Report Team 5 : Holograms - mam8684/Miguel-Mielgo-Assignment-1-INTRO-TO-CIS---CS1101200 GitHub Wiki
HOLOGRAMS
WHAT'S A HOLOGRAM AND WHAT TYPES EXIST?
Holography or graphic vision is an advanced photography technique that consists of creating three-dimensional images based on the use of light. For this, is used a laser beam which microscopically engraves a photosensitive film. Interference between two coherent light beams makes it possible for light from one of them to reflect off the object. This, when receiving a point light from the appropriate perspective, projects a three-dimensional image. The observer, without having the need for any accessory, can see them without discontinuities and varying the perspectives depending on their position.
Holography was invented in 1948 by the Hungarian physicist Dennis Gabor (he was a Hungarian physicist). However, it was perfected years later with the development of the laser, as Gabor's holograms were very primitive because his devices had not been sufficiently perfected. Originally, Gabor just wanted to find a way to improve the resolution and definition of electron microscope images. One of the most promising advances made recently has been its use for DVD players and other applications.
Some examples of holographic devices are:
Cheoptics 360: It is a video projector formed by an inverted pyramid that is capable of generating three-dimensional images within its projection space.

Heliodisplay: reproduces 2-D holograms without using a physical medium such as a screen. It allows projecting a static or moving image in the air with a certain quality, of about 27 inches, without requiring alternative media such as smoke or water and can be used in any environment without additional facilities.

MARK II: The system is based on the construction of the images by means of a joint exploration of several laser beams whose amplitude is modulated in accordance with the interference fringes of the previously calculated hologram.

MARK III: The objective of the project is to develop a domestic holographic display system. It will form monochrome 3D images with dimensions similar to a Rubik's cube.

Interactive 360 ° Light Field Display: The presented system consists of a high-speed video projector, a rotating mirror covered by a holographic diffuser and an FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) semiconductor circuit.
• Does not require special glasses.
• It is omni-directional: 360-degree 3D vision.
• Does not reproduce color.
• Allows interactivity with the holographic image.

There are different types of holograms:
Fresnel holograms: These are the simplest, most realistic and impressive holograms, but they can only be observed with the light of a laser.

Reflection holograms: The image is stored in a thick layer of emulsion and can be reproduced in white light.
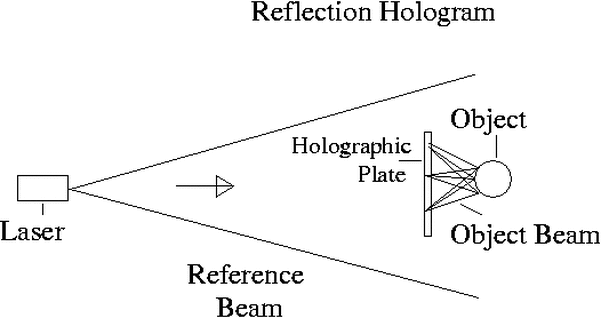
Image plane holograms: This is one in which the object is placed on the plane of the hologram. Naturally, the object cannot be physically placed since this cannot be possible, the real image of the object, which is formed by a lens or any other hologram, is the one that is placed on the photographic plane.

Rainbow holograms: With these not only is the image of the desired object reproduced, but also the real image of a horizontal slit over the observer's eyes is reproduced.

