Vision and Language - newlife-js/Wiki GitHub Wiki
by 서울대학교 한보형 교수님
Image Caption Generation

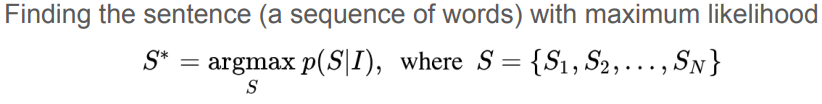
COCO Datasets
120K train + validation images
Instance level sagmentations labels with 91 object classes
5 captions per image
Metrics
-
BLEU(BiLingual Evaluation Understudy): 두 문장 사이의 n-gram overlap의 정도
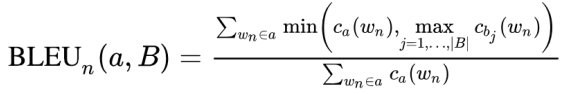
장점: automatic, easy to compute
단점: n-gram ordering 고려하지 않음, 모든 n-gram을 동등하게 다룸, 내용보다는 형식적인 유사성을 봄 -
METEOR(Metric for Evaluation of Translation with Explicit ORdering): Precision과 Recall 모두 고려
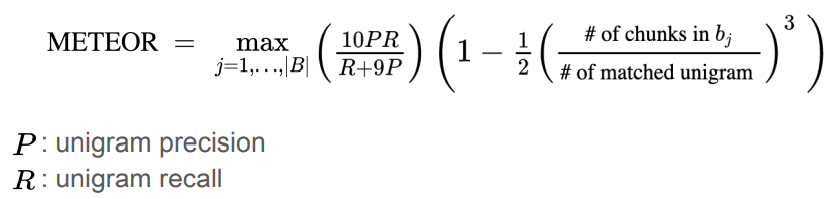
-
CIDER: TF-IDF기반 scoring

-
