - rg2/jhmr-v2 GitHub Wiki
HDF5 Hierarchy
The hierarchy used for storing projection data in HDF5 format is shown below:
num-projs: Dataset indicating the number of projections stored in this HDF5 file/group (64-bit unsigned integer)proj-XXX: Group storing data for projection XXX, e.g.proj-000for the first projection andproj-013for the fourteenth projection.cam: Group storing metadata for the projection parametersnum-cols: Dataset storing the number of columns in each projection (64-bit unsigned integer)num-rows: Dataset storing the number of rows in each projection (64-bit unsigned integer)col-spacing: Pixel spacing in column direction (mm / pixel) (e.g. 0.194 mm / pixel). This should be equal to the value stored inimg/spacing[0]. (32-bit floating point)row-spacing: Pixel spacing in row direction (mm / pixel) (e.g. 0.194 mm / pixel). This should be equal to the value stored inimg/spacing[1]. (32-bit floating point)extrinsic: Rigid mapping from world frame to camera projective frame stored as a 4x4 homogeneous matrix. (32-bit floating point)intrinsic: Projective mapping from camera projective frame onto image plane stored as a 3x3 upper-triangular matrix. (32-bit floating point)cam-coord-frame-type: String indicating the layout of the projective coordinate frame, usually set to "origin-at-focal-pt-det-neg-z". See below for a description of the possible values and their meanings.
img: Group storing image intensity data and metadatapixels: Buffer of pixels, row-major order. (32-bit floating point or 16-bit unsigned integers or 8-bit unsigned integers)dir-mat: 2x2 matrix indicating rotational alignment of image axes with a physical coordinate frame. This will be identity. (32-bit floating point)origin: Physical point with respect to a physical coordinate frame at the zero image index. This will be a 2x1 zero-valued matrix. (32-bit floating point)spacing: Pixel spacings in mm/pixel. Stored as a 2x1 matrix of 32-bit floating point values, with the first element (e.g. x) storing the spacing between column elements and the second element (e.g. y) storing the spacing between row elements.
landmarks: Group storing landmark locations in the 2D image- The name of each dataset indicates the landmark name and each value is a 2D point representing the sub-pixel location of the landmark. Each 2D point is represented as a 2x1 matrix of 32-bit floating point values, with the first element (e.g. x) storing the pixel column and the second element (e.g. y) storing the pixel row. For example, a dataset named
GSN-lwill represent the left greater sciatic notch and the 2x1 matrix indicates its projected location in the 2D image.
- The name of each dataset indicates the landmark name and each value is a 2D point representing the sub-pixel location of the landmark. Each 2D point is represented as a 2x1 matrix of 32-bit floating point values, with the first element (e.g. x) storing the pixel column and the second element (e.g. y) storing the pixel row. For example, a dataset named
orig-meta: Optional group containing metadata values from the original image format, such as the DICOM fields from a CIOS fusion image.rot-to-pat-up: Optional value, either0,90,180or270, that indicates the rotation necessary to get the patient oriented "up." This is most commonly set to0or180and depends which side of the operating table the C-arm is positioned. When an image is collected and the image has the patient oriented "updside down" then a manual 180 degree rotation is typically applied. (32-bit integer)
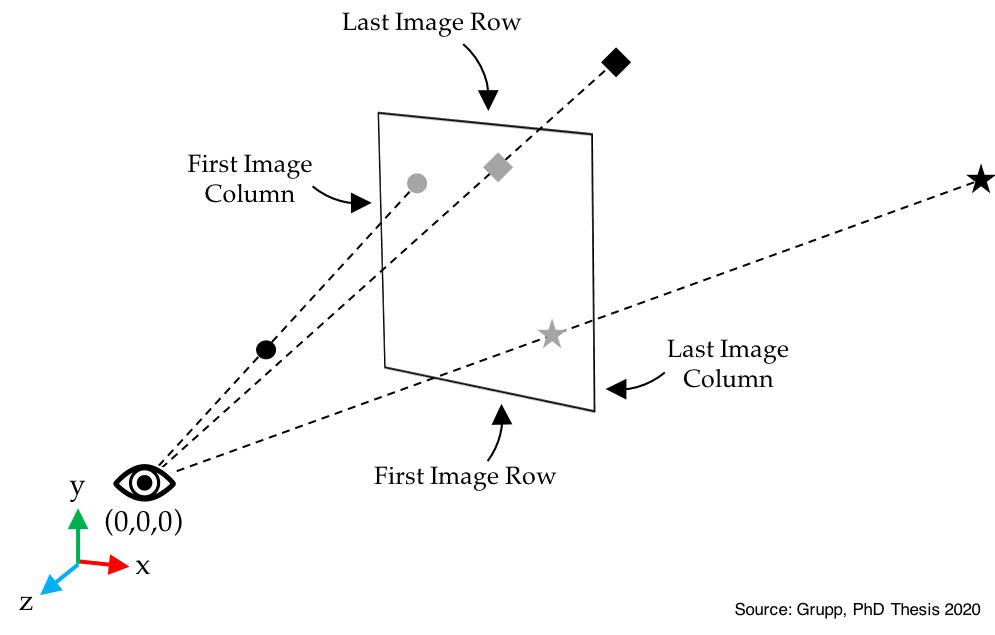
Projective Coordinate Frames
- "origin-at-focal-pt-det-neg-z" (the default option in xReg)
- The origin is located at the X-ray source,
- The X-axis is oriented according to increasing columns in the image plane,
- The Y-axis is oriented according to increasing rows in the image plane,
- The Z-axis is orthogonal to the image plane and points towards the X-ray source.
- This is sometimes referred to as OpenGL style.
- "origin-at-focal-pt-det-pos-z"
- Similar to "origin-at-focal-pt-det-neg-z," except that the direction of the Z-axis is flipped to point away from the X-ray source. In order to remain right-handed, the Y-axis is also flipped, but is still oriented according to increasing rows in the image plane.
- "origin-on-det"
- This places the origin on the detector,
- The Z-axis is orthogonal to the image plane and pointing towards the X-ray source,
- The X-axis is oriented according to increasing columns in the image plane,
- The Y-axis is oriented according to increasing rows in the image plane.
An illustration of the "origin-at-focal-pt-det-neg-z" coordinate frame layout is given below: