03.Reporting - mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse GitHub Wiki
Reporting mechanism
The command $display is commonly used to show information and report results in a verification environment. Controlling the display statements can become difficult as design would require frequent re-compilations and hence it becomes time consuming.
To overcome such scenarios, UVM Reporting provides a set of displaying commands and methods to change the number and types of print-messaging in any testbench without re-compiling the design.
UVM Reporting arguments
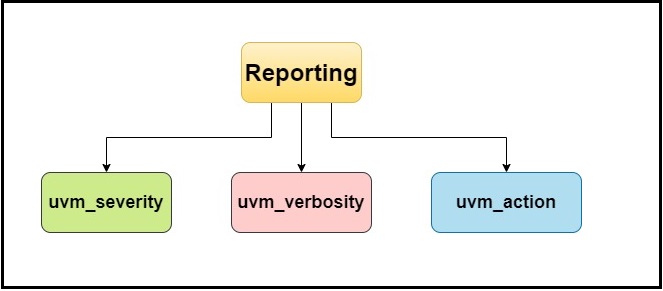
Figure.1. UVM reporting
1.UVM_severity
- uvm_severity indicates the importance of the message to be displayed.
- Examples are info, warning, error and fatal.
-
`uvm_info
Syntax: `uvm_info(ID, message, VERBOSITY);
ID - a unique id to form a group of messages.
message - The message text.
VERBOSITY - the verbosity of the message, and the default is UVM_MEDIUM.Here VERBOSITY can be UVM_NONE, UVM_LOW, UVM_HIGH, UVM_MEDIUM, UVM_FULL, UVM_DEBUG.
-
`uvm_warning
Syntax: `uvm_warning(ID, message);
Here by default verbosity is UVM_MEDIUM.
It generates the run time warning. -
`uvm_error
Syntax: `uvm_error(ID, message);
Here by default verbosity is UVM_LOW.
It emits an error severity message. -
`uvm_fatal
Syntax: `uvm_fatal(ID, message);
Here by default verbosity is UVM_NONE.
It generates a run-time fatal error, which terminates the simulation.
Code
`uvm_warning("TEST", "Warning occured");
`uvm_info("TEST","inoformation severity--1 (info_none)", UVM_NONE);
`uvm_info("TEST","information severity--2 (info_medium)", UVM_MEDIUM);
`uvm_info("TEST","information severity--3 (info_low)", UVM_LOW);
`uvm_error("TEST", "Error 1");
`uvm_error("TEST", "Error 2");
`uvm_fatal("TEST", "A fatal error has occurred")
Output
The below figure shows the output of uvm_severity code. We can observe that, there is two information severity statements we're getting from package. So here it count even the info getting from package.
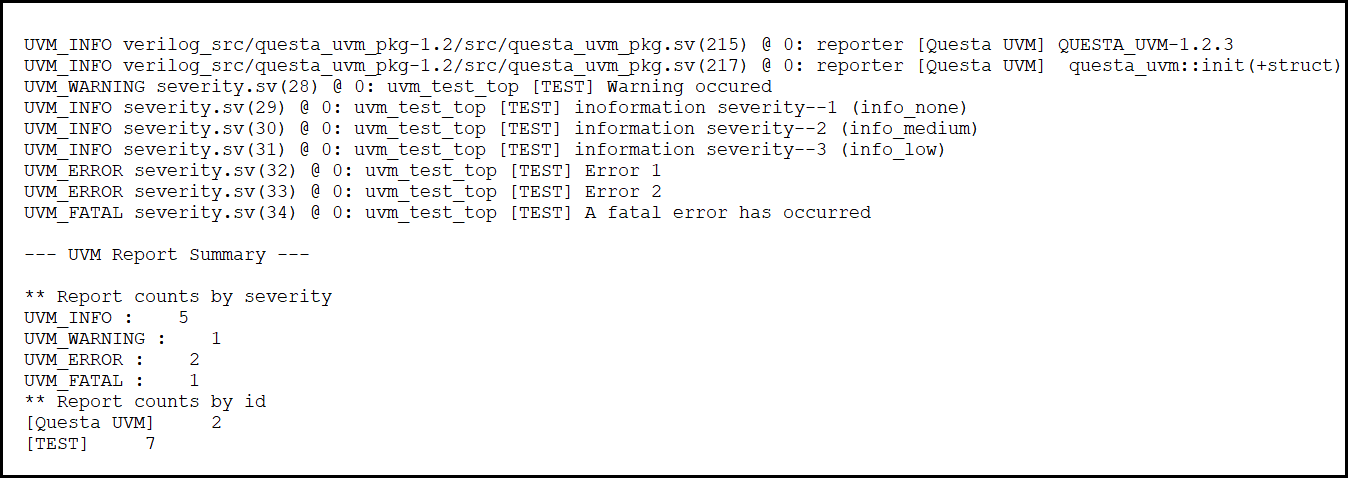
Figure.2. Output of UVM severity
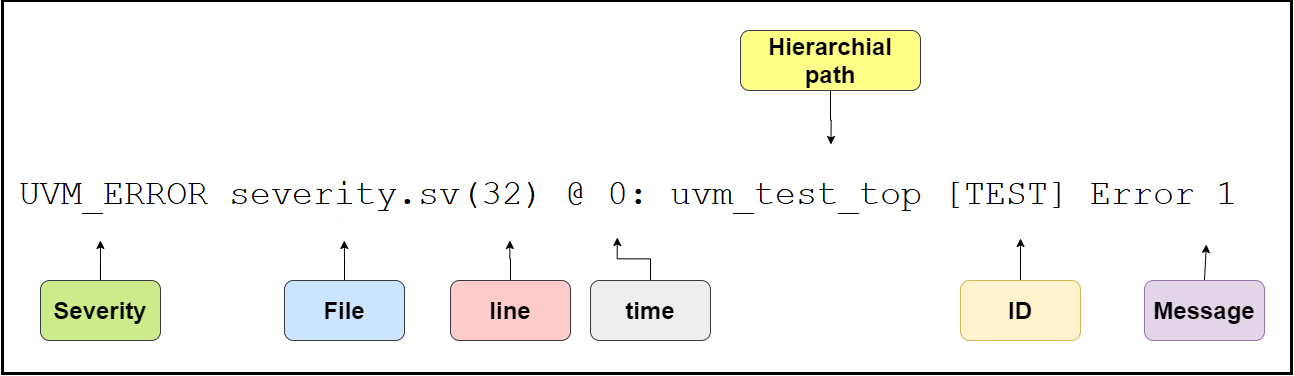
Figure.3. Output analyzation
Github lab link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/severity/severity.sv
Github Output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/severity/severity.log
Note:
- In place of ID, we can use get_full_name(), get_type_name(), get_name(). These are built in methods.
Code
`uvm_info("TEST","inoformation severity--1 (info_none)", UVM_NONE);