SPICE(Semantic Propositional Image Caption Evaluation): n-gram overlap이 필요 이상으로 높은 점수 주는 것 방지 dependency parse tree 기반 graph로 object/attribute/relation을 encoding하여 tuple을 만들어 F-score 매김
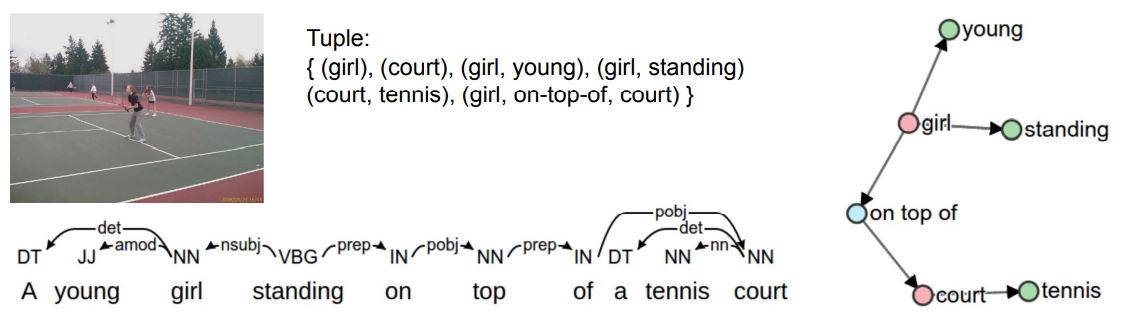
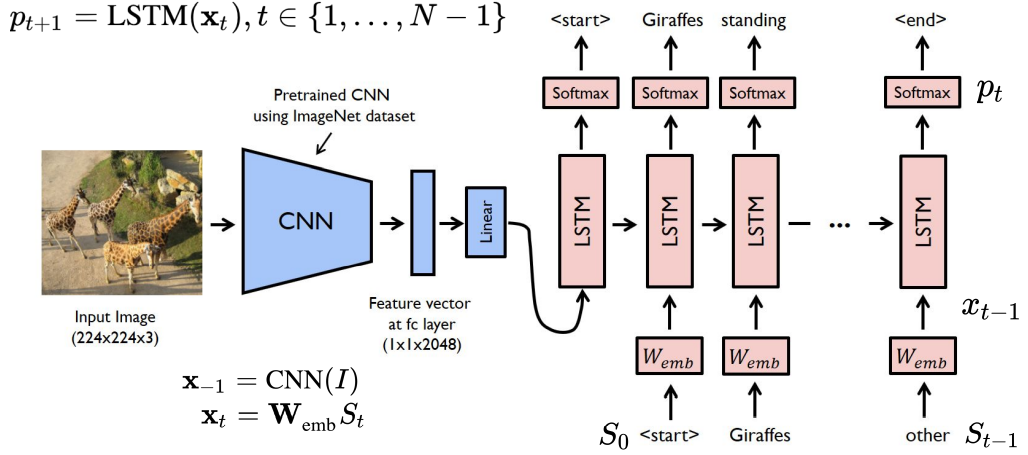
Show and Tell
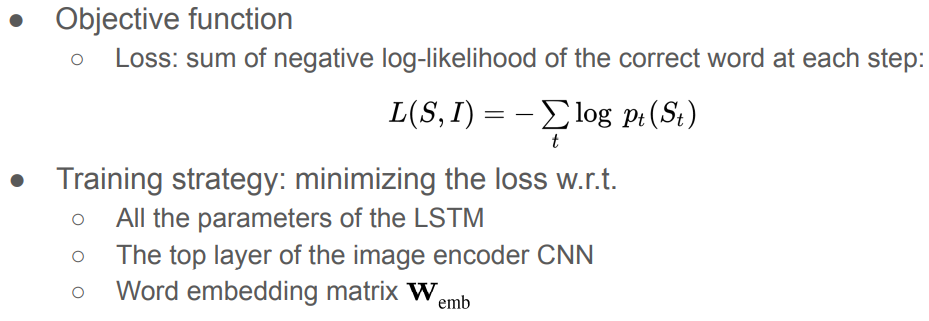
Encoder RNN을 CNN으로 대체, Decoder는 LSTM으로
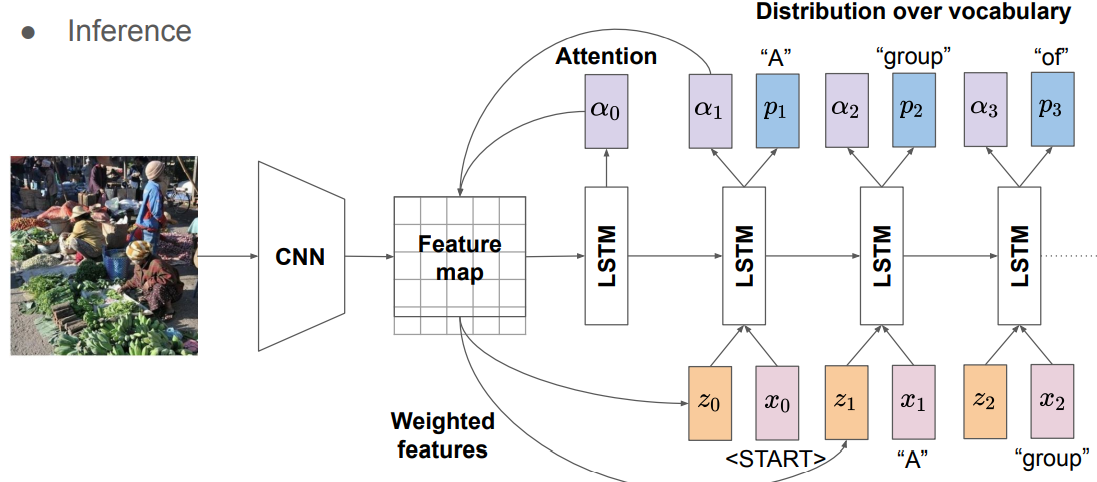
Show, Attention and Tell
LSTM이 visual(spatial) attention을 입력 받음
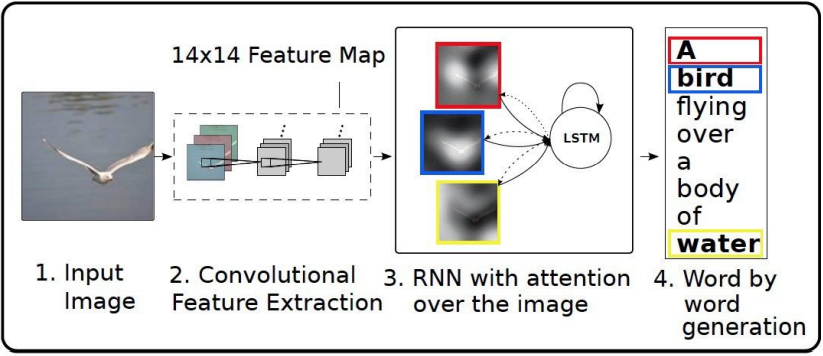
Attention Estimation: image representation과 hidden states의 MLP -> softmax
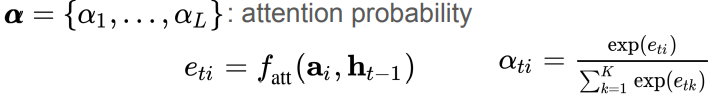
Visual Attention: hard attention(1-hot vector) or soft attention(real-valued vector)
Attention in Encoder
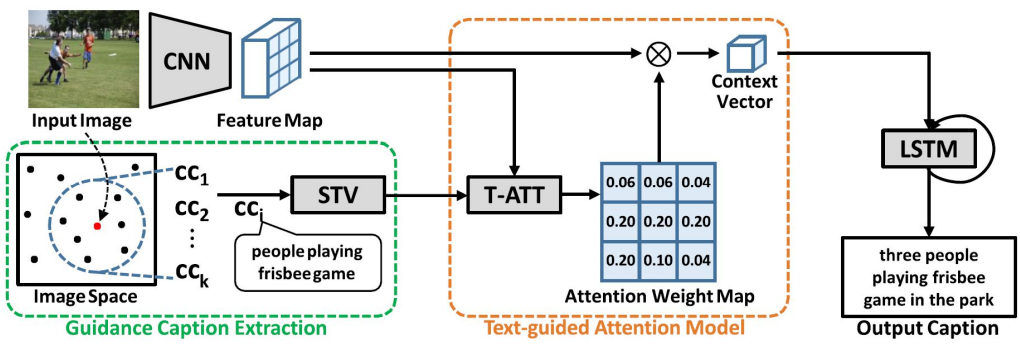
