plans - mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse GitHub Wiki
Welcome to the hi wiki! Brief overview about ASIC Verification flow useful in VLSI:
✓ Specification Understanding:
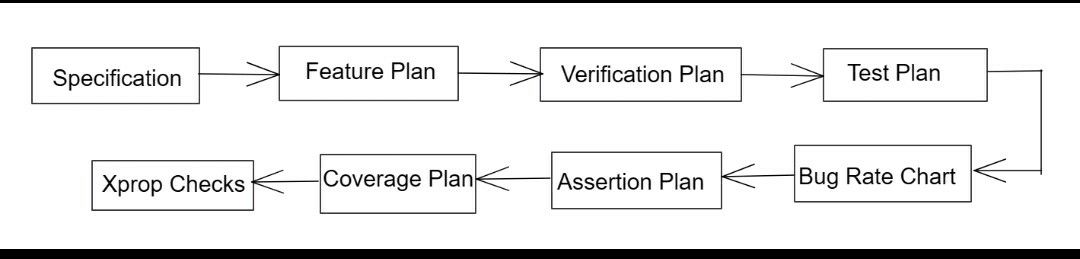
This is the first and most important step. Ideally microarchitectural specification is produced out of requirement and it needs to be thoroughly understood. The specification will provide a brief details about overall functionality, I/O ports, logic level complexity, frequency requirement, etc.
✓ Feature Plan Extraction:
In this step, as a verification engineer one needs to understand the feature that needs to be verified and prepare a document which will list all the features. This exercise will provide more indepth understanding on the feature step.
✓ Verification Planning:
In this step one needs to plan the verification infrastructure and the working of each individual UVC's related to the spec. From this step onwards the actual coding starts and one needs to code the UVC's like Driver, Monitor, scoreboard, etc.
All the details needs to be put on a document listing out the UVC and the Testbench infrastructure.
✓ Testcase Planning:
Testcase are nothing but sort of stimulus which are used to check the integrity and the functionality of the design and whether it is meeting the requirement as per the spec. Testcases are divided into two types: Directed and Random.
Directed are those which the verification engineers can anticipate but the random scenarios are those which are unpredictable.
✓ Bug Rate Chart:
Initially someone will able to catch more bugs and this bug rate chart is a document which will track all the bugs.
But once the bug rate chart starts dropping, this is the time to start coding functional coverage and introduce code coverage.
✓Assertion Plan:
This will provide more visibility into the design as one doesn't need to wait for the Testcase to end to trace the bug.
Assertions are used to increase the observability and reduce the debug effort. These needs to be coded individually and then needs to be bind with the design module.
✓Coverage plan:
Code coverage needs to be initiated by the tool and will identify how much design is exercised. If any loopholes are present, one needs to write more Testcases.
Functional Coverage will check the functionality and will inform whether all the functionality is checked. Cross Coverages also needs to be introduced for better result.
Exclusion file needs to be taken from the designer to exclude the unintended part of design.
✓ X propagation:
If any non resettable flip flops are present in the design this check will identify it and resolve it.
Finally before sign off we need to check few things:
a. All the features are verified.
b. All the bugs are rectified and no more bugs are pending.
c. FC = 100%
d. CC = 100%
e. X prop checks are clean.
f. Review with Designer completed
g. Sign off.
✓ ECO checks:
If somehow any corner case issues are missed out then ECO check.