DS in Python - liuzhen153/play-algorithm-python GitHub Wiki
列表 List
List用[ ]表示,是Python中使用最频繁且最通用的复合数据类型。
列表中的正反索引:
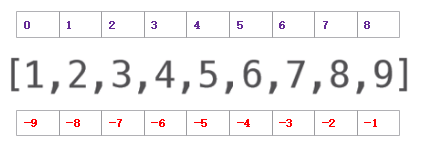
特点
- 列表中每个元素都可变(修改、删除)
- 列表是有序的,可以用索引去访问指定元素
- 列表中的元素可以是
Python中的任何对象,可以是字符串、整数、元组、也可以是list等 - 列表中值的切割可以用到变量
[头下标:尾下标],从左到右索引默认 0 开始,从右到左索引默认 -1 开始,下标可以为空表示取到头或尾 - 加号 + 是列表连接运算符,星号 * 是重复操作
基础操作
list = ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
author_list = ['Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar']
# 正数操作,截取不包含冒号右侧
print('完整列表 list:' , list)
print('第二个元素 list[1]:' , list[1])
print('第二个到第四个元素 list[1:4]:' , list[1:4])
print('第三个到最后一个元素 list[2:]:' , list[2:])
# 倒数操作,截取不包含冒号右侧
print('倒数第二个元素 list[-2]:' , list[-2])
print('倒数最后三个元素 list[-3:]:' , list[-3:])
print('倒数第二个到第四个元素 list[-4:-1]:' , list[-4:-1])
# * + 操作
print('输出列表两次 author_list * 2:' , author_list * 2)
print('两个列表组合 list + author_list:' , list + author_list)
# 元素是否存在于列表中
print('python是否在列表中:', 'python' in list)
# 迭代
print('迭代输出author_list每一项:')
for item in author_list:
print(item)
输出结果
完整列表 list: ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
第二个元素 list[1]: algorithm
第二个到第四个元素 list[1:4]: ['algorithm', 'python', 2019]
第三个到最后一个元素 list[2:]: ['python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
倒数第二个元素 list[-2]: 5.11
倒数最后三个元素 list[-3:]: [2019, 5.11, 'python']
倒数第二个到第四个元素 list[-4:-1]: ['python', 2019, 5.11]
输出列表两次 author_list * 2: ['Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar', 'Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar']
两个列表组合 list + author_list: ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python', 'Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar']
python是否在列表中: True
迭代输出author_list每一项:
Tommy
ChaoChao
Wsqstar
基础函数
list = ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
int_list = [12, 22, 30, 13, 24, 1, 10, 10.3, -1]
print('列表长度 len(list):', len(list))
# max() 和 min() 函数只支持列表元素为int和float这种可以计算数值大小的类型
print('最大值 max(int_list):', max(int_list))
print('最小值 min(int_list):', min(int_list))
# 将一个对象快速转为List
print("Str对象转为List list('Tommy'):", list('Tommy'))
输出结果
列表长度 len(list): 6
最大值 max(int_list): 30
最小值 min(int_list): -1
Str对象转为List list('Tommy'): ['T', 'o', 'm', 'm', 'y']
基础方法
list = ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
author_list = ['Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar']
list.append(author_list)
print('在末尾添加新对象 list.append(author_list):', list)
list.remove(author_list)
print("移除某个元素第一个匹配项 list.remove(author_list):", list)
list.insert(5, 'Baidu')
print("在指定位置添加新对象 list.insert(5, 'Baidu'):", list)
list.extend(author_list)
print('批量添加另一个列表中的值到末尾 list.extend(author_list):', list)
print("统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 list.count('python'):", list.count('python'))
print("找出某个元素第一次出现的索引位置 list.index('python'):", list.index('python'))
list.pop()
print("移除一个元素,默认最后一个元素 list.pop():", list)
list.pop(0)
# list.pop([index = -1])方法同del,以下例子也可以用del语句:del list[0]
print("移除第一个元素 list.pop(0):", list)