Guidance caption encoder: input image와 비슷한 space에 위치하는 image들의 caption을 가지고 guidance caption을 생성
MIXER(Mixed Incremental Cross-Entropy Reinforce)
RL-based sequence-level training
Decoder = agent, words = environment, model parameter = policy
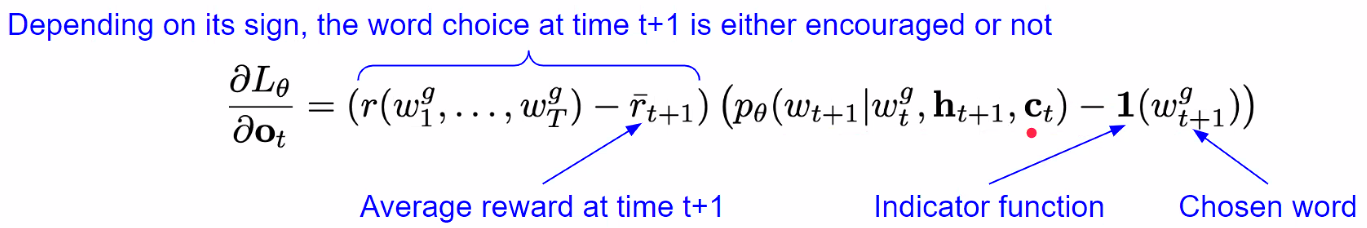
Policy Gradient Method
여러 metric의 linear combination을 metric으로 사용함

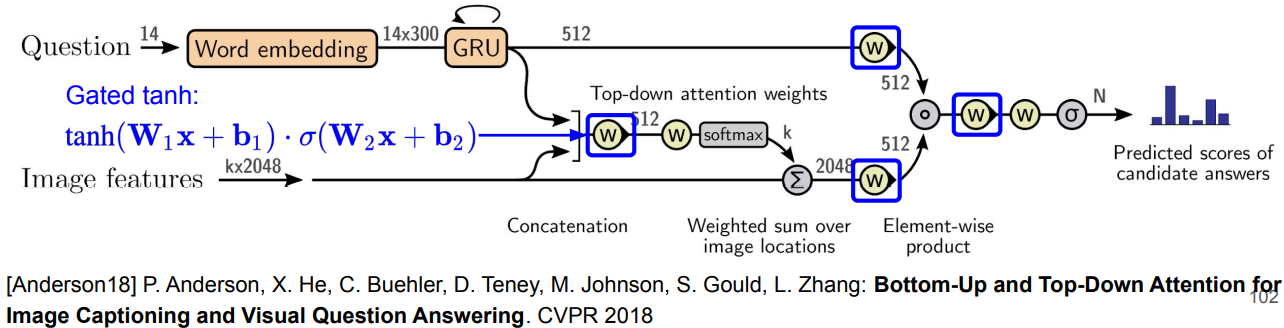
VQA(Vision Question Answering
Image와 question을 input으로 받아서 answer를 출력

Sub-problems
- Zero-shot learning: training에는 없던 class, 내용(training에 나타나지 않는 복수형, 동의어 등)에 대해서 답할 수 있는가
- Weakly supervised learning: counting 문제(물체가 몇 개인지를 답하기가 어려움)
구조
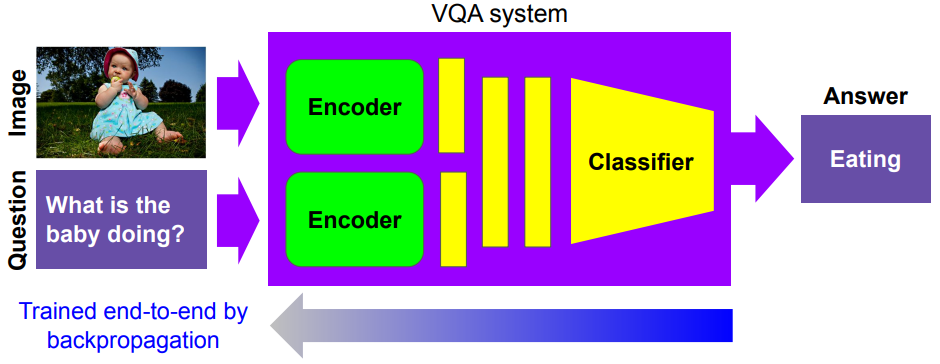
- Image encoder: CNN
