08.Database - mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse GitHub Wiki
UVM Resource Database
-
Resource is container that contain the different types of data. It is used to supply the data type to different testbenches. With the help of resource db methods we can put any data type into the resource database and with help of some resource db methods we can retrieve that data type during simulation time.
-
uvm_resource_db is parent class of uvm_config_db.
-
uvm_resource_db is a type-parameterized class that serves the same purpose as congfig_db but does not follow the hierarchical order.It is not instantiated and the methods in it are accessed using scope resolution operator because all of the functions in uvm_resource_db are static, so they must be called using the :: operator.
Ex:
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set(scope,name,val);
There are several common methods of the uvm_resource_db class that allow you to add or retrieve data. The following table highlights the most common functions used.
| Sr. No. | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | get_by_type | Get a resource by type. |
| 2. | get_by_name | Imports a resource by name. |
| 3. | set | Create a new resource, write a val to it, and set it into the database using name and scope as the lookup parameters. |
| 4. | set_default | add a new item into the resources database. |
| 5. | set_anonymous | Create a new resource, write a val to it, and set it into the database. |
| 6. | read_by_type | Read a value by type. |
| 7. | read_by_name | locate a resource by name and scope and read its value. |
| 8. | write_by_name | write a val into the resources database. |
| 9. | write_by_type | write a val into the resources database. |
| 10. | dump | Dump all the resources in the resource pool. |
Methods:
1.get_by_type
It gets the resource by the type specified as a parameter in the class. So, ‘scope’ is the only argument for this function.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::get_by_type(string scope)
2.get_by_name
This function gets a resource by using both the scope and name given when it was added to the database.he rpterr argument indicates whether to generate a warning or not if a resource match is not found.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::get_by_name(string scope, string name, bit rpterr=1)
3.set
This function creates a new resource in the database with a scope, name and value that will be used for retrieval. The accessor is used for auditting.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::set(string scope, string name , value, uvm_object_accessor = null)
4.set_default
It creates a new resource using name and scope as lookup parameters without writing a new val. The resource will have its default value.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::set_default(string scope, string name)
5.set_anonymous
It creates a new resource and writes/ sets val to it using the scope as a lookup parameter. The resource is not updated in the name map as it has no name .But is does have a scope for lookup purposes. The accessor is used for auditting.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::set_anonymous(string scope, value, uvm_object_accessor = null)
6. read_by_type
This function locates the resource using only the scope as a lookup and returns the value through an output argument.The accessor is used for auditing. The return bit indicates whether read_by_name is successful or not.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::read_by_type(string scope, value, uvm_object accessor = null)
7. read_by_name
locate a resource by name and scope and read its value. The value is returned through the output argument val. The return value is a bit that indicates whether or not the read was successful.The accessor is used for auditing. The return bit indicates whether read_by_name is successful or not.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::read_by_name(string scope, string name, value, uvm_object accessor = null)
8.write_by_name
Write a val into the database. First lookup for the resource by name and scope. If it is not located then add a new resource to the database and then write its value.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::write_by_name(string scope, string name, value, uvm_object accessor = null)
9.write_by_type
Write a val into the database. First lookup for the resource by type. If it is not located then add a new resource to the database and then write its value.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::write_by_type(string scope, value, uvm_object accessor = null)
10.dump
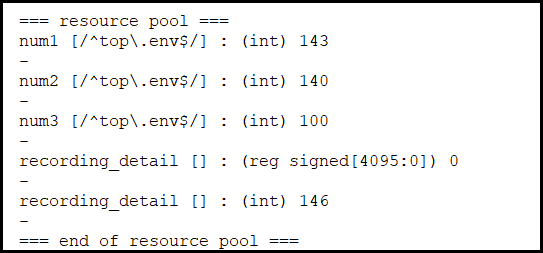
Dump all the resources in the resource pool. This is useful for debugging purposes. This function does not use the parameter T, so it will dump the same thing -- the entire database -- no matter the value of the parameter.
