IMPALA SQL_SUBQUERY - loukenny/atme GitHub Wiki
SUBQUERY
- nested query, useful for intermediary transformations
- subquery is processed before the main query
- mail/subquery 에 적절하게 필터가 사용되었는지 확인 필요
- 어느 위치에서나 사용 가능 -
SELECT,FROM,WHERE,GROUP BY,IN - 여러 개 사용 가능 -
SELECT,FROM,WHERESELECT 절- need to return a single value
- mathematical calculations
- 하나의 열로서도 사용가능
FROM 절더 복잡한 결과 반환을 원할 때, 여러개 가능(alias, join)- restructure & transform
- aggregates of aggregates
WHERE 절오직 1개의 열만 반환할 수 있음
- return info - scalar quantities, list, table
Uncorrelated subquery
- s-q does not contain a reference to the outer query
- s-q can run independently of the outer query
- commonly found w
WHERE,FROM - s-q executes only once and returns the results to the outer query
Correlated subquery
- s-q contains a reference to the outer query
- s-q cannot run independently of the outer query
- commonly found w
WHERE,SELECT - s-q executes only once and returns the results to the outer query
- 메인쿼리의 값을 서브쿼리가 사용하고, 서브쿼리의 값을 받아서 메인쿼리가 계산하는 구조의 쿼리, 쿼리 처리 시간이 걸리기 때문에
INNER JOIN사용 고려 - re-run for every row generated in the final data set
- used for advanced joining, filtering and evaluating data
| Simple | Correlated |
|---|---|
| extracting, structuring, filtering | can't be extracted on its own |
| run _independently_from the main q | dependent on the main q to excute |
| evaluated once in the whole q | evaluated in loops, signif slows down q runtime |
①
②
① = ②, WHERE 절 서브쿼리만 차이
Nested subquery
- can be correlated or uncorrelated or combination of the a two
- can reference info from the outer subquery or main query
Set Operator
| UNION | UNION ALL | INTERSECT | MINUS |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | O | X | X |
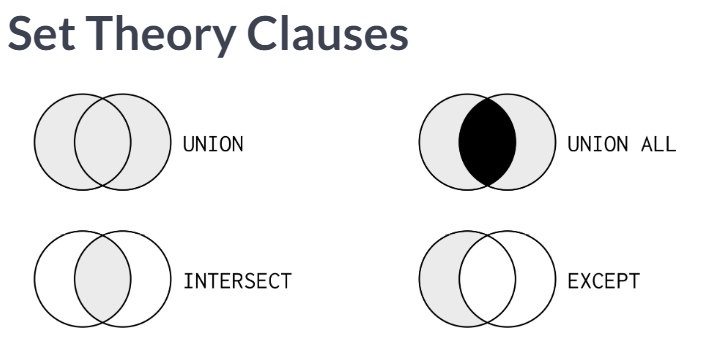
→ LEFT JOIN, NOT EXISTS as a MINUS
Subquery as a Column
① = ②
①
SELECT countries.name AS country, COUNT(*) AS cities_num
FROM cities
INNER JOIN countries
ON countries.code = cities.country_code
GROUP BY country
ORDER BY cities_num DESC, country
LIMIT 9;
② SELECT절에 서브쿼리를 바로 열로 사용할 수 있음
SELECT countries.name AS country,
(SELECT count(*)
FROM cities
WHERE countries.code = cities.country_code) AS cities_num
FROM countries
ORDER BY cities_num desc, country
LIMIT 9;
Common Table Expressions (CTEs)
- excuted once, improves query performance
- CTE is then stored in memory
- referencing other CTEs
- referencing itself
SELF JOIN① = ②
①
② CTE 사용한 경우
- 2개 이상 CTE 활용할 경우
Presence & Absence
ways to determine whether data in one table is present, or absent, in a related table IN, EXISTS는 동일한 결과를 보여줌에도 불구하고 EXISTS가 더 좋은 성능, 단순히 특정 칼럼의 값을 이용할 때에는 IN을 이용, 서브쿼리를 이용할 때는 EXISTS 사용해야 성능이 더 좋음
IN & EXISTS
IN()- () ← 특정 값 or 서브쿼리
- collects all the results from a s-q before passing to the outer query
- One major issue with using NOT IN is the way it handles NULL values
- if the columns in the s-q, being evaluated for a non-match, contain NULL values, no results are returned
SELECT WorldBankRegion,
CountryName,
Capital
FROM Nations
WHERE Capital NOT IN (SELECT NearestPop
FROM Earthquakes
WHERE NearestPop IS NOT NULL)
EXISTS()- () ← only 서브쿼리
- will stop searching the s-q when the condition is TRUE
SELECT TeamName,
TeamCode,
City
FROM Teams AS t
WHERE EXISTS
(SELECT 1 ----- 존재 하면 1을 뽑아라
FROM Earthquakes AS e
WHERE t.City = e.NearestPop);
INTERSECT & EXCEPT
INTERSECT- checks for presence
EXCEPT- checks for absence
- advantage) great for data interrogation
remove duplicates from the returned - disadvantage) the number and order of columns in the SELECT statement must be the same btwn queries
EXISTS & NOT EXISTS
both of these operators use a s-q in the WHERE filter condition
EXISTS- checks for presence
NOT EXISTS- checks for absence
- advantage) advantage over INTERSECT and EXCEPT
s-q will stop searching as soon as it evaluates to TRUE
results can contain any column from the outer query, and in any order - disadvantage) results can only contain columns from the outer query
→ restricting results to columns from the outer query only is also a disadvantage, compared to a JOIN
IN & NOT IN
IN- checks for presence
NOT IN- checks for absence
- advantage) advantage over INTERSECT and EXCEPT
results can contain any column from the outer query, and in any order - disadvantage) results can only contain columns from the outer query
→ restricting results to columns from the outer query only is also a disadvantage, compared to a JOIN
NO RESULTS RETURNED because of the way NOT IN handles NULLS in the s-q
JOIN & exclusive LOJ
INNER JOIN- checks for presence
exclusive LEFT OUTER JOIN- checks for absence
- advantage) results can contain any column, from all joined queries, in any order
→ compred to EXISTS NOT EXISTS IN NOT IN, the results are restricted to columns from the outer query only - disadvantage) exclusive LOJ requires to add the IS NULL as a WHERE filter condition