01. UVM Introduction - mbits-mirafra/UVMCourse GitHub Wiki
What is UVM ?
- Universal Verification Methodology (UVM) is a methodology based on SystemVerilog language and is not a language on its own. It is a standardized methodology that defines several best practices in verification to enable efficiency in terms of reuse and is also currently part of IEEE 1800.2 working group.
- UVM consists of a defined methodology in terms of architecting testbenches and test cases and also comes with a library of classes that helps in building efficient constrained random testbenches easily.The UVM consists of class libraries needed for the development of well constructed, reusable SystemVerilog based Verification environment.
- In simple words, UVM consists of a set of base classes with methods defined in it, the SystemVerilog verification environment can be developed by extending these base classes. Now on will refer the UVM base classes as UVM Classes.
Why do we need UVM ?
-
UVM is a well defined class library which has reusable verification components and objects already available, using them we can build a verification environment with ease.
-
Now, if we built a Verification Environment using only SV, you need to construct each and every component before using them. It is really time consuming and not possible in recent projects, which has lots of complex components to be created. For Eg, We need to create our own Driver, Monitor, Sequencer and it is not an easy task. Whereas in UVM you can directly use them by extending from the already available base class.
-
Even Coverage components are available and they follow particular phases for execution, which is very much reliable for proper verification execution.
-
The idea behind UVM is to enhance flexibility and reuse code so that the same Testbench can be configured in different ways to build different components, and provide different stimulus.
What is the advantage of UVM based testbench over System Verilog based testbench?
A simple analogy:
-
System Verilog based TB: You are asked to build a house from scratch, not much of tools are provided to you to build the house. You will build the tools first and then start building the house. You probably would have put in lot of effort to make the whole thing work. But you have the flexibility to use those tools to build other houses or develop new tools depending on your need. You will struggle to build larger houses though, not that it is impossible.
-
UVM based TB: You are again asked to build a similar house from scratch, and you are provided with not just the basic tools but some are quite sophisticated too.. You effortlessly build the house.
Note that both the houses could be equally good in terms of quality and strength but the effort you put in for the latter house is very minimal. This, however, is subjective and and many might still prefer SV based TB since they have more controllability over it and that they have the flexibility to develop necessary verification infrastructure/ libraries based on their taste and requirement.