list.reverse()
print("将列表元素反向 list.reverse():", list)
print('列表排序,建议查看菜鸟教程获得更好的讲述:' , 'https://www.runoob.com/python/att-list-sort.html')
list2 = list.copy()
print("列表复制,我是list复制来的list2 list.copy():", list2)
list2.clear()
print('list2清空后 list2.clear():', list2)
# 复制和使用 = 赋值不同,复制产生了新的列表,对list2的任何操作不影响list
print('list2清空后的list:', list)
# 使用 = 赋值时,所有的操作都会影响到list本身
list3 = list
print('我是赋值来的list3:', list3)
list3.clear()
print('list3清空后 list3.clear():', list3)
print('list3清空后的list:', list)
输出结果
在末尾添加新对象 list.append(author_list): ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python', ['Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar']]
移除某个元素第一个匹配项 list.remove(author_list): ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
在指定位置添加新对象 list.insert(5, 'Baidu'): ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'Baidu', 'python']
批量添加另一个列表中的值到末尾 list.extend(author_list): ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'Baidu', 'python', 'Tommy', 'ChaoChao', 'Wsqstar']
统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 list.count('python'): 2
找出某个元素第一次出现的索引位置 list.index('python'): 2
移除一个元素,默认最后一个元素 list.pop(): ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'Baidu', 'python', 'Tommy', 'ChaoChao']
移除第一个元素 list.pop(0): ['algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'Baidu', 'python', 'Tommy', 'ChaoChao']
将列表元素反向 list.reverse(): ['ChaoChao', 'Tommy', 'python', 'Baidu', 5.11, 2019, 'python', 'algorithm']
列表排序,建议查看菜鸟教程获得更好的讲述: https://www.runoob.com/python/att-list-sort.html
列表复制,我是list复制来的list2 list.copy(): ['ChaoChao', 'Tommy', 'python', 'Baidu', 5.11, 2019, 'python', 'algorithm']
list2清空后 list2.clear(): []
list2清空后的list: ['ChaoChao', 'Tommy', 'python', 'Baidu', 5.11, 2019, 'python', 'algorithm']
我是赋值来的list3: ['ChaoChao', 'Tommy', 'python', 'Baidu', 5.11, 2019, 'python', 'algorithm']
list3清空后 list3.clear(): []
list3清空后的list: []
元组 Tuple
Tuple用( )表示,可以理解为一个固定列表,一旦初始化就不能再修改,只能对元素进行查询。
特点
- 元素只读,不支持对元素进行添加、修改(删除)
- 代码更安全
- 内置大多数方法和
List差不多
基础操作
tuple1 = ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python')
# 空元组
empty_tup = ()
# 只有一个元素的元组,需要最后添加逗号,如果不加逗号,两边的括弧会被认为是数学公式中的小括号
one_item_tup = ('Tommy',)
print('元组示例:', tuple1)
print('空元组:', empty_tup)
print('只有一个元素的元组:', one_item_tup)
# 截取、*、判断元素是否存在、迭代等操作同列表
print('截取、+、*、判断元素是否存在、迭代等操作同列表')
输出结果
元组示例: ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python')
空元组: ()
只有一个元素的元组: ('Tommy',)
截取、+、*、判断元素是否存在、迭代等操作同列表
无关闭运算符
任何以逗号分隔的无符号对象,默认为元组
m = 'play', 'algorithm', 'python', 18+6.6j, -4.24e93
x, y = 1, 2
print('m的值是:', m)
print('x, y的值是:', x, y)
输出结果
m的值是: ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', (18+6.6j), -4.24e+93)
x, y的值是: 1 2
基础函数
print('len(tuple) min(tuple) max(tuple)和列表用法相同')
print("Str对象转为Tuple tuple('Tommy'):", tuple('Tommy'))
输出结果
len(tuple) min(tuple) max(tuple)和列表用法相同
Str对象转为Tuple tuple('Tommy'): ('T', 'o', 'm', 'm', 'y')
震惊,元组居然能改变?