syntax
uvm_resource_db#(type T =uvm_object)::dump()
Code Snippet:-
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
class environ extends uvm_env;
`uvm_component_utils(environ)
int a,b,c,b1,d;
function new(string n="environ",uvm_component p=null);
super.new(n,p);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
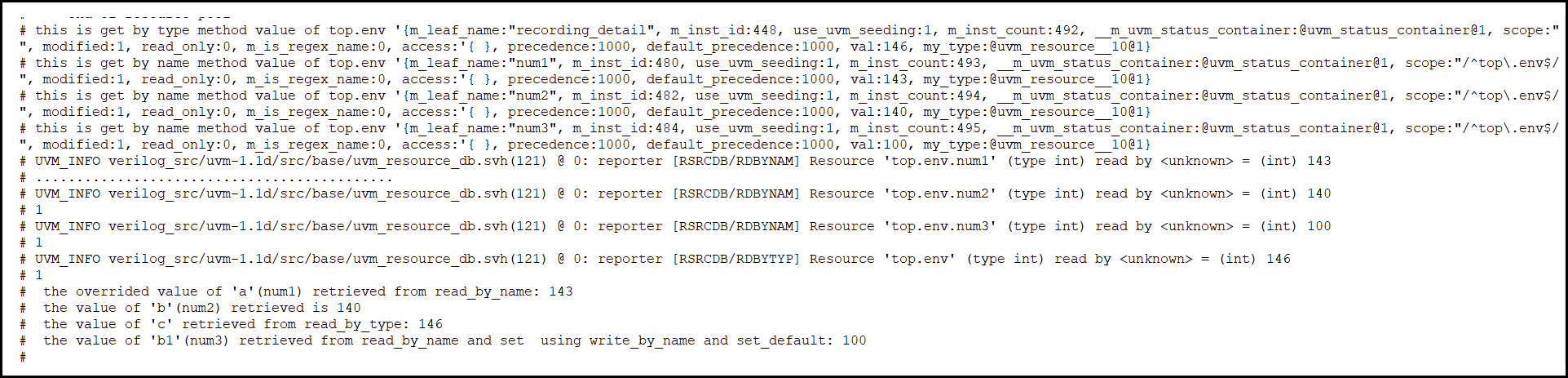
$display("this is get by type method value of top.env %p", uvm_resource_db#(int)::get_by_type("top.env"));
$display("this is get by name method value of top.env %p", uvm_resource_db#(int)::get_by_name("top.env","num1"));
$display("this is get by name method value of top.env %p", uvm_resource_db#(int)::get_by_name("top.env","num2"));
$display("this is get by name method value of top.env %p", uvm_resource_db#(int)::get_by_name("top.env","num3"));
//$display("this is get by name method value of top.env %p", uvm_resource_db#(int)::get_by_name("top.env","num4"));
uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_name("top.env","num1",a);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::get_by_name("top.env","n",0);
//uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_name("top.env","num4",b);
$display("............................................");
$display (uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_name("top.env","num2",b));
$display (uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_name("top.env","num3",b1));
$display (uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_type("top.env",c));
//$display (uvm_resource_db#(int)::read_by_type("top.env",d));
$display(" the overrided value of 'a'(num1) retrieved from read_by_name: %0d",a);
$display(" the value of 'b'(num2) retrieved is %0d",b);
$display(" the value of 'c' retrieved from read_by_type: %0d",c);
//$display(" the value of 'c'(num4) retrieved is %0d",d);
$display(" the value of 'b1'(num3) retrieved from read_by_name and set using write_by_name and set_default: %0d",b1);
endfunction
endclass
class test extends uvm_test;
environ e;
`uvm_component_utils(test)
function new(string n="environ",uvm_component p=null);
super.new(n,p);
endfunction
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
e=environ::type_id::create("e",this);
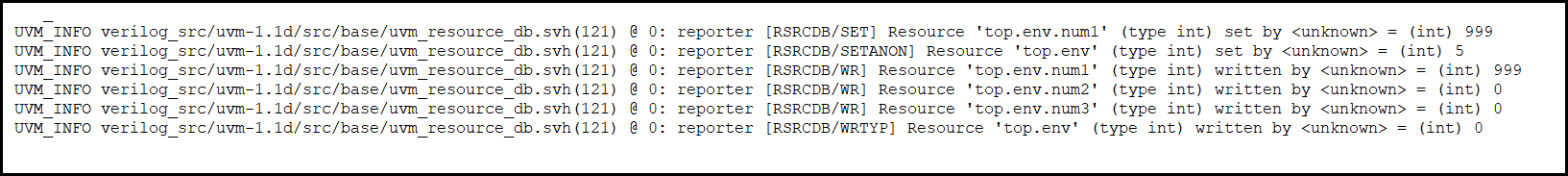
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set("top.env","num1",999);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set_default("top.env","num2");//takes no value
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set_default("top.env","num3");
//uvm_resource_db#(int)::set_default("top.env","num4");
uvm_resource_db#(int)::set_anonymous("top.env",5);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::write_by_name("top.env","num1",143); //overrides num1
// uvm_resource_db#(int)::write_by_name("top.env","num4",143);//shows error
uvm_resource_db#(int)::write_by_name("top.env","num2",140);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::write_by_name("top.env","num3",100);
uvm_resource_db#(int)::write_by_type("top.env",146);
//uvm_resource_db#(int)::write_by_type("top.env",79); multiple values cannot be put
uvm_resource_db#(int)::dump();
endfunction
endclass
module top;
initial begin
run_test("test");
end
endmodule
Output:-
UVM Configuration Database
Using uvm_config_db, is a base class which is derived from uvm_resource_db used to create a variable in the Database and set a value for that variable in any testbench components and the variables can be get into other testbench components without knowing their existence in the hierarchy.
