3D Representation - newlife-js/Wiki GitHub Wiki
by 서울대학교 김영민 교수님
Geometry Representation
Implicit representation
surface points(x,y,z)를 직접적으로 알지는 못하지만, 특정 relationship을 가짐
일반적으로 f(x, y, z) = 0으로 표현(예: x^2 + y^2 + z^2 - 1 = 0)
예) algebraic surfaces(surface를 수식으로 표현), constructive solid geometry(Boolean Operation을 이용), level set methods(공간을 grid로 나누어서 surface로부터 떨어진 정도를 수로 표현하여 f를 근사), blobby surfaces, fractals
f=0이 surface, f>0 외부, f<0 내부
Boolean Operation(union, intersection)을 이용해서 새로운 geometry를 만들 수 있음
예) algebraic surfaces, constructive solid geometry, level set methods, blobby surfaces, fractals

Explicit representation
모든 point(x, y, z)가 직접적으로 주어짐
예) triangle meshes, polygon meshes, subdivision surfaces, NURBS, point clouds
3D Projection

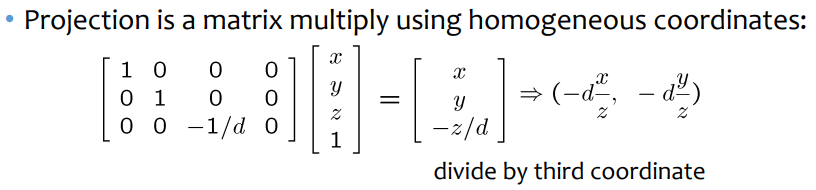
3D points를 camera coordinate system으로 conversion
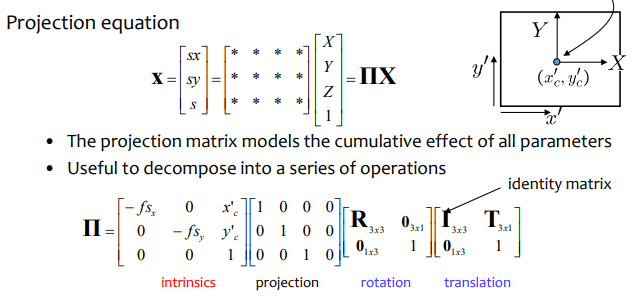
Problem formulation
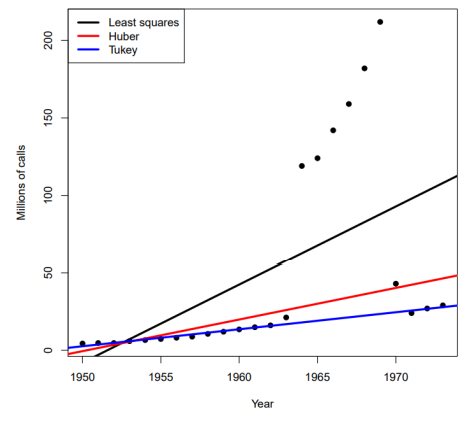
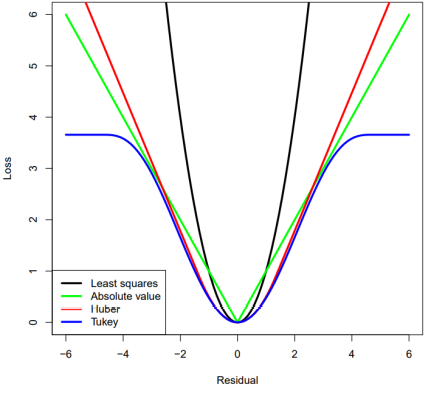
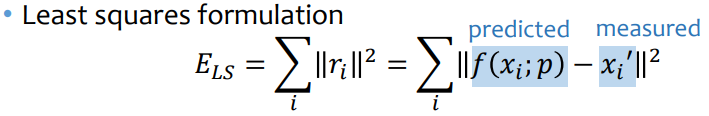 ※ 3d modeling(projection)에서는 아웃라이어가 많이 있기 때문에, 이를 무시하도록 loss function을 고도화함(Robust regression)
※ 3d modeling(projection)에서는 아웃라이어가 많이 있기 때문에, 이를 무시하도록 loss function을 고도화함(Robust regression)
Pose Estimation
2D point projections으로부터 물체의 3D pose를 estimate하는 것(PnP: Perspective-n-point-problem)