`uvm_info(get_name(),"get_name() information severity--3 (info_low)", UVM_LOW);
`uvm_info(get_full_name(),"get_full_name() inoformation severity--1 (info_none)", UVM_NONE);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(),"get_type_name() information severity--2 (info_medium)", UVM_MEDIUM);
Output
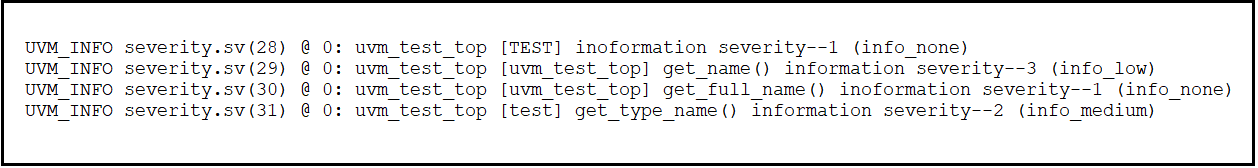
Figure.4. Using other method for ID
- In the above code snippet, we can observe that we've used TEST as first severity ID, where we'll get that ID name in output.
- In second, we used get_name(), where we'll get full hierarchy of the testbench, i.e [uvm_test_top].
- In third, we used get_full_name(), which is same as get_name().
- At last, we used get_type_name(), where we'll get only class name which we created, i.e [test].
Github lab link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/severity_id/severity.sv
Github Output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/severity_id/severity.log
-
In message, if you want to get values from input as display statement, we can use
$sformatf("%0d", variable)`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_NONE]value of d is %0d",d), UVM_NONE);
github code link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example3/Example.sv
github output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example3/top.log
UVM severity methods
-
uvm_report_info(ID, message, VERBOSITY, filename, line);
ID - a unique id to form a group of messages.
message - The message text
verbosity - the verbosity of the message and the default is UVM_MEDIUM.
filename/line - If required to print filename and line number from where the message is issued, use macros, as shown in below code snippet. -
uvm_report_warning(ID, message, VERBOSITY, filename, line);
The the default is UVM_MEDIUM. -
uvm_report_error(ID, message, VERBOSITY, filename, line);
The the default is UVM_LOW. -
uvm_report_fatal(ID, message, VERBOSITY, filename, line);
The the default is UVM_NONE.
code
uvm_report_info("TEST","inoformation severity--1 (info_none)", UVM_NONE);
uvm_report_info("TEST","inoformation severity--1 (info_none)", UVM_NONE,`__FILE__,`__LINE__);
uvm_report_error("TEST", "Error 1",UVM_NONE,`__FILE__,`__LINE__);
uvm_report_warning("TEST", "Warning occured", UVM_NONE,`__FILE__,`__LINE__);
uvm_report_fatal("TEST", "A fatal error has occurred", UVM_NONE,`__FILE__,`__LINE__);
Output
The below figure shows the output of uvm_severity method code. We can observe that, there is two information severity statements we're getting from package. So here it count even the info getting from package.
