Module - lms-org/lms GitHub Wiki
Modules get initialized by the framework, get executed during cycle time and have access to data channels and configs.
In config repos they are contained in external/modules. Each module should be in it's own git repository.
The folder structure is standardized as followed:
- src - folder containing *.cpp files
- my_module.cpp - Module implementation
- interface.cpp - Interface for the framework
- include - folder containing *.h files
- my_module.h - Module declaration
- configs - folder containing default *.lconf and *.xml files
- CMakeLists.txt - Compile commands for CMake
- README.md - Module description and information in Markdown syntax
CMakeLists.txt
Example:
set(SOURCES
src/interface.cpp
src/my_module.cpp
)
set(HEADERS
include/my_module.h
)
include_directories(include)
add_library(my_module MODULE ${SOURCES} ${HEADERS})
target_link_libraries(my_module PRIVATE lmscore imaging)
The module should be linked with all libraries it's depending on and lms.
my_module.h
#ifndef MY_MODULE_H
#define MY_MODULE_H
#include <lms/module.h>
/**
* @brief LMS module
**/
class MyModule : public lms::Module {
public:
bool initialize() override;
bool deinitialize() override;
bool cycle() override;
};
#endif // MY_MODULE_H
my_module.cpp
#include "my_module.h"
bool MyModule::initialize() {
// open file descriptors, allocate dynamic memory
// open data channels
return true;
}
bool MyModule::deinitialize() {
// close file descriptors and delete dynamic memory
return true;
}
bool MyModule::cycle() {
// do computations
return true;
}
interface.cpp
The interface.cpp is included in every module's source folder and is the interface between the core framework and a module.
Example code:
#include <your_module.h>
#include <lms/module.h>
// Assuming your module class is named YourClass
LMS_MODULE_INTERFACE(YourModule)
The getInstance function will be called by lms::Loader during framework startup.
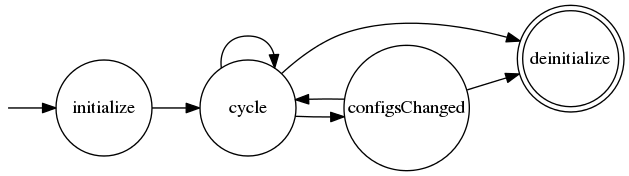
Life cycle
- bool initialize()
- Called before the first cycle() call
- Get read or write access to data channels
- Return false if initialization failed
- bool cycle()
- run-method of the module
- read from data channels, do computations and write into data channels
- read configs
- bool deinitialize()
- Called before the module is removed from the execution-loop or before the framework exits.
- void configsChanged()
- Called after changes to any config file has been detected
Nesting modules (TODO)
There can be one or more modules inside the ModuleContainer-folder. For example you can have:
- sockets (ModuleContainer)
- socketclient (Module)
- socketserver (Module) or
- scheduler (ModuleContainer = Module)
Structure: One module:
- modules
- MODULE1
- CMakeLists.txt
- MODULE1
Two modules in one module container
- modules
- MODULE_CONTAINER
- CMakeLists.txt
- MODULE1
- CMakeLists.txt
- MODULE2
- CMakeLists.txt