Differentiable Rendering
2D image level evidence를 3D scene integration(3D object reconstruction, pose estimation)에 이용
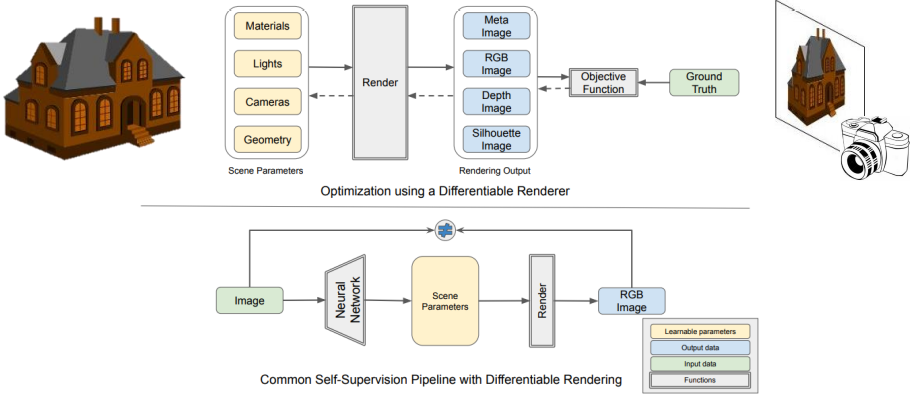
Rendering
Scene parameters(shape, material, camera, lighting)로부터 image(RGB, Depth)를 만들어내는 것
- Rasterization: 3D scene의 color를 그대로 pixel에 projection(그림자가 없음)
- Ray tracing: 복잡한 빛의 작용을 모두 고려하여 projection(그림자 등 다양한 빛의 의한 현상을 담음)
Light, Light sources, Materials and shapes, Cameras를 모델링에 사용
■ Triangular Mesh Rendering
각 pixel에 해당하는 triangle을 찾고, triangle을 screen space로 projection camera에 가장 가까운 triangle의 color를 interpolation을 통해서 계산(Rasterization)
triangular mesh는 기본적으로 미분이 불가능
approximated gradients: 미분이 불가능한 부분을 blur시켜서 미분가능하도록 변환
approximated rendering: 3D scene 자체를 blur / object를 density parameter로 정의
Global illumination: 다른 surface points로부터의 반사된 빛까지 모델링(Monte Carlo estimation of rendering equation)
**
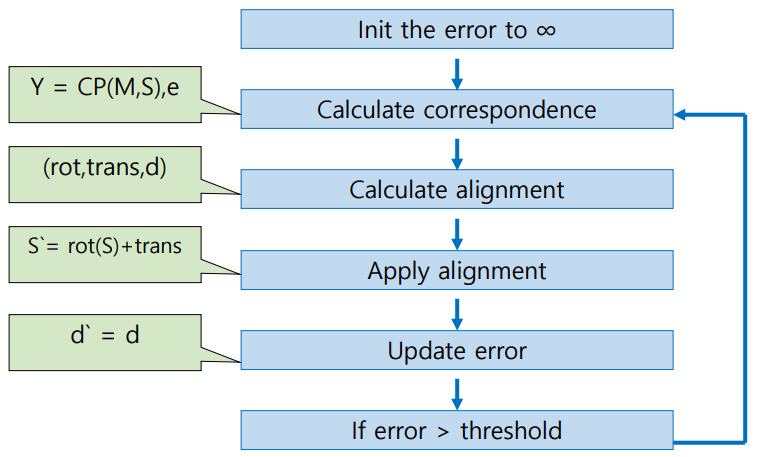
ICP(Iterative Close Point)
Pairwise Alignment
2개의 3D scan model이 overlapping하는 부분이 있을 경우 연결하는 것
(하나의 object에 대해 여러 3D scan 데이터를 이어서 완전한 하나의 3D model을 만들 수 있음)
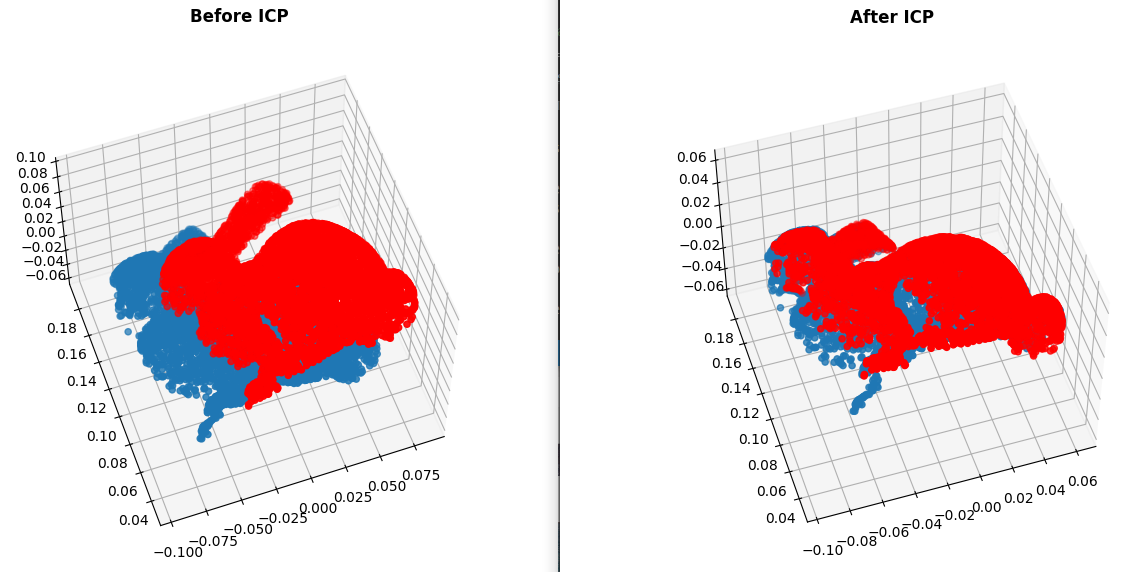 ※ application: shape inspection, motion estimation, appearance analysis, texture mapping, tracking
※ application: shape inspection, motion estimation, appearance analysis, texture mapping, tracking