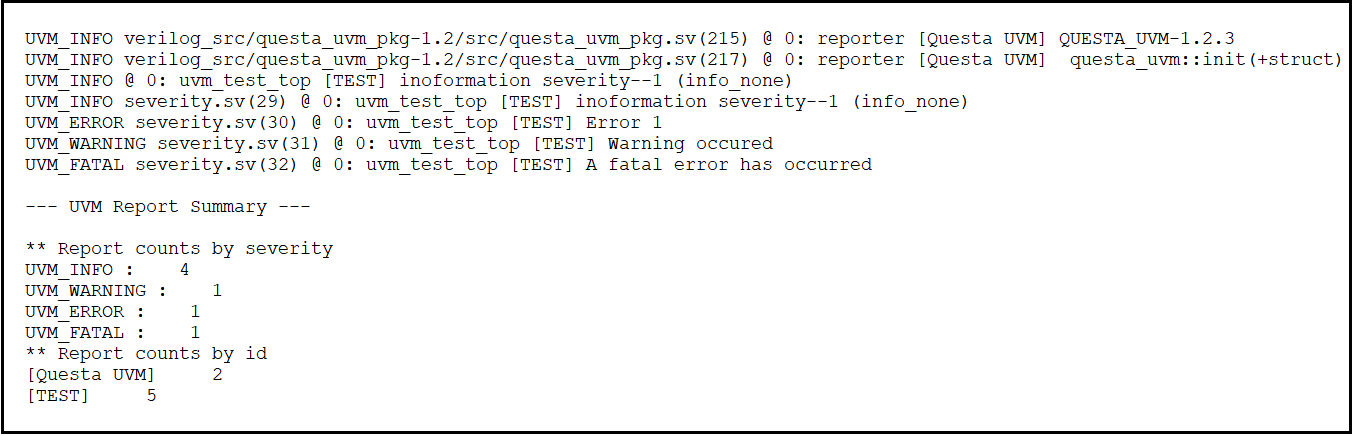
Figure.5. UVM severity method output
- In the above code snippet, observe that in first method, we didn't use file and line, so in the output there is no filename and line number.
- In the second method, there is a presence of file and line macro . So in the output there is a filename and line number.
- In remaining method we used file and line, so we'll get filename and line number.
- And for error, warning and fatal method, we can use any verbosity.
Github lab link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/severity_method/severity.sv
Github Output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/severity_method/severity.log
NOTE
The main difference between severities and its method is, in output, i.e in severities we'll get filename and line number without mentioning its macros, but in case of function we'll not get without using macros.
Code Severity Control
There are two methods listed here and the order of precedence from low to high
we have a set of report severity override, which changes all reports of a given current severity to be new severity.
We can also change a severity, by a combination of current severity and report ID using set report severity ID, override to change those reports to a new severity.
Now these method calls are not hierarchically only affect a single component to which they are compiled.
Also these methods can be called using a hierarchical path name so again call these inside of a test class,
it gives you the ability to turn them on and off by switching between tests
In order of percedence(low to high)
-
change a severity
set_report_severity_override(current_severity,new_severity) -
change by severity ID pair
set_report_severity_id_override(current_severity, id, new_severity)
Example:
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
class driver extends uvm_driver;
`uvm_component_utils(driver)
function new(string name="",uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
`uvm_warning("TEST", "warning occured");
`uvm_info("TEST","information severity--1 (info_none)", UVM_NONE);
`uvm_info("TEST","information severity--2 (info_medium)", UVM_MEDIUM);
`uvm_info("TEST","information severity--3 (info_low)", UVM_LOW);
`uvm_error("TEST", "Error 1");
`uvm_error("TEST", "Error 2");
`uvm_fatal("FATAL", "A fatal error has occurred")
endtask
endclass
module top;
driver dri;
initial begin
dri=driver::type_id::create("dri",null);
dri.set_report_severity_override(UVM_ERROR,UVM_WARNING);
dri.set_report_severity_id_override(UVM_FATAL,"FATAL",UVM_ERROR);
run_test();
end
endmodule
explanation:
- The code is a driver class that extends the uvm_driver class.
- It sets the report severity override to UVM_ERROR,UVM_WARNING, and UVM_FATAL.
- Then it calls run_test() which is defined in the top module.
- The code attempts to create a driver class with the name "dri" and then set the severity of all messages generated by that driver to UVM_ERROR,
- UVM_WARNING, or UVM_FATAL.
- The code above also sets the severity id override for those messages to be "FATAL", which is then used as a value for the report severity id override.
- The last line in this code runs a test task that will generate some warnings and errors.
output:
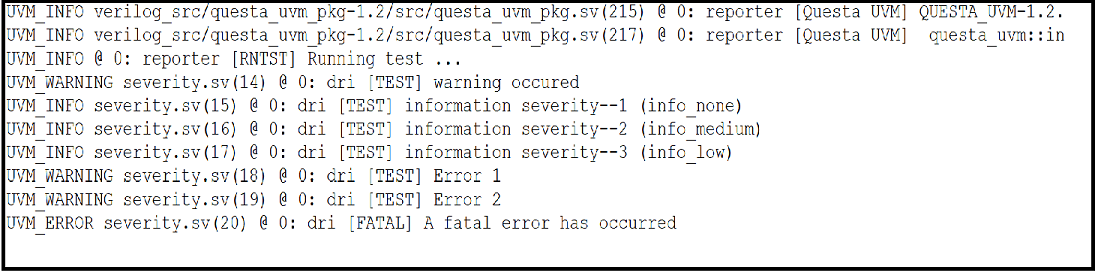
output explanation:
- The code starts with a UVM_INFO severity.sv(14) at 0: reporter [TEST] warning occured.
