Computer Vision - newlife-js/Wiki GitHub Wiki
by 카이스트 윤국진 교수님
Introduction
Visual Intelligence
사람이 인식하는 대로 컴퓨터가 이미지를 인식하도록 하는 것
- 3D Perception: pattern or texture, object identity or shape, multiple visual cues로부터 3D 구조를 인식하는 것
- Semantic Object-level Perception / Semantic Segmentation
- Color Perception
- Motion Perception
3D reconstruction
- Camera self-calibration
- Stereo Vision: 다른 시점의 사진들(disparity)을 통해 3D를 sensing(stereo matching, stereopsis)하는 것
- 3D Urban Modeling
Motion
- Stereo Visual Odometry(SVO): 여러 대의 카메라의 streaming 데이터로 경로 측정
- Simultaneous Localization and Mapping(SLAM): 주변 환경의 지도를 작성
Scene
- Ground Plane Detection
- Road surface profile estimation
- Semantic segmentation
Object
- Object detection/recognition/categorization
- Object tracking/Multi-object tracking
- Tracking and Re-identification: 이미지에서 사라졌다 돌아온 물체를 동일한 물체로 인식하는 것
Human
- Face Detection
- 2D/3D Pose Estimation
Conventional vs DL based VI
Conventional
- Model each process(using math)
- No need to collect training images
- Domain이 많이 필요함(collect data, pre-processing, feature design, model design)
DL based
- Do not explicitly model
- Need to prepare training images
- Need to be generalized for unseen data
- Domain이 별로 필요 없음(collect data)
- 하지만 Domain 없이 network design을 하게 되면 많은 trial-and-error가 필요하고, 결과 분석이 어려움
Performance
- Regression tasks(visual odometry, camera calibration): Conventional > DL based
- Classification tasks(detectionn, stereo matching, sementic segmentation): Conventional < DL based
CNN(Convolutional Neural Network)
pixel 전부를 fully connected로 연결하면 parameter가 너무 많음
- local connectivity: pixels only related to nearby pixels(determines kernel size)
- translation invariance: pixels share the same weights(patch별로 weight를 다르게 쓸 필요가 없음) filter의 개수만큼 feature map(channel)이 나옴
-> Feature를 뽑아내는 Convolutional filter를 사용해 input data를 스캔하는 neural network 사용
convolutional filter가 깊어질수록 고차원의 feature를 뽑아낼 수 있음
■ Pooling(subsampling): reduce extracted activation map(max/average/min pooling)
-> large distortions become smaller, so more invariance
Image Formation and Camera Model
Pinhole Model

pinhole size가 크면 여러 방향에서의 빛의 average되어 blur되고, 작으면 회절로 인해 blur됨
-> Lens를 사용

위 식이 성립하도록 거리를 조정하면 pinhole model이 적용되어 focus가 잘 맞음
■ Depth of Field: 초점이 잘 맞는 범위
aperture를 작게 하면 DoF가 늘어남
※ Real Lens는 색수차, Vignetting, 광각 왜곡, lens glare같은 문제가 발생함
Camera Calibration
Camera coordinate

-> Image coordinate(좌표가 음수가 되지 않도록 원점을 corner로 옮겨줌)
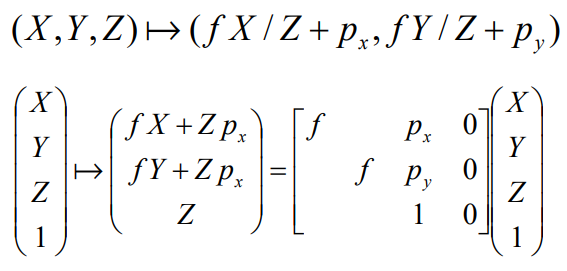
-> Pixel coordinate(어느 pixel로 매핑되는지)
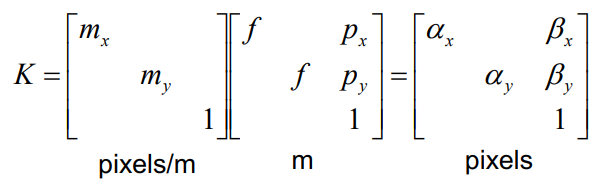
이 K matrix를 통해 3차원 정보가 pixel에 어떻게 매핑되는지를 알 수 있고, 이를 통해 calibration을 함
focal length(f), principle point(p_x, p_y), pixel size(m_x, m_y)가 내부 변수(intrinsic parameters)
※ world coordinate에서 camera coordinate로 변환하기 위해서는 center를 옮겨주고 rotation만 해주면 된다.
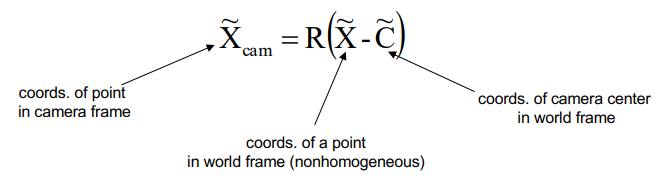