Scene point(S)에 rotation(R)과 transition(t)을 적용했을 때 model point(M)과 같아지도록 align
- Center of Mass: M과 S 각각의 중심(μ)을 M, S로부터 빼주어 center를 일치하도록 align
- S_centered, M_centered의 내적을 한 Covariance Matrix를 계산한 후 SVD를 하면,
R = VU^T
t = μ_m - Rμ_s
현실에서는 M과 S의 correspondence point가 주어지지 않음
-> closest points가 correspond한다고 가정
closest points: argmin_m[euclian_distance(M, S_projected)] for each s_projected
Volumetric Representation
Signed Distance Function
표면보다 가까우면 -d, 표면보다 멀면 +d로 물체와의 거리를 표시하는 함수
(confidence가 클수록 기울기가 큼)
물체의 특성(두께 등)에 따른 weight를 가중치로 주어서 가중치 합을 사용
(반대쪽을 바라보는 surface들이 서로 영향을 주지 않게 하기 위해서 어느 정도 멀면 weight가 줄어들도록 함)
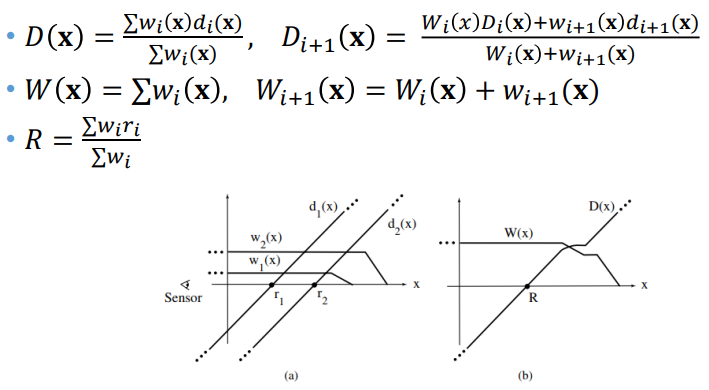
여러 signed distance function을 합쳤을 때, 0이 되는 지점들이 surface
O-CNN(Octree-based CNN)
모든 공간의 촘촘한 data에 대해서 CNN연산을 수행하면 시간/메모리 낭비가 크므로,
surface가 있는 부분의 resolution을 더 촘촘하게 표현
하나의 cube를 8개로 잘게 나누어가며 표현하므로 octree
searching, pooling등의 연산이 octree에서 더 효율적
full-voxel vs octree
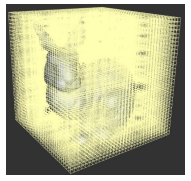
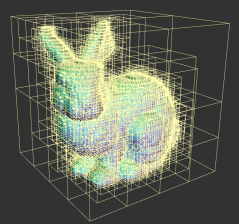
Conversion between 3D representations
■ Point Cloud(다양한 3D scanner들로부터의 input) -> Mesh
Mesh로 변경을 하게 되면 parameterization, decimation, filtering 등 다양한 geometry processing이 가능해짐
Sample points로부터 implicit function fitting을 통해 zero isosurface를 추출(points -> implicit -> mesh)
Marching cubes(squares)
implicit representation으로부터 triangle mesh를 만들어냄