WHERE AND WHEN WE SAW THE FIRST HOLOGRAM
First created in the 1940s, the holographic method was originally proposed to use x-rays. Although practical for the development of advanced electron microscopes, the idea pioneered by physicist Dennis Gabor was not successful in the creation of the first optical hologram, as x-rays are not visible with the naked eye. Then holograph was used in 1962 by Dr. Yuri N. Denisyuk from Russia. He combined holography in 1908 Nobel Laureate Gabriel Lippmann’s work in natural color photography. Denisyuk produced a white light reflection hologram for the first time and it could be viewed in light form from an ordinary incandescent light bulb. Also in 1968 Dr Stephen A. Benton invented the White light transmission holography while researching holographic television at Polaroid Research Laboratories. In 1972 Lloyd Cross developed the integral hologram by combining the white light transmission holography with conventional cinematography to produce the first moving 3D Image. When viewed, the composite images are synthesized by the human brain as a 3D image.
In the 1970s Victor Komar and his colleagues at the All Union Cinema and Photographic Research Institute in Russia, developed a prototype for a projected holographic movie. Images were recorded with a pulsed holographic camera. The developed film was projected onto a holographic screen that focused the dimensional image out to several points in the audience.
Holographic artists have greatly increased their technical knowledge of the discipline and now contribute to the technology as well as the creative process. The art form has become international, with major exhibitions being held throughout the world. Today, numerous types of holograms are used in everyday life unbeknownst to the users. One example of this is the rainbow transmission hologram, which takes advantage of reflective and illumination materials to project a small holographic image. This technique is commonly used to ensure credit card or banknote security authentication.
However, the most familiar hologram depiction is that of a Denisyuk hologram, which uses white light to illuminate the visualization of the 3D holographic objects that can be projected onto a surface. Generally these holograms depict stationary objects, but advancing technology is continually improving the ability to project and view moving and changing scenes.
Although far from the depictions present in science fiction media, today's holograms are advancing at a rapid pace. Useful in everyday security applications, holograms will continue to develop and assist in the creation of science fiction's most creative holographic developments. Several types of holograms can be made. The very first holograms were transmission holograms, which were viewed by shining laser light through them. A later refinement, the rainbow transmission hologram, allowed viewing by white light and is commonly seen today on credit cards as a security feature and on product packaging. These versions of the rainbow transmission holograms are formed as surface relief patterns in a plastic film, and they incorporate a reflective aluminum coating which provides the light from behind to reconstruct their imagery. Another kind of common hologram is the true white light reflection hologram which is made in such a way that the image is reconstructed naturally using light on the same side of the hologram as the viewer.
One of the most promising recent advances in the short history of holography has been the mass production of low cost, solid-state lasers typically used by the millions in DVD recorders and other applications, but sometimes also useful for holography. These cheap, compact, and solid state lasers can compete well with the large, expensive gas lasers previously required to make holograms, and are already helping to make holography much more accessible to low budget researchers, artists, and dedicated hobbyists. However, the most familiar hologram depiction is that of a Denisyuk hologram, which uses white-light to illuminate the visualization of the 3D holographic objects that can be projected onto a surface. Generally, these holograms depict stationary objects, but advancing technology is continually improving the ability to project and view moving and changing scenes.
Although far from the depictions present in science fiction media, today's holograms are advancing at a rapid pace. Useful in everyday security applications, holograms will continue to develop and assist in the creation of science fictions most creative holographic developments.
The difference between Hologram and Holograph is that a Holograph is a document that’s strictly handwritten by the author and Hologram is a Photographic recording of a light. However, the light which makes up a real scene is not only specified by its amplitude and wavelength and by its phase. In a photograph, the phase of the light from the original scene is lost, and with it the three dimensional effect. In a hologram information from both the intensity and the phase is recorded. When illuminating the hologram with the appropriate light, it diffracts part of it into exactly the same wave which emanated from the original scene, according retaining the three dimensional appearance. Although color holograms are possible, in most cases the holograms are recorded monochromatically.
HOW HOLOGRAM WORK?
Even though holograms tend to look like complex and demanding concepts, it is not difficult to create a hologram because it does not require a lot of tools. All you need is are following items:
-
Laser: The most common lasers in holography field are red lasers, mostly helium-neon (HeNe) ones. There are holography experiments that are based on diodes. These diodes are from red laser pointers, which are not usually stable and coherent. That is the thing that makes it very problematic to get a quality picture. According to the type of laser we are using we will determine whether we need a shutter or not. Shutter is a device that helps us control exposure.
-
Lenses: Holography is usually called “lens less photography”, but it actually does ask usage of lenses. There is a difference between camera’s lenses and holography lenses where camera’s lenses focus the light while holography lenses make the beam split apart.
-
Beam splitter: Device that is capable of using mirrors and prisms in order to separate one beam of light into couple of them.
-
Mirrors: These are used in order to direct the light beams into right locations and directions. Mirrors must be extremely clean together with beam splitter as well as lenses.
-
Holographic film: It has the ability of recording light at extremely high resolution. High resolution is crucial for creation of a hologram. The holographic film is consisted of light-sensitive compounds that are placed on transparent surface same as photographic film. Despite their similar construction photographic and holographic film do have some differences. One of them is that holographic film must have a capability of recognizing very minute changes in light which appears in microscopic distances. In brief, it has to have almost perfectly fine grain. There are some cases where some holograms which are using red laser depend on emulsions that react the most strongly to red light.
There can be found huge variety of ways that can be used for arranging those mentioned tools, but we will use a basic transmission hologram for our setup at this moment.