It’s almost like making some class variables global or public. Any testbench component can place handles and get handles to objects. In the database, handles are identified by assigned ‘type’ and ‘name’.
There are two uvm_config_db functions, set() and get().
Any verification component using set() will set the variable into db and can also give permission and visibility of the variable for any one of the verification components.
The variable can be shared globally or made available to one or more specific testbench components.
Verification components using get() check if there is a shared handle matching the used parameters. The get() function defines the object type, the name and hierarchical path to the object searched for.
syntax:
uvm_config_db#(type)::method(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, type value);
where as,
contxt and inst_name are used to give the scope for the variable who have the permission to access the variable from db.
field_name is used to give a variable name which is going to be stored into db.
value is when it is set() method then it is the value for the variable declared.
value is when it is get() method then it is the variable where the value from db has to be stored.
All the functions in uvm_config_db#(T) are static, so they must be called using the :: operator.
For example:
uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this, "*", "A",10);
The parameter value "int" identifies the configuration type as an int property.
set() method
Create a new or update an existing configuration setting for field_name in inst_name from cntxt. The setting is made at cntxt
If the cntxt is "null" then we need to add the full name of cntxt to the inst_name for giving scope.
If the cntxt is "this" then no need of adding the full name of cntxt to the inst_name for giving scope.
The cntxt hierarchy is used to determine the setting's precedence in the database. Settings from hierarchically higher levels have higher precedence. A precedence setting starts from uvm_top, and each hierarcical level below the top is decremented by 1.
syntax:
static function void set(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, T value);
get() method
Get the value from field_name which is in inst_name, using component cntxt as the starting search point.
inst_name is an explicit instance name relative to cntxt and may be an empty string if the cntxt is the scope of that instance.
field_name is the specific field in the scope that is being searched for.
syntax:
static function bit get(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, inout T value);
exists() method
Before setting a new field_name into db it Check if the field_name is available in inst_name, using component cntxt as the starting search point. The function returns 1 if a config parameter exists and 0 if it doesn't exist.
syntax:
static function bit exists(uvm_component cntxt, string inst_name, string field_name, bit spell_chk=0);
code snippet:
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
class driver extends uvm_driver;
`uvm_component_utils(driver)
int base_start_value;
string name;
function new(string name = "driver",uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction:new
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
//----------------------------CHECKING IN DB---------------------------------
if(uvm_config_db#(int)::exists(this,"","sample"))
begin:BEGIN_IF_EXIST_1
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
if(uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this,"","sample",base_start_value))
begin:BEGIN_IF_GET_1
`uvm_info(get_type_name,"getting value from sample",UVM_LOW)
`uvm_info(get_type_name,$sformatf("base_start_value = %0d",base_start_value),UVM_LOW)
end:BEGIN_IF_GET_1
else
begin:BEGIN_ELSE_GET_1
`uvm_error(get_type_name,"The base start value was not getting from sample")
end:BEGIN_ELSE_GET_1
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
end:BEGIN_IF_EXIST_1
else
begin:BEGIN_ELSE_EXIST_1
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
if(uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this,"","base_value",base_start_value))
begin:BEGIN_IF_GET_2