- This is followed by a UVM_WARNING severity.sv(14) at 0: dri [TEST] warning occured, which is followed by a UVM_ERROR severity.sv(20) at 0: dri [FATAL] A fatal error has occurred
2.UVM_Verbosity
In UVM there are multiple levels of verbosity. such as UVM_NONE, UVM_LOW, UVM_MEDIUM (Default), UVM_HIGH, UVM_FULL, UVM_DEBUG. The default Verbosity is UVM_MEDIUM.In case of default Verbosity level i.e. UVM_MEDIUM, any messages with UVM_HIGH or above are filtered out.
| SL.NO | verbosity_level | Verbosity_default_value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | UVM_NONE | 0 | The Verbosity configuration is always be printed, it cannot be disabled |
| 2. | UVM_LOW | 100 | The Verbosity configuration is printed if it is UVM_LOW and above i.e UVM_NONE |
| 3. | UVM_MEDIUM | 200 | The Verbosity configuration is printed if it is UVM_MEDIUM and above i.e UVM_NONE, UVM_LOW |
| 4. | UVM_HIGH | 300 | The Verbosity configuration is printed if it is UVM_HIGH and above i.e UVM_NONE, UVM_LOW, UVM_MEDIUM |
| 5. | UVM_FULL | 400 | The Verbosity configuration is printed if it is UVM_FULL and above i.e all above Verbose level |
| 6. | UVM_DEBUG | 500 | The Verbosity configuration is printed if it is UVM_DEBUG and above i.e all above verbose level |
Table1: UVM VERBOSITY LEVEL
Example1: In this example we use simple module with verbosity level including the uvm macros and importing uvm_pkg i.e all uvm class.
code snippet:
//Access to all uvm macros
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
//Access to all uvm pkg i.e all uvm class
import uvm_pkg::*;
module top;
initial begin:B1
//UVM_NONE is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm none i.e 0", UVM_NONE);
#5;
//UVM_NONE is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", UVM_LOW);
#5;
//UVM_MEDIUM is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm medium i.e 200", UVM_MEDIUM);
#5;
//UVM_LOW is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", UVM_LOW);
#5;
//UVM_LOW is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", UVM_LOW);
#5;
//UVM_LOW is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm none i.e 0", UVM_NONE);
end:B1
endmodule
OUTPUT:
Here in the below figure shows the output for the different verbosity level
Fig.1: output of verbosity level using simple module block
Github lab link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/tree/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example1
Github Output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example1/top.log
Example2: In this example we use simple module with Verbosity values, including the uvm macros and importing uvm_pkg i.e all uvm class.
code snippet:
//Access to all uvm macros
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
//Access to all uvm pkg i.e all uvm class
import uvm_pkg::*;
module top;
initial begin:B1
//UVM_NONE is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm none i.e 0", 0);
#5;
//UVM_NONE is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", 100);
#5;
//UVM_MEDIUM is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm medium i.e 200", 200);
#5;
//UVM_LOW is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", 100);
#5;
//UVM_LOW is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", UVM_LOW);
#5;
//UVM_LOW is LOWER THEN UVM_DEFAULT IT IS PRINTED
`uvm_info("TOP", "verbosity level is uvm none i.e 0", UVM_NONE);
end:B1
endmodule
OUTPUT:
Here, in this figure we know that we can also pass the default verbosity level values instead of using uvm verbosity level.
Fig.2: output of verbosity level values using simple module
Github lab link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/tree/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example2
Github Output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example2/top.log
Important Notes:
- A message with the Verbosity level UVM_NONE cannot be disabled.
- Verbosity level cannot filter out the uvm_fatal, uvm_error & uvm_warning.
