AI 개론 - newlife-js/Wiki GitHub Wiki
AI 기초
by 서울대학교 장병탁 교수님
AI란?
- Thinking Humanly: Cognitive modeling approach, build human-level general intelligence
- Thinking Rationally: Laws of thought approach, thinks right, normative than descriptive(deriving correct conclusions)
- Acting Humanly: Turing test approach, behave intelligently like humans
NLP, Knowledge representation, Automated reasoning, Machine Learning - Acting Rationally: Rational agent approach, behaves rationally or does the right thing
achieve best expected outcome, maximize goal achievement
※ Rational Agent: entity that perceives and acts, 인간처럼 인식하지는 않더라고 best performance를 산출하는 agent를 만드는 것
- Intelligent(rationality) Agents: choose action that maximizes the performance
- Problem-Solving Agents: problems / solutions / search algorithms
- Knowledge-Based Agents: deduce actions from the knowledge, represent knowledge using logic(명제, first-order logic)
Information Theory
- Information: x를 관측함으로 인해 얻게 되는 정보량, 확률이 낮은 사건일 수록 얻는 정보량이 많다.

- Entropy: 문제의 불확실성을 나타냄

- Mutual Information:
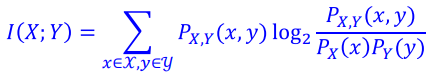
- Relative entropy(KL Divergence):

Temporal Reasoning
intepret the present, understand the past, predict the future

Inference in Temporal Models
- Filtering: 과거 evidence를 통해서 현재의 상태를 estimation / P(X_t|e_1:t)
- Prediction: 과거 evidence를 통해서 미래의 상태를 estimation / P(X_t+k|e_1:t)
- Smoothing: 과거의 상태를 더 잘 estimate(essential for learning) / P(X_k|e_1:t)
- Most likely explanation: 가장 그럴듯한 path를 찾는 것 / argmax_X_1:t{P(X_1:t|e_1:t)}
Probabilistic Reasoning
Bayesian network
Directed acyclic graph(DAG) representing a full joint probability distribution of random variables
※ Approximate Inference for Bayesian Networks
- Draw N samples from a sampling distribution
- Compute an approximate posterior probability
- Show this converges to the true probability
■ Methods
Direct sampling
Rejection sampling
Likelihood weighting
Markov chain Monte Carlo(MCMC)
Utility-Based Agents
Markov Decision Process(MDP)
Sequential decision problem for fully observable, stochastic environment with a Markovian transition model and additive rewards
ex: 바둑, 로봇 움직임 등
- states / actions / transition model / reward function
- policy: action을 선택하는 solution, optimal policy(highest expected utility)를 찾는 문제
- Bellman Equation으로 optimal policy 구함
※ POMDP: Partially Observable MDP
Advanced ML
by 서울대학교 최진영 교수님
Linear Regression
Regression: a process that finds a parametric model f_hat that gives the best fit of f for the observed samples
y_i = f_hat(x_i) + ε_i
ε_i -> iid, zero mean, variance σ^2
MLE(Maximum Likelihood Estimation): 정규분포 내에서 잔차(ε_i)가 나타날 확률의 곱(i=`..n)이 가장 크도록 하는 θ를 구하는 것
= LSE 문제와 같음(ε_i이 0에 가까울수록 확률곱은 커지고, Least square가 작아지므로)

Bias(underfitting) and Variance(overfitting)
Bias: 추정치 평균과 실제값 평균의 차이가 크다 -> underfitting(training error)
Variance: 관측 sample에 따라서 추정치 estimation의 변화가 크다 -> overfitting(validation error)

변수의 개수가 많으면 overfitting, 적으면 underfitting
-> 변수의 개수를 늘려가면서 validation error가 커지는 시점을 택하거나, PCA, regularization 사용