`uvm_info(get_type_name,"getting value from base value",UVM_LOW)
`uvm_info(get_type_name,$sformatf("base_start_value = %0d",base_start_value),UVM_LOW)
end:BEGIN_IF_GET_2
else
begin:BEGIN_ELSE_GET_2
`uvm_error(get_type_name,"The base start value was not getting from base value")
end:BEGIN_ELSE_GET_2
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
end:BEGIN_ELSE_EXIST_1
//----------------------------CHECKING IN DB---------------------------------
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
uvm_config_db#(string)::get(this,"","my_name",name);
`uvm_info(get_type_name,$sformatf("[dri] name = %0s",name),UVM_LOW)
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
endfunction:build_phase
endclass:driver
class environment extends uvm_env;
`uvm_component_utils(environment)
driver dri;
string avengers,name;
function new(string name = "environment",uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction:new
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
dri = driver::type_id::create("dri",this);
//----------------------------CHECKING IN DB---------------------------------
if(uvm_config_db#(int)::exists(null,"uvm_test_top","base_value"))
begin:BEGIN_IF
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this,"dri","sample",30);
`uvm_info(get_type_name,"sample value set successfully",UVM_LOW)
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
end:BEGIN_IF
else
begin:BEGIN_ELSE
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
uvm_config_db#(int)::set(this,"dri","base_value",20);
`uvm_info(get_type_name,"base value set successfully",UVM_LOW)
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
end:BEGIN_ELSE
//----------------------------CHECKING IN DB---------------------------------
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
uvm_config_db#(string)::set(this,"dri","my_name","kumar");
`uvm_info(get_type_name,"my name set successfully",UVM_LOW)
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
if(uvm_config_db#(string)::get(this,"","captain",avengers))
`uvm_info(get_type_name,$sformatf("avengers = %0s",avengers),UVM_LOW)
else
`uvm_error(get_type_name,"The captain we are not getting into test")
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
endfunction:build_phase
endclass:environment
class test extends uvm_test;
`uvm_component_utils(test)
environment env;
int a;
function new(string name = "test",uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction:new
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
env = environment::type_id::create("env",this);
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
uvm_config_db#(string)::set(this,"env","captain","America");
uvm_config_db#(string)::set(this,"*","my_name","vinay");
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
if(uvm_config_db#(int)::get(this,"","base_value",a))
`uvm_info(get_type_name,$sformatf("a = %0d",a),UVM_LOW)
else
`uvm_error(get_type_name,"The base value we are not getting from test")
//----------------------------GETTING FROM DB--------------------------------
endfunction:build_phase
endclass:test
module top;
initial begin:BEGIN_I
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
uvm_config_db#(int)::set(null,"uvm_test_top","base_value",10);
//----------------------------SETTING TO DB----------------------------------
run_test("test");
end:BEGIN_I
endmodule:top
output:
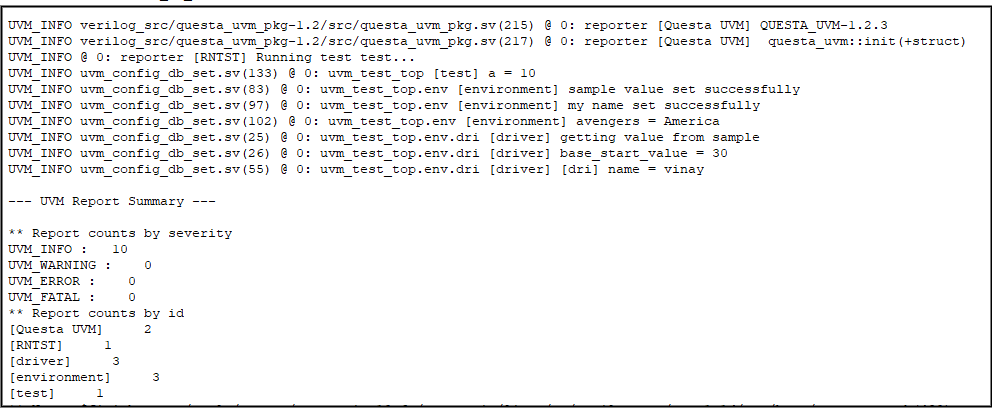
Fig-6: output for set(), get() and exists() method.
Github lab link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_Team_BJT/uvm_config_db/uvm_config_db_set.sv
Github log_file link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_Team_BJT/uvm_config_db/uvm_config_db_set.log
note:
- In runtime if you want for get the tracing info about set() and get() methods use
+UVM_CONFIG_DB_TRACEcommand line arguments.
1.How can we set 2 values of data using uvm_config_db ?
We can set as many values at same time by using only 'uvm_config_db' set and get method once.
Configuration values are set in the uvm_config_db class using the set() method and retrieved using the get() method. uvm_config_db is a parameterized class that is parameterized with the data type of object that is being set or get.