space를 discretize해서 grid 형태로 만들고, 내부는 (-) 외부는 (+)로 할당
(-)와 (+) 사이의 edge에서 0을 interpolation 계산하여 연결함
장점: multi-purpose, fast and parallelizable, simple to implement
단점: badly shaped(skinny) triangles를 만들 수 있음
Poisson Surface Reconstruction
oriented point cloud로부터 smooth한 surface를 만드는 방법

■ Mesh -> Point Cloud
point cloud가 더 expressive하고 ML에도 사용할 수 있음
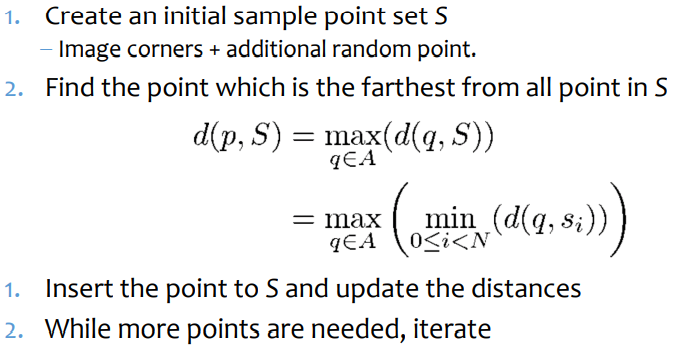
Farthest point sampling
Sampling된 point들에서 가장 멀리 있는 point를 sample로 선택하는 greedy algorithm
point 사이의 거리를 측정하는 다양한 방법이 있음(색도 고려 가능)
- On-Surface Distances(Geodesics): Dijkstra's algorithm을 이용해 거리를 측정
Mesh의 형태에 따라 어느 정도 에러는 존재함
Neural Implicit Surfaces
3D 좌표로부터 surface 내부인지 외부인 지(occupancy)를 출력하는 neural network(implicit function)
DeepSDF
occupancy 대신 SDF를 출력

표면 근처에서만 의미를 갖도록 loss function에는 clamp를 사용
■ Code shaped network
다양한 shape에 대해서 SDF를 예측할 수 있도록 input에 code를 넣은 network
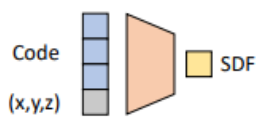
-> Auto-decoder: 별도의 encoding 없이 학습(back-propagation)을 통해서 code도 optimization을 해서 SDF를 예측
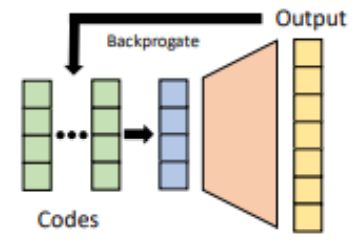
network size는 작지만, 아주 많은 point에 대해 sdf를 구해야 shape를 생성할 수 있어서 inference time이 길다
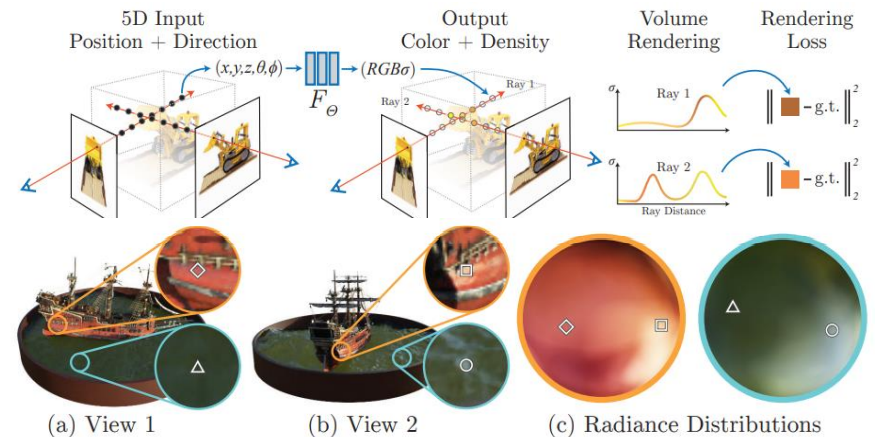
Neural Volume Rendering
3D position -> local RGB color & differential opacity/density(4D)
NeRF(Neural Radiance Fields)
DeepSDF architecture를 채용하여 density와 color를 예측