Graylog - mirpag/SEC-350-Final-Project GitHub Wiki
These notes were taken directly from https://github.com/mirpag/SEC-350-02/wiki/Lab2.2 and https://github.com/mirpag/SEC-350-02/wiki/syslog
These instructions were used to install graylog and its dependencies on log01: https://docs.graylog.org/docs/centos
sudo yum install java-11-openjdk-headless.x86_64
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install pwgen
Add the repository file /etc/yum.repos.d/mongodb-org.repo with the following contents:
[mongodb-org-4.2]
name=MongoDB Repository
baseurl=https://repo.mongodb.org/yum/redhat/$releasever/mongodb-org/4.2/x86_64/
gpgcheck=1
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://www.mongodb.org/static/pgp/server-4.2.asc
Install the latest version of mongodb and then enable and start the service
sudo yum install mongodb-org
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable mongod.service
sudo systemctl start mongod.service
sudo systemctl --type=service --state=active | grep mongod
Install the Elastic GPG key
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
Add the repository file /etc/yum.repos.d/elasticsearch.repo with the following contents:
[elasticsearch-7.x]
name=Elasticsearch repository for 7.x packages
baseurl=https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/oss-7.x/yum
gpgcheck=1
gpgkey=https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
enabled=1
autorefresh=1
type=rpm-md
Modify the Elasticsearch configuration file
sudo tee -a /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml > /dev/null <<EOT
cluster.name: graylog
action.auto_create_index: false
EOT
Start Elasticsearch
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
sudo systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
sudo systemctl --type=service --state=active | grep elasticsearch
Install Graylog
sudo rpm -Uvh https://packages.graylog2.org/repo/packages/graylog-4.2-repository_latest.rpm
sudo yum install graylog-server graylog-enterprise-plugins graylog-integrations-plugins graylog-enterprise-integrations-plugins
Read the instructions within the configurations file and edit as needed, located at /etc/graylog/server/server.conf. Additionally add password_secret and root_password_sha2 as these are mandatory and Graylog will not start without them.
To create your root_password_sha2 run the following command:
echo -n "Enter Password: " && head -1 </dev/stdin | tr -d '\n' | sha256sum | cut -d" " -f1
To create your password_secret use pwgen
Copy both of these passwords to the config file!!! It will not work without them.
In addition to this, set http_bind_address to IP of the machine you can connect to
Install apache
sudo yum install httpd
In the /var/www/index.html file, add the following configuration:
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerName graylog.example.org
ProxyRequests Off
<Proxy *>
Order deny,allow
Allow from all
</Proxy>
<Location />
RequestHeader set X-Graylog-Server-URL "http://graylog.example.org/"
ProxyPass http://127.0.0.1:9000/
ProxyPassReverse http://127.0.0.1:9000/
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable graylog-server.service
sudo systemctl start graylog-server.service
sudo systemctl --type=service --state=active | grep graylog
First, allow UDP and TCP 514 for syslog traffic permanently
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=514/udp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=514/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --reload
Now, edit the /etc/rsyslog.conf file to receive syslog messages over ports 514 tcp and udp. Uncomment the following lines and restart the service

Check to see if rsyslog is listening appropriately to these ports

Create the following file: /etc/rsyslog.d/sec350.conf and restart rsyslog on web01

💡 the line in sec350.conf means:
user=syslog facility
notice=syslog priority
@=UDP, @@ means TCP, so we are only going to send UDP
172.16.50.5=Remote Syslog Server
On log01, tail -f the /var/log/messages file
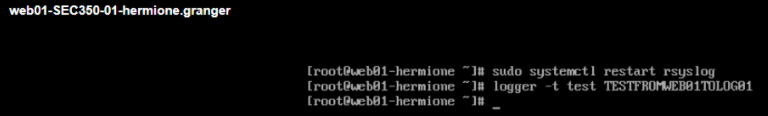
On web01, use the local logger utility to send a syslog message

💡Having all of our remote logs stuffed into log01's /var/log/messages or /var/log/secure is not helpful. Remote logs should be segregated and ideally stored on reliable and redundant storage in a manner that supports dealing with discrete event types. We are going to store logs in a directory hierarchy in order to provide this organization.

on log01
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gmcyber/sec350-share/main/03-sec350.conf
1) systemctl restart rsyslog
3) ls -lR --color /var/log/remote-syslog/
4) cat /var/log/remote-syslog/web01-miranda/2022.02.30.SEC350.log
on web01
2) logger -t SEC350 Testing web01->log01 custom rsyslog configuration
Edit /etc/rsyslog.d/sec350.conf
user_notice @172.16.50.5
authpriv.* @172.16.50.5
Restart rsyslog
systemctl restart rsyslog
To create a dashboard, go to the dashboard section in Graylog. Then, click the plus button on the left-hand side of the screen. Now, you can add different values to your dashboard!
Here is how the authentication dashboard turned out:

We did have some difficulties getting Graylog up and running. Though the system said that Graylog was downloaded, when we tried to start the service it said that python3 was not available. In addition to this, mongodb was not downloaded. To fix this, sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade was run on the ubuntu-big-group12 machine (our log management server). Then, the previous steps were run again. We had to ensure that all dependencies were up and running so we could actually get to Graylog on our management machine.