We can set the Verbosity level of a uvm_component individually or hierarchically using following commands:
command:
class_handle_name.set_report_verbosity_level(UVM_VERBOSITY);
Example:
env.set_report_verbosity_level(UVM_HIGH);
Example.3:To set the verbosity level and print the statements. code snippet:
//Access the uvm macros
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
// Access the uvm package i.e uvm class
import uvm_pkg::*;
//component class
class dilip extends uvm_driver;
rand bit[3:0] d;
//factory registration
`uvm_component_utils(dilip);
//All component in the uvm base class as default constructor expecting two arguments
function new(string name = "", uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
task display();
//start of test sequence
$display("");
$display("[%0t] \t Default verbosity level of uvm is %0d[UVM_MEDIUM]",$time,UVM_MEDIUM);
$display("");
#1;
//The verbosity level lower then UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_NONE]value of d is %0d",d), UVM_NONE);
$display("");
#2;
//The verbosity level lower then UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_LOW]value of d is %0d",d), UVM_LOW);
$display("");
#3;
//The verbosity level lower then or equal UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_MEDIUM]value of d is %0d", d),UVM_MEDIUM);
$display("");
#4;
//The verbosity level higher then the UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY then it will not printed
`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_HIGH]value of d is %0d",d), UVM_HIGH);
$display("");
#5;
//The verbosity level higher then the UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY then it will not printed
`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_FULL]value of d is %0d",d), UVM_FULL);
$display("");
#6;
//The verbosity level higher then the UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY then it will not printed
`uvm_info("DILIP", $sformatf("[UVM_DEBUG]value of d is %0d",d), UVM_DEBUG);
$display("");
//end of test sequence
endtask
endclass
module tb;
//class handle
dilip dk;
initial begin:B1
//Here we creating the object, using factory overriding
dk = dilip::type_id::create("dk",null);
//TO SET THE UVM VEROSITY LEVEL
dk.set_report_verbosity_level(UVM_DEBUG);
//object.randomize();
void'(dk.randomize());
//object.method
dk.display();
end:B1
endmodule:tb
output:
Here in the given below figure shows the output for setting the versobity level. The verbosity level is set by using set_report_verbosity_level(UVM_DEBUG). so that all verbosity level are displayed. the verbosity level is only used for `uvm_info severity.
Fig.3: shows the output of verbosite level
github code link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/tree/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example3
github output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example3/top.log
Example.4: To set the verbosity level of uvm_component and print the statements
code snippet:
//Access the all uvm macros
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
//Access the uvm package i.e uvm class
import uvm_pkg::*;
//component class
class driver extends uvm_driver;
//factory registration
`uvm_component_utils(driver);
//All component in the uvm base class as default constructor expecting two arguments
function new(string name = "", uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
//Build phase responsible for building all the lower level components, execute in bottom-up manner
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
//run phase execute in the parallel run phase comes under task
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
//start of test sequence
phase.raise_objection(this);
#1;
//The verbosity level lower then UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm none i.e 0", UVM_NONE);
#2;
//The verbosity level lower then UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", UVM_LOW);
#3;
//The verbosity level lower then or equal UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm medium i.e 200", UVM_MEDIUM);
#4;
//higher the verbosity value then that of UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will not be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm high i.e 300", UVM_HIGH);
#5;
//higher the verbosity value then that of UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will not be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm full i.e 400", UVM_FULL);
#6;
//higher the verbosity value then that of UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will not be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm Debug i.e 500", UVM_DEBUG);
//end of test sequence
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
module tb;
//class handle
driver drv;
initial begin
//Here we creating the object, using factory overriding
drv = driver::type_id::create("drv",null);
//TO SET THE UVM VERBOSITY LEVEL
drv.set_report_verbosity_level(UVM_DEBUG);
run_test();
end
endmodule
OUTPUT:
Here, in the below figure shows the output for verbosity level where we set the level of verbosity, the run_test(); will give the UVM_report about severity, the verbosity level is used only for `uvm_info. if we do not set verbosity level it will by default execute the statement which is equal to UVM_MEDIUM and above verbosity levels
Fig.4: Shows the output for setting the verbosity level
Github lab code link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/tree/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example4
Github output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example4/top.log
To Know the value of the UVM_verbosity_level which we have set using set verbosity command, we use the below command
Command:
class_handle.get_report_verbosity_level()
Example4:
drv.get_report_verbosity_level()
Example.5: To get the UVM verbosity level of uvm_component and print the statements
code snippet:
//Access the all uvm macros
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
//Access the uvm package i.e uvm class
import uvm_pkg::*;
//component class
class driver extends uvm_driver;
//factory registration
`uvm_component_utils(driver);
//All component in the uvm base class as default constructor expecting two arguments
function new(string name = "", uvm_component parent);
super.new(name,parent);
endfunction
//Build phase responsible for building all the lower level components, execute in bottom-up manner
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
//run phase execute in the parallel run phase comes under task
task run_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.run_phase(phase);
//start of test sequence
phase.raise_objection(this);
#1;
//The verbosity level lower then UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm none i.e 0", UVM_NONE);
#3;
//The verbosity level lower then UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm low i.e 100", UVM_LOW);
#3;
//The verbosity level lower then or equal UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm medium i.e 200", UVM_MEDIUM);
#4;
//higher the verbosity value then that of UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will not be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm high i.e 300", UVM_HIGH);
#6;
//higher the verbosity value then that of UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will not be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm full i.e 400", UVM_FULL);
#6;
//higher the verbosity value then that of UVM_DEFAULT VERBOSITY will not be printed
`uvm_info("DRV", "verbosity level is uvm debug i.e 500", UVM_DEBUG);
//end of test sequence
phase.drop_objection(this);
endtask
endclass
module tb;
//class handle
driver drv;
initial begin
//Here we creating the object, using factory overriding
drv = driver::type_id::create("drv",null);
//To Know the UVM_DEFAULT_VERBOSITE VALUE
$display("To get the verbosity level value", drv.get_report_verbosity_level());
run_test();
end
endmodule
OUTPUT:
Here, in the below figure shows the output for default verbosity level of uvm. it will print or gives the information about the statement whose verbosity level is equal to or less than UVM_MEDIUM. To know the default verbosity in the uvm will use a command drv.get_report_verbosity_level(). The run_test() will give the UVM_REPORT details.