先来看一个例子:
tuple = ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', ['Tommy','ChaoChao'])
print('原始tuple为:', tuple)
# 修改Tommy为liuzhen153,ChaoChao为chaochaoZ
tuple[3][0] = 'liuzhen153'
tuple[3][1] = 'chaochaoZ'
print(tuple)
print('修改了某些内容的tuple为:', tuple)
# 在['liuzhen153', 'chaochaoZ']里新增wsqStar
tuple[3].append('wsqStar')
print('添加了某些内容的tuple为:', tuple)
输出结果
原始tuple为: ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', ['Tommy', 'ChaoChao'])
('play', 'algorithm', 'python', ['liuzhen153', 'chaochaoZ'])
修改了某些内容的tuple为: ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', ['liuzhen153', 'chaochaoZ'])
添加了某些内容的tuple为: ('play', 'algorithm', 'python', ['liuzhen153', 'chaochaoZ', 'wsqStar'])
分析
这里看似元组中的元素改变了,其实可以看出,元组中的第四个元素是一个列表,我们改变的是列表中的值,元组所指的这个元素是『列表』并没有改变。
这个涉及到Python中的可变对象和不可变对象,List是可变对象,Tuple便是不可变对象。
字典 Dict
Dict用{ }表示,是可变的,且可存储任意类型对象,其概念基于生活中的字典原型,使用『名称-内容』对数据进行构建。
特点
- 字典中的数据必须以键值对(key-value)形式出现
- 键不可重复(键重复时,只会记住该键对应的最后一个值);值可重复
- 键(key)是不可变对象,不能进行修改;值(value)是可以修改的,可以是任意对象
基础操作
Dict根据key来计算value的存储位置。如果key可变,每次计算相同key得出的结果不同,那Dict内部就乱套了。
# 键必须不可变,所以可以用数字,字符串或元组充当,所以用列表就不行
dict1 = {'name':'Tommy', 'age':25, 'sex':'male', 'extra':'unmarried'}
dict2 = {38.5:'Today is hot', ('x','y'):(1,2)}
print('dict1:', dict1)
print('dict2:', dict2)
# 访问某个元素
print("dict1里的name dict1['name']:", dict1['name'])
print("dict2里的('x','y') dict2[('x','y')]:", dict2[('x','y')])
# 修改某个元素
dict1['age'] = 26
print("修改dict1里的age为26 dict1['age'] = 26:", dict1)
# 删除某个元素
del(dict1['extra'])
print("删除dict1里的extra del(dict1['extra']):", dict1)
# 同一个键出现多次,只会记住最后一次
dict3 = {'name':'Tommy', 'age':25, 'name':'liuzhen153', 'name':'Liuzhen'}
print('dict3:', dict3)
# 键是否在dict中存在
print("键name是否在dict1中存在'name' in dict1 :" , 'name' in dict1)
# 迭代
print('迭代输出dict1每一项:')
for key in dict1:
print(key, dict1[key])
输出结果
dict1: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 25, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried'}
dict2: {38.5: 'Today is hot', ('x', 'y'): (1, 2)}
dict1里的name dict1['name']: Tommy
dict2里的('x','y') dict2[('x','y')]: (1, 2)
修改dict1里的age为26 dict1['age'] = 26: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 26, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried'}
删除dict1里的extra del(dict1['extra']): {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 26, 'sex': 'male'}
dict3: {'name': 'Liuzhen', 'age': 25}
键name是否在dict1中存在'name' in dict1 : True
迭代输出dict1每一项:
name Tommy
age 26
sex male
基础函数
dict = {'name':'Tommy', 'age':25, 'sex':'male', 'extra':'unmarried'}
print("计算dict长度,即键的总数 len(dict):", len(dict))
输出结果
计算dict长度,即键的总数 len(dict): 4
基础方法
dict = {'name':'Tommy', 'age':25, 'sex':'male', 'extra':'unmarried'}
dict1 = {'age':27, 'company':'Baidu'}
print("返回所有键 dict.keys():", dict.keys())
print("判断dict中是否存在某个键 dict.__contains__('tall'):", dict.__contains__('tall'))
print("返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值 dict.get(key, default=None):", dict.get('lover','Chaochao'))
print("dict.get()不会修改dict:", dict)
print("返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值并新增该键值对 dict.setdefault(key, default=None):", dict.setdefault('lover','Chaochao'))
print("dict.setdefault()会修改dict:", dict)
print('dict.items()返回可供遍历的键值对:')
for k,v in dict.items():
print(k, v)
dict.update(dict1)
print('dict.update(dict1)会将dict1中的键/值更新到dict里,相同键会更新值,不存在的会新增:', dict)
print('返回字典中所有的值 dcit.values():', dict.values())
p = dict.pop('tall', 'not exits this key')
print("dict.pop(key[,default]) 删除key 所对应的值,返回值为被删除的值。key值不给出时返回default值 dict.pop('tall', 'not exits this key'):", p)
print('现在的dict:', dict)
p = dict.popitem()
print("随机删除并返回被删除的一组键值对,如果字典已为空,会出现异常dict.popitem():", p)
print('随机删除键值对后的dict:', dict)
dict_copy = dict.copy()
print('我是dict复制来的dict_copy:', dict_copy)