- Sentence Encoder: RNN
- Answer Generation
Flat Classification: 모든 클래스를 동등하게 취급
CLEVR Dataset
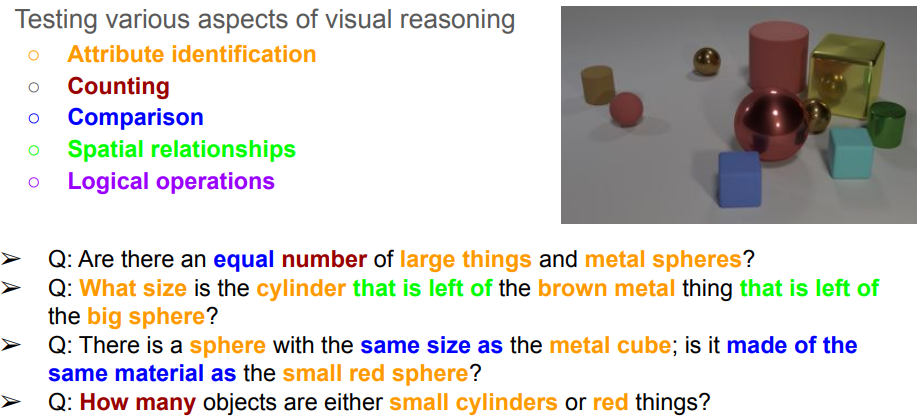
- Compositional generalization 가능한지 test

Evaluation
Accuracy = min{# of humans that said ans/3, 1} (3명 이상이 대답한 답과 같으면 1, 여러 답이 정답일 수 있음)
 -> blue or green이면 acc=1
-> blue or green이면 acc=1
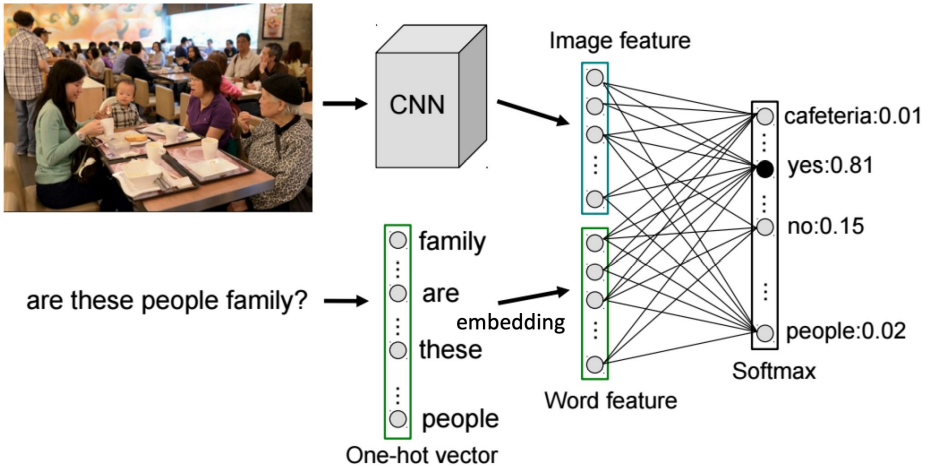
IMG+BoW
가장 간단한 base algorithm
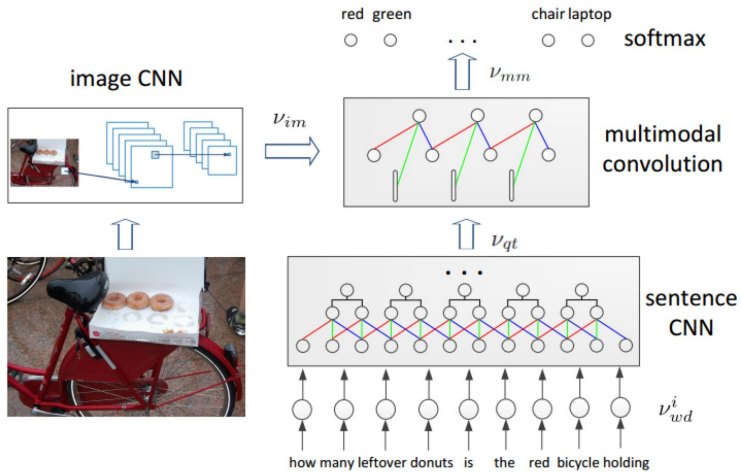
Multiple CNNs
Image CNN + Sentence CNN + Multimodal convolution
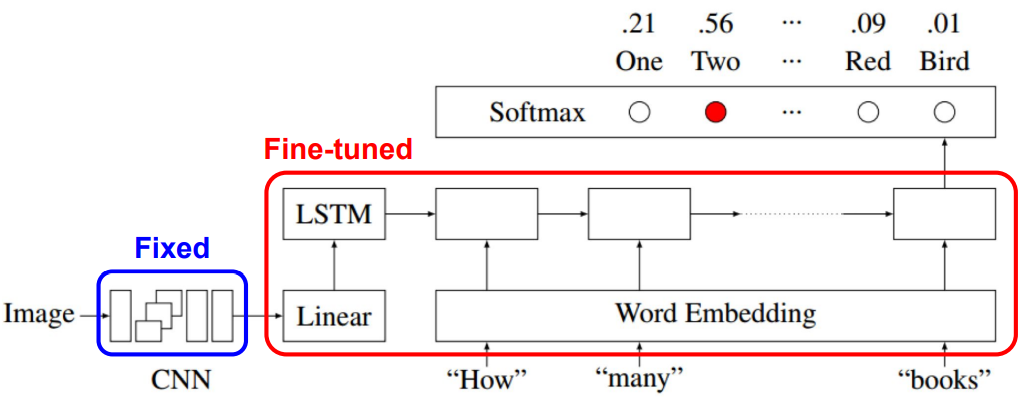
VIS_LSTM
Image representation을 LSTM의 첫 word로 넣음
LSTM의 마지막 cell에 classifier를 달아줌
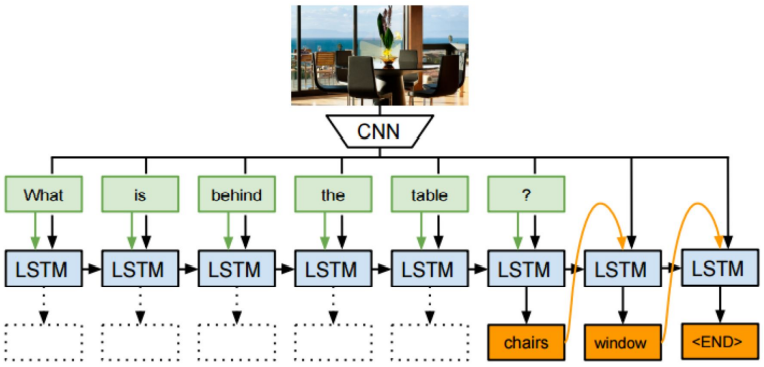
Neural-Image-QA
Image Representation을 LSTM의 모든 cell에 넣어줌