Fig.5: Shows the output for getting the default verbosity level
Github lab code link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/tree/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example5
Github output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/verbosity/Example5/top.log
3. UVM_action
UVM_action is the behaviour of the simulator during each uvm_severity defined.
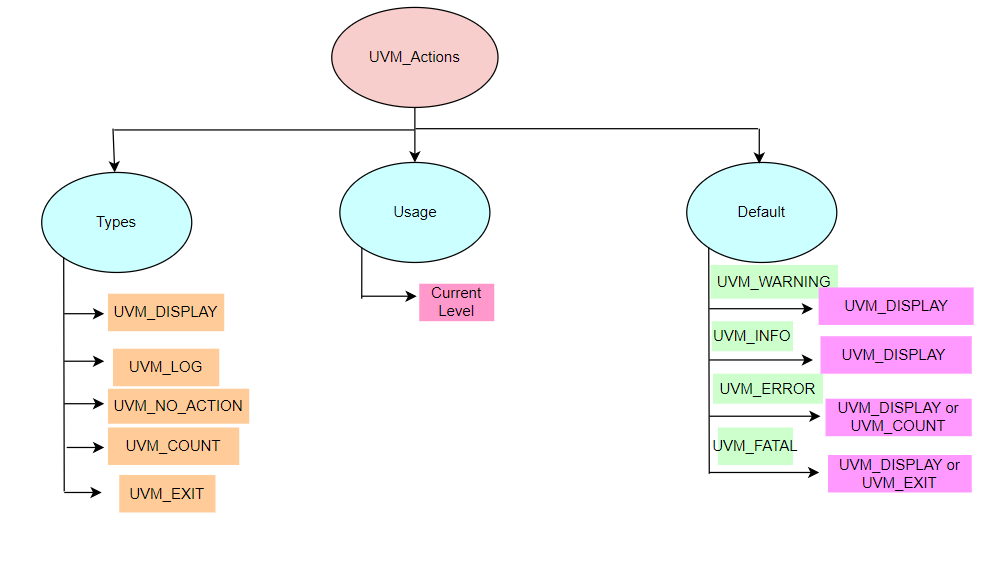
Fig 1 : UVM_action
There are in total six Simulator behaviours which can be associated with a particular UVM Reporting Severity depending upon the users choice.
-
UVM_EXIT
Exit from simulation immediately. -
UVM_COUNT
Increment global error count -
UVM_DISPLAY
Display message on console -
UVM_LOG
Captures message in a named file -
UVM_CALL_BACK
Calls callback method -
UVM_NO_ACTION
It will not display the output for the particular severity used. Example: class_handle.set_report_severity_action(UVM_INFO, UVM_NO_ACTION)
Here, in this above example it will not display the output statement for the UVM_INFO severity. because the action decide the output statement
The default simulator action associated with each of these Severity.
- UVM_FATAL - UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_EXIT
- UVM_ERROR - UVM_DISPLAY | UVM_COUNT
- UVM_WARNING - UVM_DISPLAY
- UVM_INFO - UVM_DISPLAY
code snippet
`include "uvm_macros.svh"
import uvm_pkg::*;
class rpting extends uvm_component;
`uvm_component_utils(rpting)
function new(string name,uvm_component parent);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
task run();
uvm_report_info(get_full_name(),
"This is information 1",UVM_NONE,`__FILE__,`__LINE__);
uvm_report_info(get_full_name(),
"This is information 2",UVM_LOW);
uvm_report_info(get_full_name(),
"This is information 3",150);
uvm_report_info(get_full_name(),
"This is information 4",UVM_MEDIUM);
uvm_report_warning(get_full_name(),
"Warning Messgae from rpting",UVM_LOW);
uvm_report_error(get_full_name(),
"Error Message from rpting \n\n",UVM_LOW);
endtask
endclass
module top;
rpting rpt1;
rpting rpt2;
rpting rpt3;
initial begin
rpt1 = new("rpt1",null);
rpt2 = new("rpt2",null);
rpt3 = new("rpt3",null);
//Do nohing when error message occur
rpt1.set_report_severity_action(UVM_ERROR,UVM_NO_ACTION);
// capture the message in named file
rpt2.set_report_id_action("rpt2",UVM_LOG);
// terminate when error message occur
rpt3.set_report_severity_id_action(UVM_ERROR,"rpt3",UVM_EXIT);
run_test();
end
endmodule
Simulator Action Methods Usage
UVM allows to bind a Reporting Severity with a particular valid Simulator Action. Usually its done inside the start_of_simulation() phase.
Actions can be assigned using set_report_*_action() functions. These can be done for one or all in the priority order from lowest to highest.