Regularization
- Ridge: L2-norm
- Lasso: L1-norm
- Elastic: Ridge + Lasso
Nonlinear Regression
- High-order polynomial linear model
- Sine/cosine basis linear model
- Radial basis linear model: 특정 포인트(center)들과의 거리를 사용한 변수의 선형 결합
- Piecewise linear model: 구간 별 linear regression의 결합
- Neural network model
Evaluation Metrics
Precision & Recall
Precision(=sensitivity): TP/(TP+FP), Recall: TP/(TP+FN) Specificity: TN/(TN+FP)
ROC(Receiver Operating Characteristic) curve / AUC(Area Under curve)
x축: 100 - specificity y축: sensitivity
Acurracy
(TP + TN)/all
F1 score
2 * Precision*Recall / (Precision + Recall)
Gaussian Process Regression
regression 함수 f에 gaussian 분포의 perturbation을 가해 존재할 수 있는 여러 곡선을 구하는 것
각 x에 대해서 y를 gaussian 분포로 제시
 λ를 조절하면서 uncertainty의 정도를 조절한다.
λ를 조절하면서 uncertainty의 정도를 조절한다.
λ가 작으면 관측값이 주변에 영향을 미치지 못해서 uncertainty가 커지고, 크면 너무 많이 미쳐서 underfit이 되어버림
참고
Bayesian Framework
AI: 학습(Learning/Training)과 추론(inference)으로 이루어짐
추론: P(A|B)[Posteriori Probability]
학습: P(B|A)[Likelihood Probability] * P(A)[Priori Probability]

Information (Theory)
- 정보량(=surprise =uncertainty): 얼마나 알고 있는 지가 아니라 해당 사건으로 인한 정보의 가치를 나타냄, 일어날 확률이 적은 사건일수록 가진 정보량이 큼.
- Entropy: average amount of information, E[I(X)] = -E[log(p_k)] = -∑p_k*log(p_k)
확실한 사건에 대해서는 entropy가 0에 가까우므로 학습할 필요가 적음.
KL Divergence

q_k(x;W): k가지 class에 대한 output probability
p_k(x): 정답 probability
q_k를 p_k에 가깝도록 학습시키는 것이 목표
Mutual Information: Output Y의 관측에 의해 알 수 있는 X의 uncertainty

X와 Y가 independent하다면 I(X;Y) = 0
Conidtional Entropy(Y가 관측되었을 때의 X의 entropy): H(X|Y) = H(X, Y)-H(Y)
Joint Entropy: H(X, Y)
Bayesian Learning
Bayesian Therom을 이용해 데이터 set D로부터 θ의 분포를 추정하는 것, p(θ|D)
Nonparametric Density Estimation
in practice, unimodal하지 않은 density function으로서 존재하는 경우가 많음(multimodal density)
nonparametric density estimation을 위한 다양한 방법이 있음
- Histogram: x축을 잘게 나누어서 해당 bin에 존재하는 데이터의 갯수로 분포를 표현(p = k/nV)
V를 고정한 상태에서 k의 변화가 density를 추정함. - KNN: 특정 데이터 x에서 근접한 k개의 데이터를 포함할 때까지 V를 키워가는 방법 k를 고정한 상태에서 V의 변화가 density를 추정함(V가 크다는 것은 density가 낮음을 말함).
- Parzen Windows: uniform distribution(1/h for x-h/2 ~ x+h/2)이 커널인 KDE
histogram과 마찬가지로 V(h^d)를 고정한 상태에서 k의 변화(커널함수의 합)으로 density 추정 - GMM(Gaussian Mixture Model): x가 여러 개의 Gaussian 분포 중 어느 분포에 속할 확률이 높은지로 density 추정

EM(Expectation-Maximization)을 이용해서 최적 파라미터들을 찾는다. - MH(Metropolis Hastings): 임의의 proposal distibution이 주어졌을 때, p(x)에 대한 MCMC 샘플링을 하는 알고리즘
proposal distribution Q(x'|x)을 통해 이전 샘플링(x)을 참고하여 다음 샘플링(x')을 예측
acceptance probability 를 이용해서 다음 샘플을 기각할지 받아들일지 결정
를 이용해서 다음 샘플을 기각할지 받아들일지 결정 - Gibbs Sampling: 다른 모든 변수는 고정하고 한 변수씩 샘플링해 나가 새로운 Markov Chain을 형성하는 MCMC의 한 방법
새롭게 형성된 Markov Chain을 통해서 sample을 얻는다
참고
■ MCMC(Markov Chain Monte Carlo)
참고
샘플링 알고리즘으로, 높은 차원의 문제를 빠른 수렴 속도로 해결 가능
stationary distribution이 target distribution p(x)가 되도록 Markov Chain을 설정하는 것
바로 이전 샘플만 다음 샘플의 추출에 영향을 주는데도 확률 분포를 거의 정확히 모방함
※ Markov Chain
한 상태 x_i에서 x_j로 이동할 조건부 확률분포[T(X_j|x_i)]가 주어져 있음
상태 사이를 충분히 많은 횟수 이동하게 되면 각 상태의 방문횟수의 비율이 특정 확률분포(stationary distribution)로 수렴