LSTM 자체에서 word를 예측
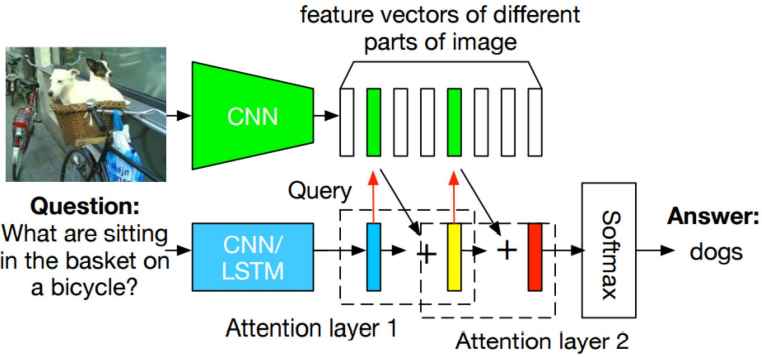
Stacked Attention Network
Image CNN + Question CNN(or LSTM) + Attention model
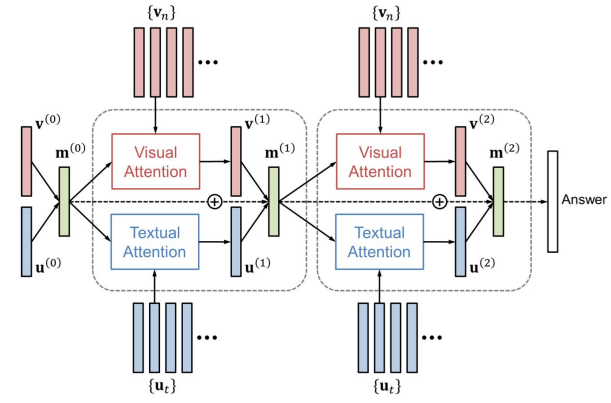
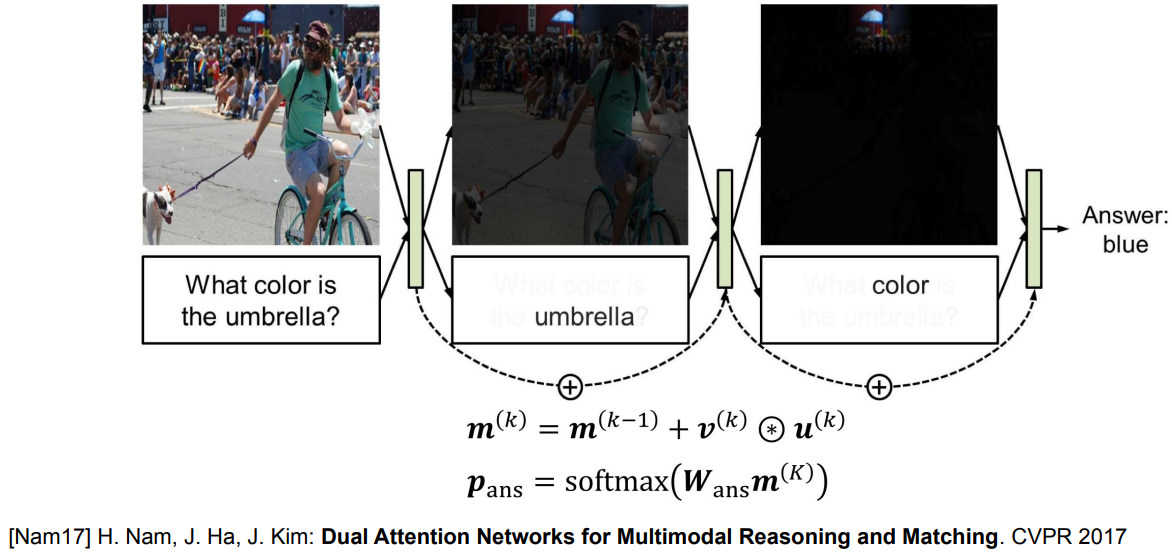
Dual Attention Network
Multi-step visual and textual attention models
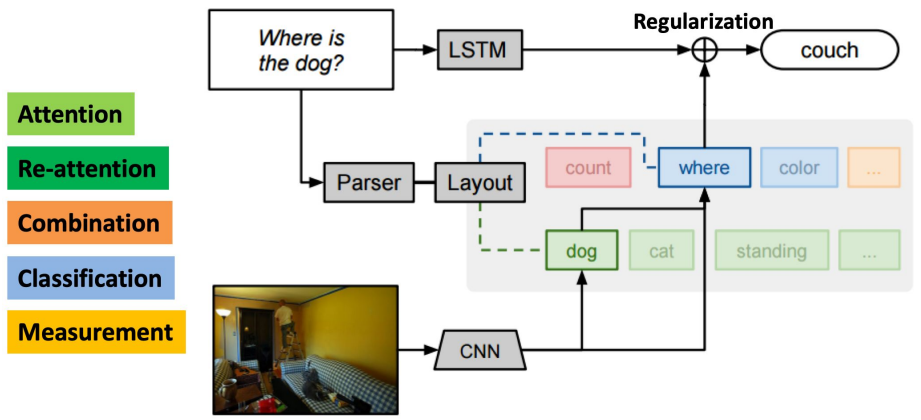
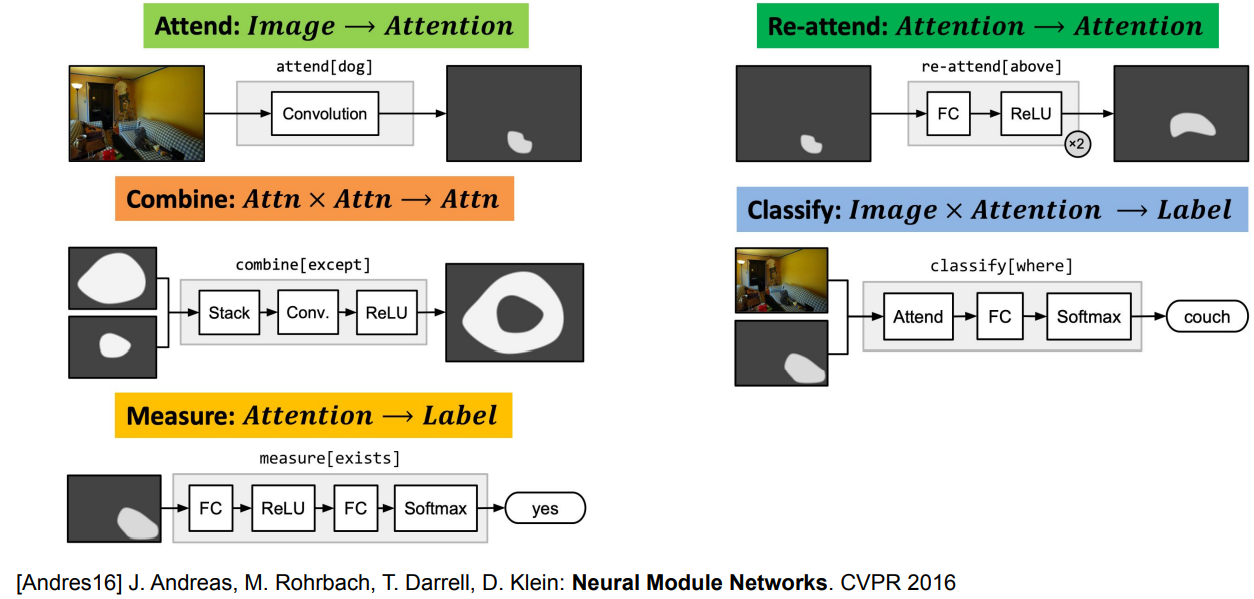
Neural Module Networks
여러 종류의 모듈의 조합으로 예측
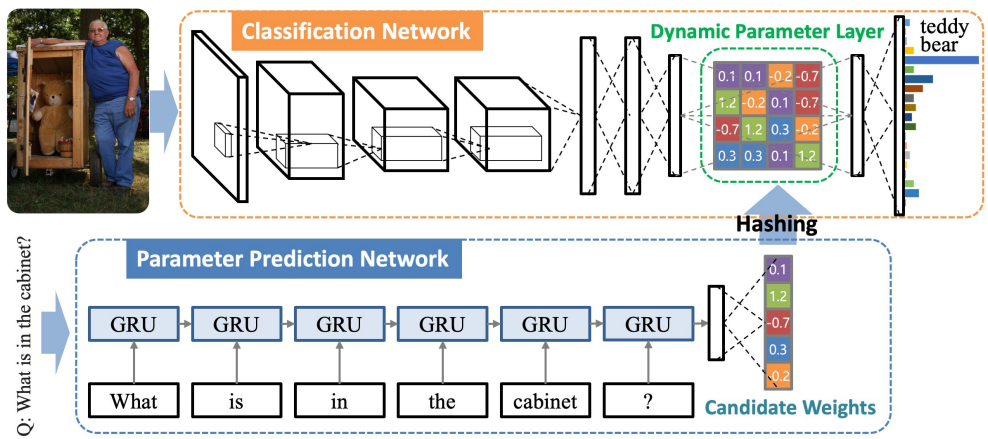
Dynamic Parameter Prediction
Question에 따라서 Image CNN FC의 weight이 달라지도록 함(CNN의 input으로 들어가는 게 아님)
Hashing을 통해 parameter sharing하도록 해서 parameter 수를 줄임
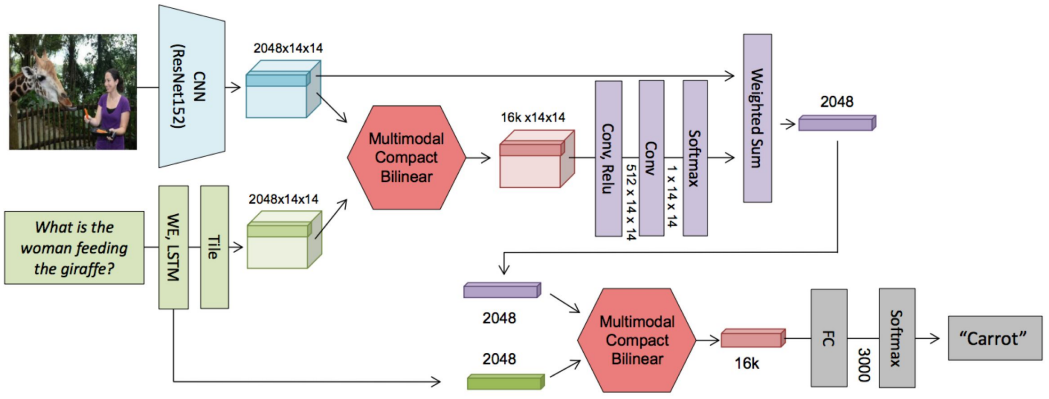
Multimodal Compact Bilinear Pooling(MCB)