Current Level
set_report_severity_action(Severity, Action);set_report_id_action(ID, Action);set_report_severity_id_action(Severity, ID, Action);
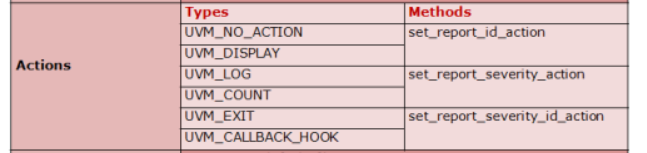
Fig 2: Action Methods in UVM Reporting
Code Snippet 1
rpt1.set_report_severity_action(UVM_ERROR,UVM_NO_ACTION);
rpt2.set_report_id_action("rpt2",UVM_LOG);
rpt3.set_report_severity_id_action(UVM_ERROR,"rpt3",UVM_EXIT);
Output
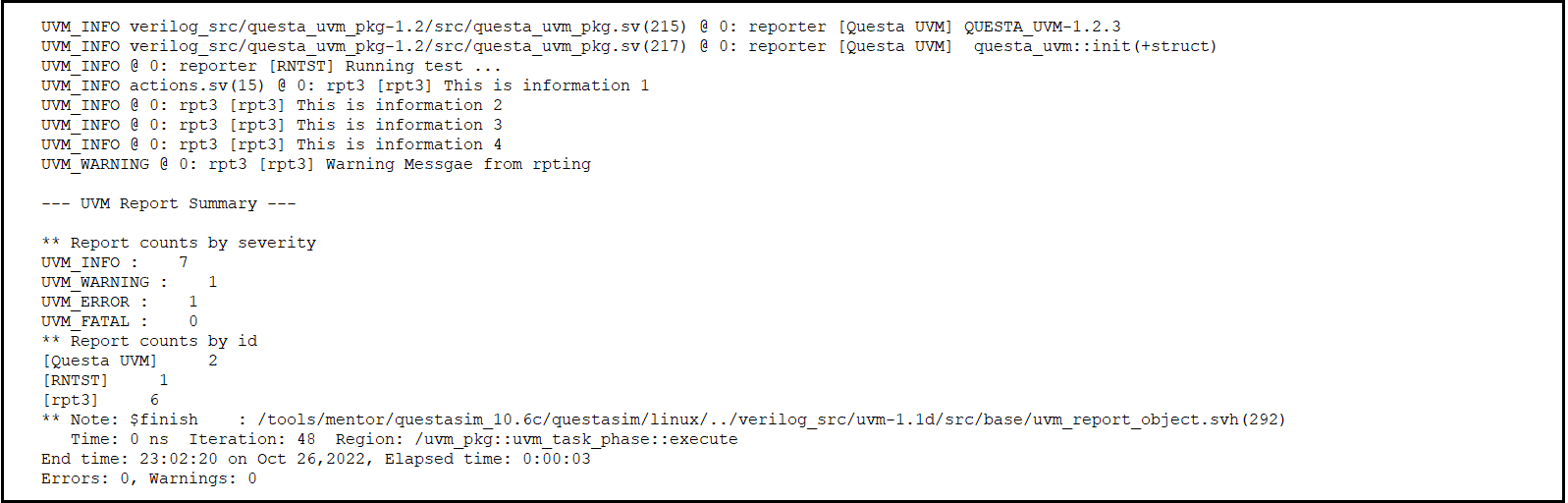
Fig 3: Code snippet 1 Output
Explanation
Here in this first set_report_severity_id_action() is called and when uvm_error message comes it will exit from the simulation and it will not execute other two functions.
Github code link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/uvm_actions/example2/actions_example2.sv
Github output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/uvm_actions/example2/top.log
Code Snippet 2
rpt1.set_report_severity_action(UVM_ERROR,UVM_NO_ACTION);
rpt2.set_report_severity_action(UVM_INFO,UVM_COUNT);