On the previous image we can clearly see how a hologram is created. We will describe it in following steps:
-
The laser is pointed directly at the beam splitter, that separates the beam of light into two beams.
-
Mirrors are supposed to direct these two beams in order for those beams to hit their wanted target.
-
Each and every beam passes directly through out a diverging lens and then becomes wide range of light instead of narrow beam.
-
Each beam has it own task. Object beam is the one that reflects off of the object directly on the photographic emulsion.
-
The second beam is called reference beam. Its task is to hit the emulsion but with reflecting just off of the mirror and nothing else.
VIRTUAL REALITY & HOLOGRAMS
First of all, in order to start with a good foot on this topic, the best thing to do is stating what a virtual reality is. According to Oxford Languages virtual reality is “the computer-generated simulation of a three-dimensional image or environment that can be interacted with in a seemingly real or physical way by a person using special electronic equipment, such as a helmet with a screen inside or gloves fitted with sensors.”
Now that we know what virtual reality is let’s take the next step: the connection between virtual reality and holograms. Nowadays, we all know about this new apparatus called oculus rift. However, one of the latest researches from Facebook on this apparatus it is giving a whole other dimension on virtual reality; the addition of how holograms work.

Getting deeper in this research, researchers Andrew Maimone and Juren Wang started working on a project called holographic optics for thin and light weight virtual reality. Howbeit, what are the connections between holograms and virtual reality? Well, this project merges the potential of holographic optics and polarization-based optical folding; In other words, technological breakthrough that might be useful on state-of-the-art sunglasses-like hardware.
In addition to this, according to the explanation of researchers Andrew Maimone and Juren Wang, “To illustrate the difference, the figure below shows the gamut of human-visible colors. A common set of colors reproducible on many displays today is the sRGB color space (illustrated by the smaller triangle). Note that it can capture only a small fraction of the colors that we can actually see. In contrast, the outer triangle represents the much larger set of colors that can be reproduced using the lasers on one of our research prototype displays. This allows the reproduction of vivid and saturated colors. Think of a brightly lit neon sign or the iridescent sheen of a butterfly wing.”

WHY ARE HOLOGRAM USEFUL NOWADAYS?
After acquiring different knowledge on what holograms are, where and when we discovered and/or find out about them, and how holograms work and its possible connection with virtual reality, we all think as a team that the best idea to clarify is:
So, why are holograms useful for us?
First of all, according to an article written by Ms. Garcia on the OpenMind BBVA article website (https://www.bbvaopenmind.com/en/technology/digital-world/holography-more-useful-in-real-life-than-in-science-fiction/) :
“Holography is a very effective instrument for carrying out very high precision measurements. When an object is illuminated, the pattern of light beams that appears after passing it, and which can be picked up on a photographic plate, is unique, like a fingerprint. To see if there has been any kind of change in an object, it is possible to capture that pattern (called the wavefront) at different times and compare them. This makes it possible to determine with great accuracy, if any deformations have occurred on any object, even if the changes are as small as the wavelength of the light used.”
In addition to this, it should be remarked that holograms are tough to falsify as it is almost impossible to get the same exact wavefront from something. Therefore, nowadays different banknotes around the world that are using this technology in order to prevent external people to falsify money and commit bank corruption.