Rotation(R), Translation(t)가 camera의 외부 변수(extrinsic parameters)
-> 좌표를 알고 있는 6개의 point를 찍어서 pixel과 매핑을 하면, P matrix를 구할 수 있고
SVD 및 선형대수를 이용해서 내부/외부 변수를 구할 수 있음
Projective Geometry
3x3 matrix로 plane projective transformation을 수행하여 다른 image coordinate에서의 plane을 변환할 수 있음(homography)
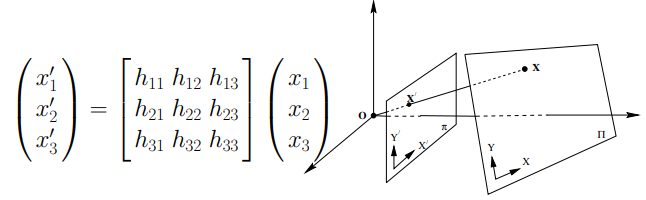
Vanishing Points(소실점)
projection of a point at infinity

- 두 평행선은 같은 vanishing point를 갖는다.
Vanishing Line
여러 vanishing point를 이으면 vanishing line이 됨
한 plane 상의 vanishing point들은 모두 같은 vanishing line에 위치함
Cross Ratio
projective transformation을 해도 변하지 않는(projective invariant) 길이의 비율
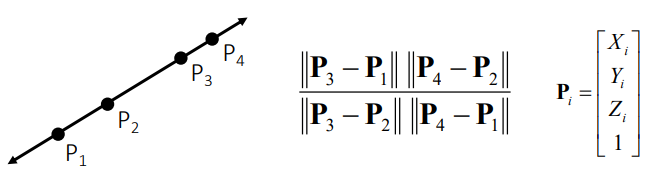
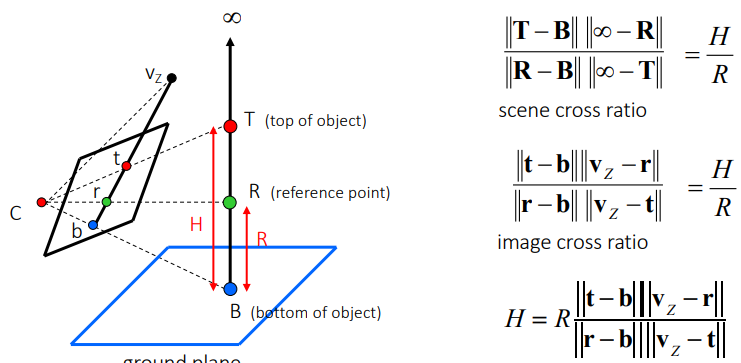
이를 이용해서 height measuring이 가능
Low-level Vision Tasks
3D Sensing
estimating depth, distance or 3D Shape
Shape(structure)-from-X: sensing 3D using visual cue 'X'(shading, silhouette, stereo, ...)
Depth estimation
- Time of flight: 빛이 돌아오는 시간을 이용
- Structure light
- Stereo matching
- Structure from motion: 여러 image로부터 3D structure를 얻음
Stereo
- Disparity: 두 image간의 difference
- stereopsis: ability to perceive depth from disparity
- Stereo vision: design algorithms that mimic stereopsis
For 3D Reconstruction,
Camera calibration
Correspondence search(find disparity)
3D computation
■ Triangulate on two images of the same point to recover depth
동일한 point가 어딘지를 찾기 위해 사진을 비교
■ Image rectification
두 이미지 plane을 동일한 plane상으로 Re-project(warping)

■ Pixel Matching
가장 비슷한 pixel을 찾는 것
- Local methods
ICA(Intensity Conservation Assumption)을 가정하고 비교
pixel 단위로 비교하면 ambiguity가 크므로, window기반 매칭을 수행 - Global methods
cost function을 minimizing하는 depth surface를 찾음
cost function: Data cost(likelihood) + Discontinuity cost(prior)
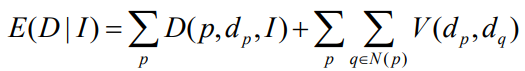
Challenges
Photometric variations(밝기의 차이), occlusion, texture-less areas, repetitive patterns, reflections
※ Active Stereo
패턴이 있는 illuminant를 쏴서 반사되는 이미지를 촬영하여, 패턴과 이미지를 비교하는 방법
패턴 디자인이 중요, 인간이 지각할 수 없는 illuminant를 이용하는 것도 필요
passive stereo는 있는 그대로의 이미지 2개를 비교하는 것
Optical Flow
motion cue가 perception에 큰 역할을 함
optical flow는 밝기 패턴의 변화와 연관된 velocity의 2D distribution을 말함
※ Motion Field: 3차원에서의 움직임을 2D로 projection한 것
두 이미지로부터 pixel motion을 estimate하는 것..
- 주변 pixel 중 같은 색깔을 갖는 pixel을 찾는다.
color constancy(같은 point는 같은 color를 가짐), small motion(point는 너무 멀리 움직이지 않음)을 가정
위 가정으로는 아래와 같이 equation 1밖에 얻지 못함(변수는 2개)
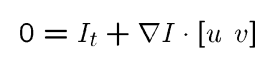
주변 픽셀(window)들도 같은 방향으로 같은 크기만큼 움직인다(u, v)고 가정하면 u, v를 구할 수 있음
※ Local Patch Analysis: 한 이미지만 보고도, motion을 구할 수 있을지(위 equation 해를 구할 수 있을지) 판단
edge나 low texture region은 해를 구하기 어려움
※ small motion 가정이 틀리게 되면(가까운 물체는 많이 움직임), resolution을 줄여서 분석