Output
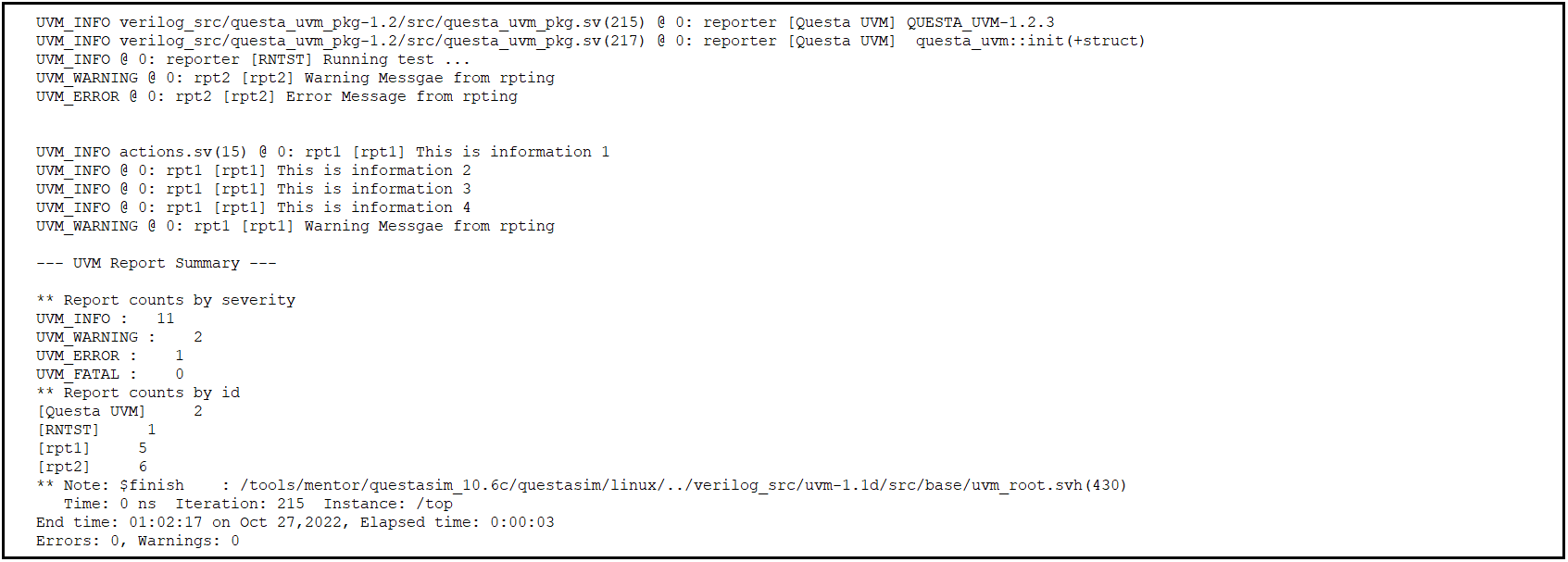
Fig 4: Code Snippet 2 Output
Explanation
In this code for rpt2, it will count for uvm_info message but it will not displayed on to the output console and for rpt1, when uvm_error message comes it will do nothing as show in output.
Code Snippet 3
//rpt1.set_report_severity_action(UVM_ERROR,UVM_NO_ACTION);
//rpt2.set_report_severity_action(UVM_INFO,UVM_COUNT);
rpt3.set_report_severity_action(UVM_ERROR,UVM_DISPLAY);
Output
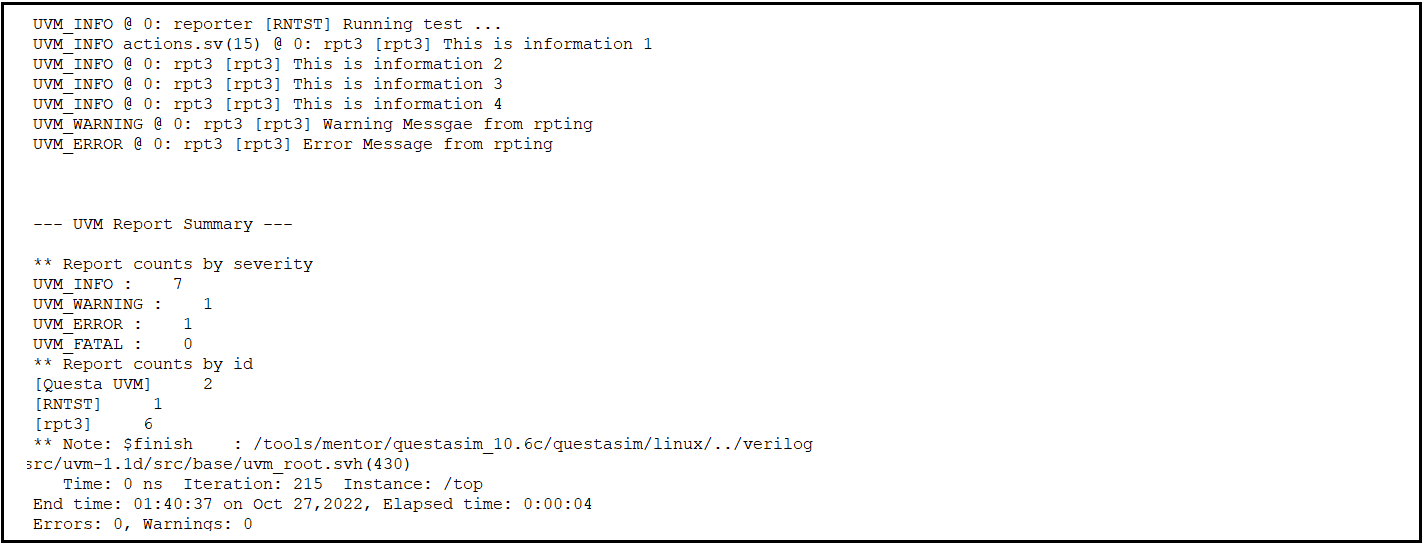
Fig 5: Code Snippet 3 Output
Explanation
Here in this for rpt3, it will display the uvm_error messages (i.e one in this case) on to the output console as shown in ouptut.
Github code link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/uvm_actions/example1/actions_example1.sv
Github output link: https://github.com/mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse/blob/b7_team_kachori/reporting/uvm_actions/example1/top.log