UVM Testbench Architecture
A typical UVM testbench contains several components. First, let’s look at a simple UVM testbench diagram.
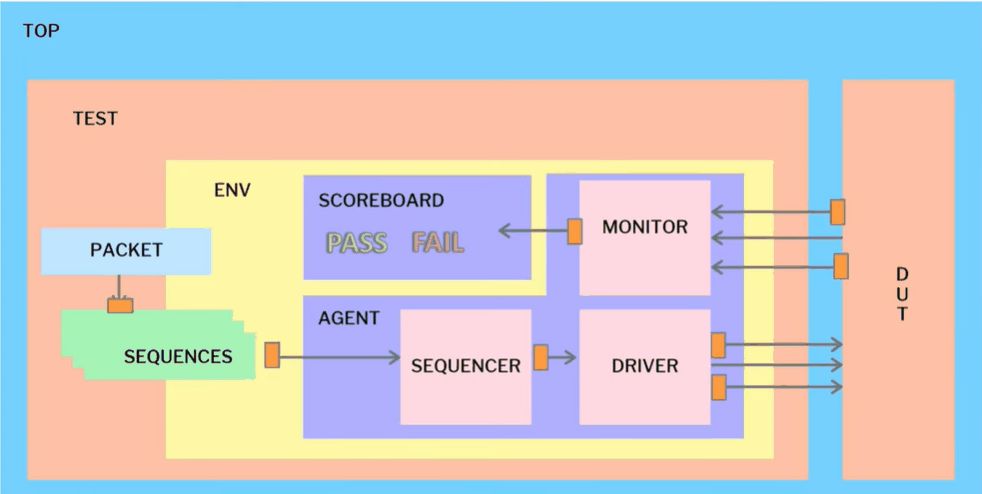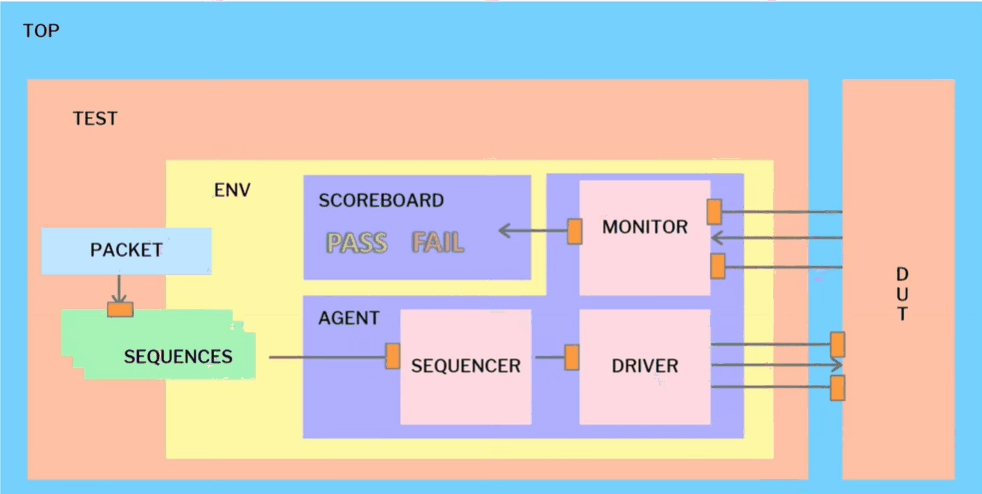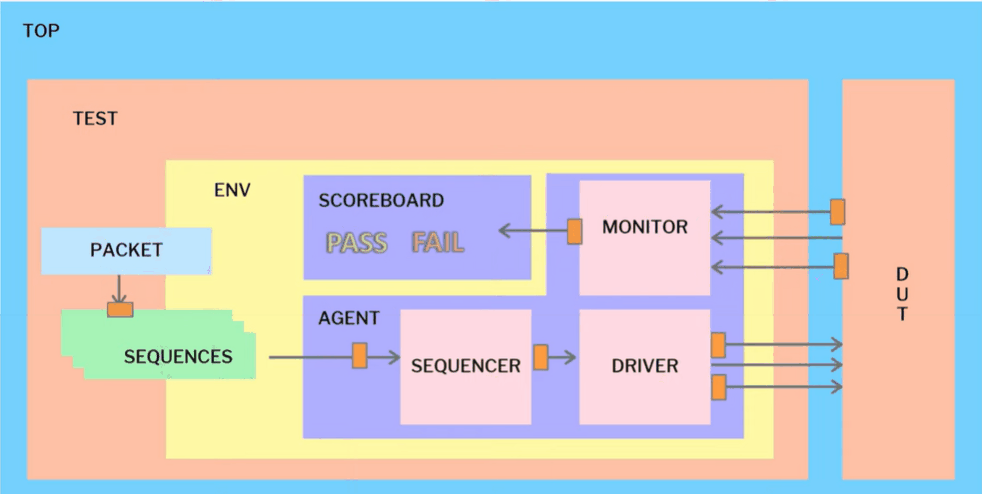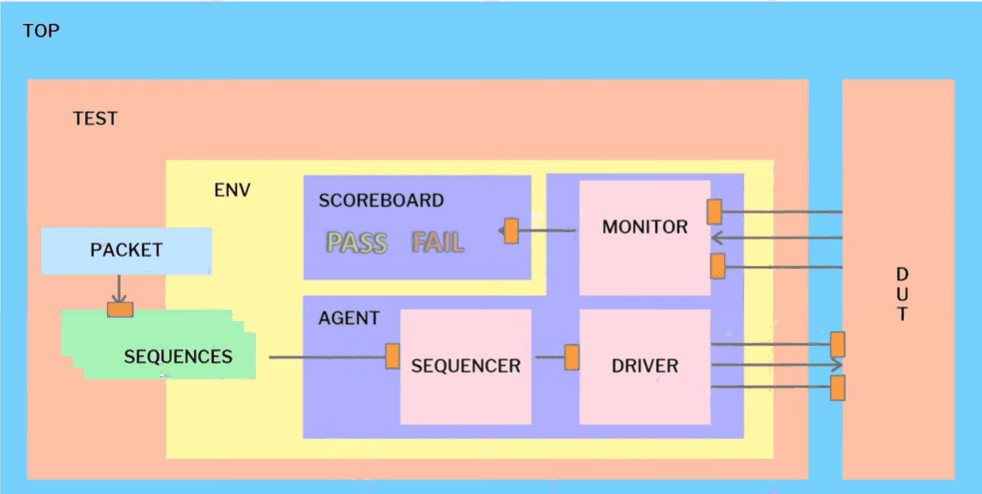
Fig-1 Gifs for UVM testbench architecture
There are several components are within this diagram.
- Top Module: Top module consists of the test class, DUT and interface. It consists of all verification components and any assertion are passed in top module of the design.
- UVM_Test:The UVM Test is the top-level UVM Component in the UVM Testbench. .Test contains environment and other configuration properties. Test is written by extending uvm_test.
- UVM_Environment: UVM_Environment consist of UVM Agents, UVM Scoreboards, or even other UVM Environments. The top-level UVM Environment encapsulates all the verification components targeting the DUT.Environment is written by extending uvm_env.
- UVM Agent: Agent is a top class that encapsulates driver, sequencer and monitor in general.The UVM Agent is a hierarchical component that groups together other verification components that are dealing with a specific DUT interface.
- UVM_Sequencer: Sequencer generates data transactions to driver.The sequencer govern the flow of request and response sequence items between sequence and the driver via TLM ports.Sequencer is written by extending the uvm_sequencer.
- UVM Sequence: A UVM Sequence is an object that contains a behavior for generating stimulus. Sequences make the main stimuli for verification. Sequence send data items to sequencer that are created either with constrained random or directed data. Sequence is written by extending the uvm_sequence.
- UVM Driver: UVM driver is an active component that drive signals to the interface of the design. Transaction level objects are obtained from the Sequencer and the UVM driver drives them to the DUT through an interface handle. Driver is written by extending the uvm_driver.
- UVM Monitor: UVM monitor captures signals from the design interface and translate it into transaction level data objects. Active monitor that is present in active agent captures inputs of the design via interface handle and send the packets to scoreboard via analysis ports. Passive monitor captures output of the design via interface handle and send to scoreboard via analysis port. Uvm monitor is written by extending uvm_monitor.
- UVM_Scoreboard: The UVM Scoreboard’s main function is to check the behavior of a certain DUT. The UVM Scoreboard usually receives transactions carrying inputs and outputs of the DUT through UVM Agent analysis ports. Scoreboard is written by extending uvm_scoreboard. Active agent and Passive agents are connected to scoreboard via TLM analysis ports and the design functionality and correctness is checked within the scoreboard.