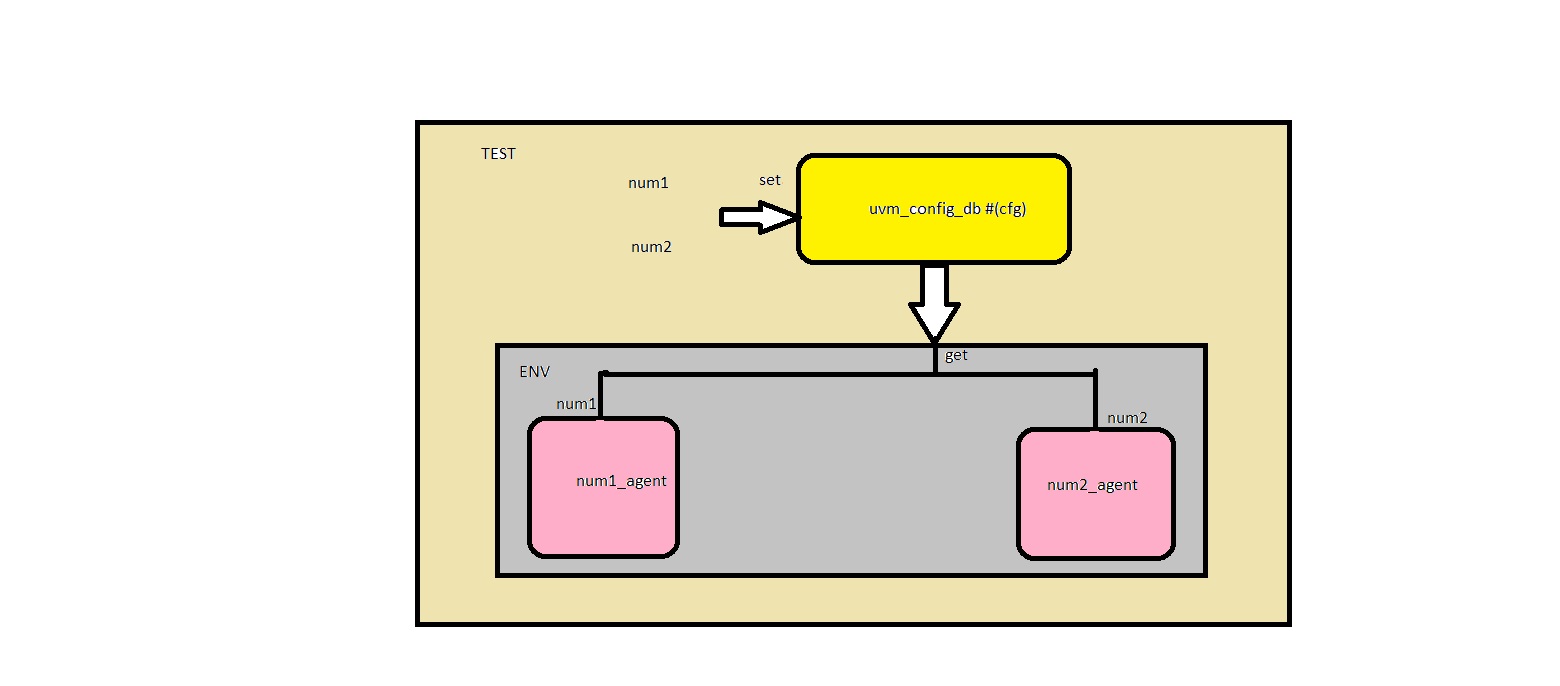
Fig 1: uvm_config example
CODE
We can set two values for num1 and num2 to identify the number of input values.
class cfg extends uvm_object;
`uvm_object_utils(cfg)
int num1;
int num2;
endclass
Test class will contain a handle for environment and a handle for cfg class
class basic_test extends uvm_test;
env env_h;
cfg cfg_h;
endclass
function void basic_test::build_phase(uvm_phase phase)
//create object for cfg
cfg_h = cfg::type_id::create("cfg_h",this);
//Randomization
cgf.randomize();
//set database of cfg class type
uvm_config_db #(cfg)::set (this,"env_h","cfg",cfg_h)
env_h = env::type_id::create("env_h",this);
endfunction
Environment class will contain a handle of cfg class and a dynamic array of handles for num1_agent and num2_agent.
In the build phase, configuration database is retrieved, and depending on the values of num1 and num2, required number of agents are created.
class env extends uvm_env;
cfg cfg_h;
num1_agent agt_num1[];
num2_agent agt_num2[];
endclass
function void env:build_phase(uvm_phase phase)
if (!uvm_config_db #(cfg)::get (this,"","cfg",cfg_h))
`uvm_fatal(get_type_name(),"Failed to get cfg in env")
endfunction