Joint Representation of Image and Question
concatenation, element-wise multiplication, bilinear pooling(outer-product of two vectors)
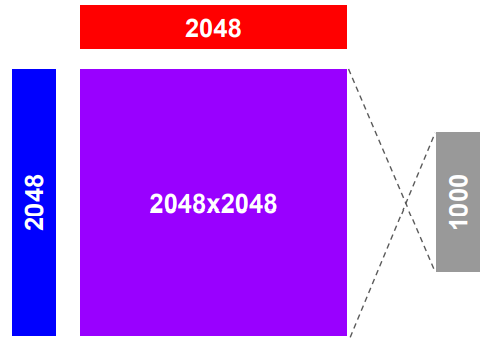
bilinear pooling으로 인해 dimension이 너무 커짐
-> Compact bilinear pooling(count sketch + FFT)
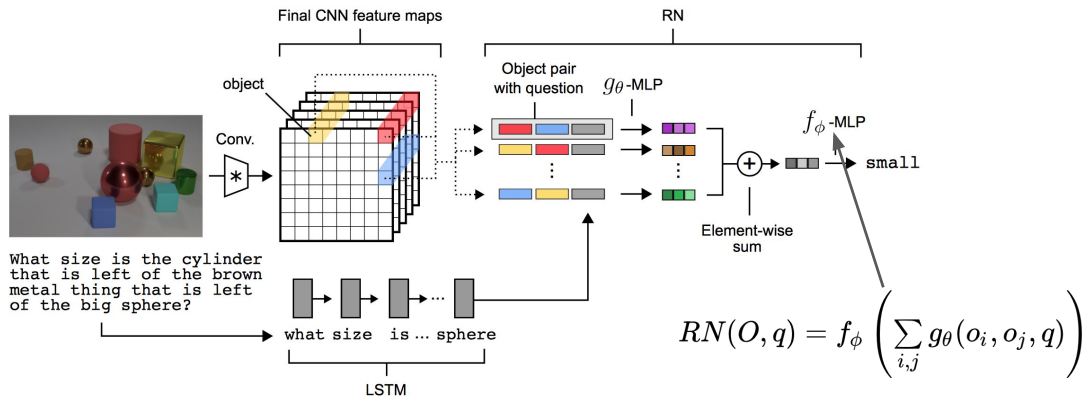
Relational Network
all pairs of objects 간의 관계를 모델링
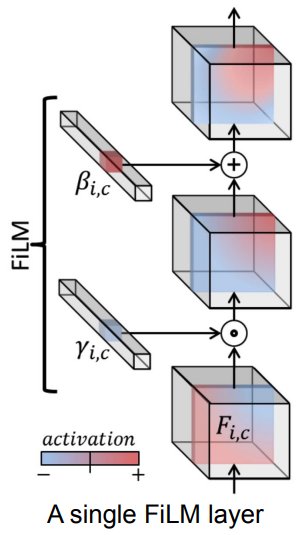
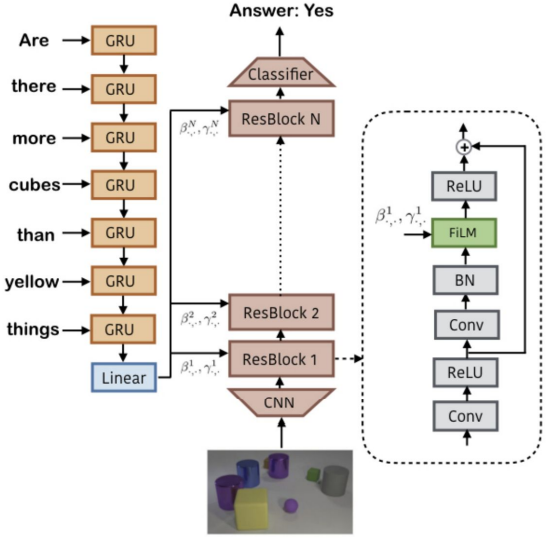
FiLM(Feature-wise Linear Modulation)
affine transform을 통해서 neural network output에 adaptively influence...
Bottom-Up and Top-Down Attention Models
Faster R-CNN을 base로 bounding box로 attention을 생성(Bottom-up attention)하여 top-down attention과 결합
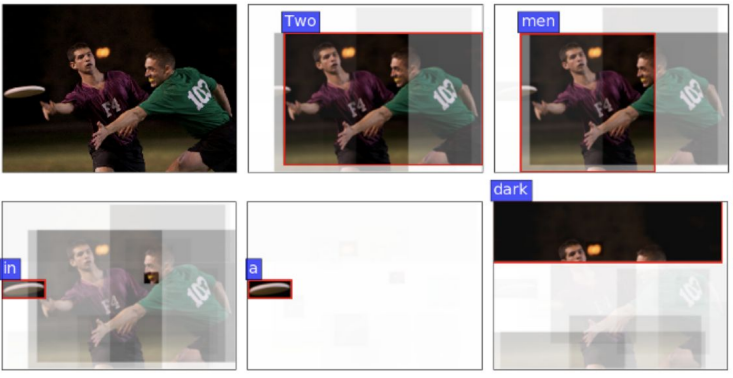