From another point, holograms are useful for us nowadays at museums but, how can we prove this?
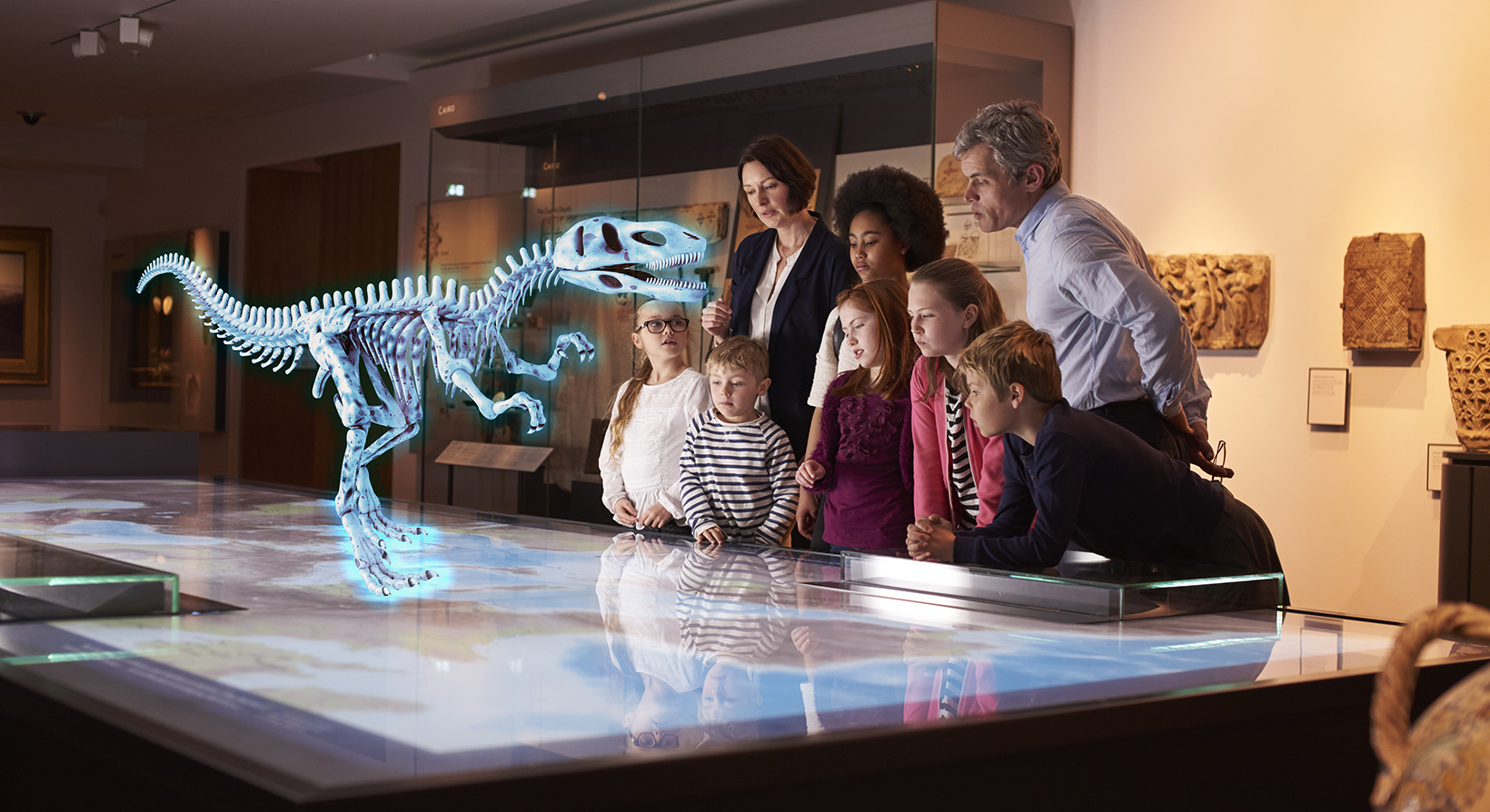

Well, it is not that complicated to get. Since ancient times, people have been stealing valuable artistic drawings and original sculptures from famous artists of all different eras. Due to these problems, one of the state-of-the-art researches will be the upcoming solution: holograms!
Why? Well let’s put the next current example, it is the case of the Lindow Man; a 2300-year-old mummy, that is well preserved in a chamber of the British Museum of London, the use of this case is that is hologram because in order to research from it and keep studying it without damaging and, without any doubt, to keep it away from robbery or disrepair.

FUTURE WORK
After discussing and explaining all we know nowadays about holograms, what could be the future of this? Will it be valuable over time and beneficial?
Probably, on our opinion as a team, we think that the future of holograms will be established on banknotes, valuable artistic drawings and original sculptures from famous artists of all different eras, and VR and AR videogames. Like we have been saying this far, holograms are the state-of-the-art technological breakthrough nowadays and it really has a bright future ahead that will help us in our daily lives and will be involved in society.
Lastly but not least, regarding our course, holograms will really be useful on this field when talking about information storage:
Just saying, imagine creating an optical hologram of a page with information and then someone smash it and destroy it, thanks to this hologram you can reconstruct this page without any problem at all, making holographic data and information pretty reliable for tomorrow unlike SD, CD, DVD, and other types of data gathered.

REFERENCES
-
Ask Difference published March 26, 2018, from https://www.askdifference.com/holograph-vs-hologram.
-
García, Bibiana. “Holography: More Useful in Real Life than in Science Fiction.” OpenMind, 16 Apr. 2018, www.bbvaopenmind.com/en/technology/digital-world/holography-more-useful-in-real-life-than-in-science-fiction/.
-
Niurka Guerra, M. (2017). La holografía. Retrieved November 18, 2020, from https://www.monografias.com/trabajos98/holografia/holografia.shtml
-
Research, B. (2020, June 29). Holographic optics for thin and lightweight virtual reality. Retrieved November 20, 2020, from https://research.fb.com/blog/2020/06/holographic-optics-for-thin-and-lightweight-virtual-reality/
-
Wilson, T. (2020, June 30). How Holograms Work. Retrieved November 20, 2020, from https://science.howstuffworks.com/hologram.htm
-
https://github.com/mam8684/Miguel-Mielgo-Assignment-1-INTRO-TO-CIS---CS1101200/tree/master/Readme