- Captioning model: two-level LSTM
Top-down attention LSTM(region attention) + Language LSTM(caption generation)
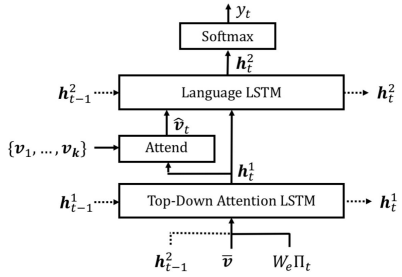
- VQA model
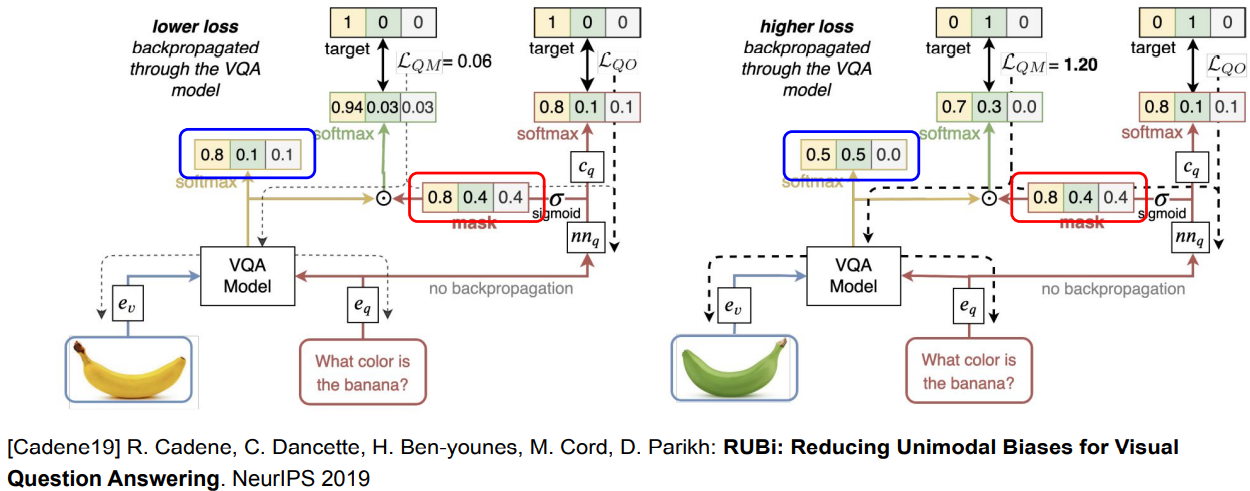
RUBi(Reducing Unimodal Biases)
preventing biases by masking predictions
question만으로도 answer를 추론할 수 있는데, 이 과정에서 mask를 뽑아내서 VQA model의 bias를 reduce하도록 함
-> question만으로 추론할 수 없는 example에서 loss가 더 크므로, 이런 example들에 더 집중하여 학습할 수 있도록 함
MultiModal Representation Learning
VL-BERT(Visual-Linguistic BERT)
Linguistic: features from subwords
Masking된 subwords / Zero-out된 RoI의 class를 예측
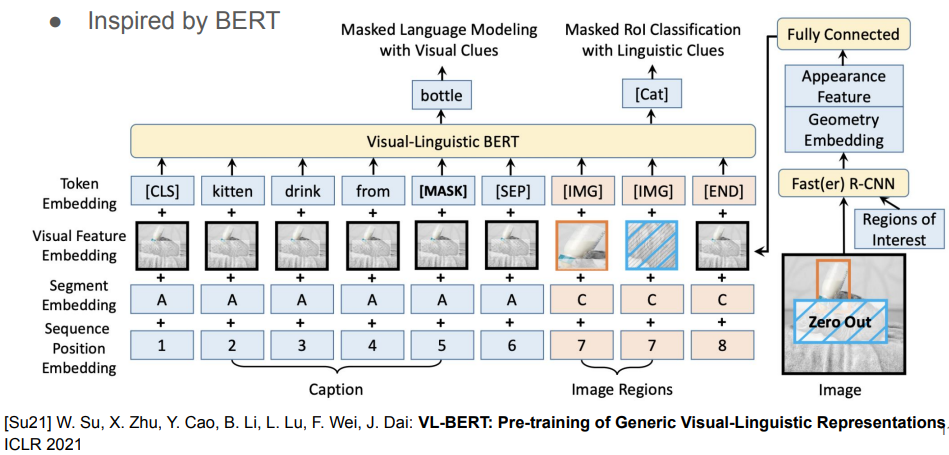 Visual: RoI features extracted from object detectors in images
Visual: RoI features extracted from object detectors in images
VirTex
high-quality annotation을 사용하여 pretrain하여 transfer
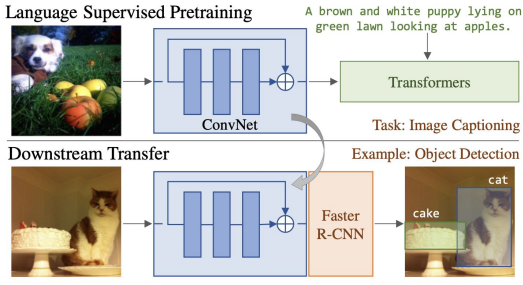
[Desai21] K. Desai, J. Johnson: VirTex: Learning Visual Representations from Textual Annotations. CVPR 2021
SOHO(Seeing Out of the bOx)
encoding된 image의 각 grid를 Visual dictionary의 index로 채워 넣어서 embedding feature를 구성
text embedding과 concat하여 BERT에 입력
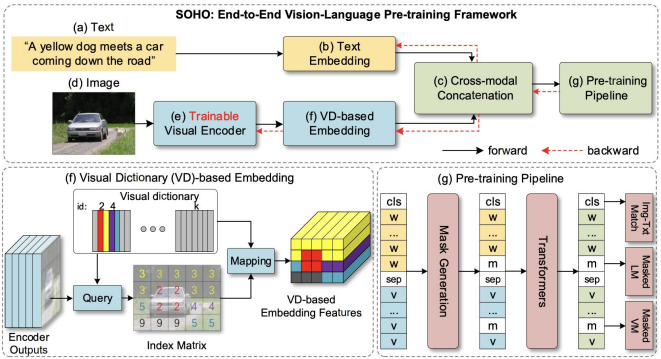
[Huang21] Z.Huang, Z.Zeng, Y.Huang, B.Liu, D.Fu, J.Fu: Seeing Out of tHe bOx: End-to-End Pre-training for Vision-Language Representation Learning. CVPR 2021
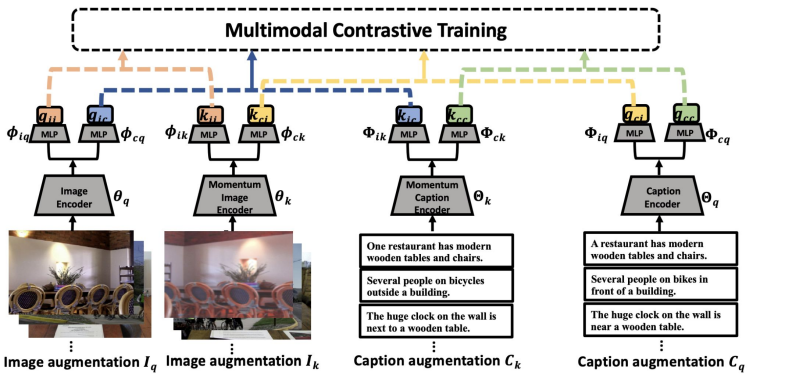
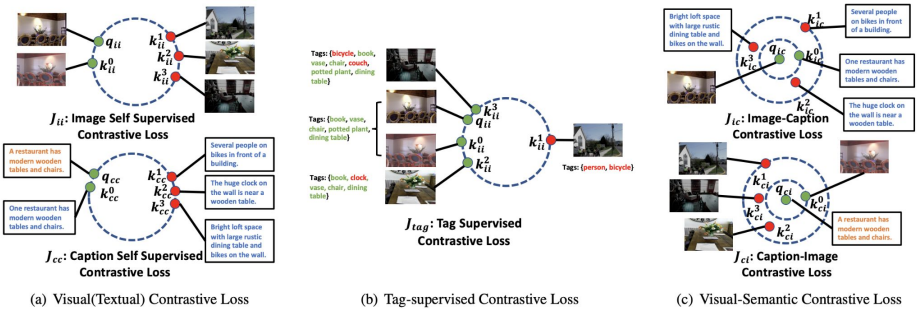
Multi-Modal Contrastive Learning