dict_copy.clear()
print('dict_copy清空后 dict_copy.clear():', dict_copy)
# 复制和使用 = 赋值不同,复制产生了新的字典,对dict_copy的任何操作不影响dict
print('dict_copy清空后的dict:', dict)
# 使用 = 赋值时,所有的操作都会影响到dict本身
dict3 = dict
print('我是赋值来的dict3:', dict3)
dict3.clear()
print('dict3清空后 dict3.clear():', dict3)
print('dict3清空后的dict:', dict)
输出结果
返回所有键 dict.keys(): dict_keys(['name', 'age', 'sex', 'extra'])
判断dict中是否存在某个键 dict.__contains__('tall'): False
返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值 dict.get(key, default=None): Chaochao
dict.get()不会修改dict: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 25, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried'}
返回指定键的值,如果值不在字典中返回default值并新增该键值对 dict.setdefault(key, default=None): Chaochao
dict.setdefault()会修改dict: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 25, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao'}
dict.items()返回可供遍历的键值对:
name Tommy
age 25
sex male
extra unmarried
lover Chaochao
dict.update(dict1)会将dict1中的键/值更新到dict里,相同键会更新值,不存在的会新增: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 27, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao', 'company': 'Baidu'}
返回字典中所有的值 dcit.values(): dict_values(['Tommy', 27, 'male', 'unmarried', 'Chaochao', 'Baidu'])
dict.pop(key[,default]) 删除key 所对应的值,返回值为被删除的值。key值不给出时返回default值 dict.pop('tall', 'not exits this key'): not exits this key
现在的dict: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 27, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao', 'company': 'Baidu'}
随机删除并返回被删除的一组键值对,如果字典已为空,会出现异常dict.popitem(): ('company', 'Baidu')
随机删除键值对后的dict: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 27, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao'}
我是dict复制来的dict_copy: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 27, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao'}
dict_copy清空后 dict_copy.clear(): {}
dict_copy清空后的dict: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 27, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao'}
我是赋值来的dict3: {'name': 'Tommy', 'age': 27, 'sex': 'male', 'extra': 'unmarried', 'lover': 'Chaochao'}
dict3清空后 dict3.clear(): {}
dict3清空后的dict: {}
集合 Set
Set和字典一样用{ }表示,不同的是其元素不是键值对,而是一个无序的不重复元素序列。
集合更接近数学上集合的概念,可以通过集合判断数据的从属关系,也可以通过集合把数据结构中重复的元素减掉。集合可做集合运算,可添加和删除元素。
特点
- 元素无序且不重复
- 可做集合运算
基础操作
print('创建一个空集合必须用set()函数,因为如果直接用{}是用来创建一个空字典的:set():', set())
print('将一个字符串转为集合set(Str):', set('Tommy'))
list = ['play', 'algorithm', 'python', 2019, 5.11, 'python']
# 集合中元素无序且不重复,python将只会留下一个
set1 = set(list)
print('将一个列表转为集合 set(list):', set1)
# 判断元素是否在集合内
print("python是否在集合内 'python' in set1:", 'python' in set1)
# 迭代
print('迭代set :')
for item in set1:
print(item)
# 集合运算
set2 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set3 = {1, 2, 7, 8}
print('减法,set2中包含但set3中不包含的元素 set2 - set3:', set2 - set3)
print('按位或运算,set2和set3中包含的所有元素 set2 | set3:', set2 | set3)
print('按位与运算,set2和set3中都包含的元素 set2 & set3:', set2 & set3)
print('按位异或运算,set2和set3中不同时包含的元素 set2 ^ set3:', set2 ^ set3)
输出结果
创建一个空集合必须用set()函数,因为如果直接用{}是用来创建一个空字典的:set(): set()
将一个字符串转为集合: {'y', 'o', 'T', 'm'}
将一个列表转为集合: {'algorithm', 2019, 5.11, 'python', 'play'}
python是否在集合内 'python' in set1: True
迭代set :
algorithm
2019
5.11
python
play
减法,set2中包含但set3中不包含的元素 set2 - set3: {3, 4, 5, 6}
按位或运算,set2和set3中包含的所有元素 set2 | set3: {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
按位与运算,set2和set3中都包含的元素 set2 & set3: {1, 2}
按位异或运算,set2和set3中不同时包含的元素 set2 ^ set3: {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
基础函数
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
print('set的长度 len(set):', len(set1))
输出结果
set的长度 len(set): 6
基础方法
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
set1.add(0)
print('添加元素 set1.add(0)', set1)
# 计算差集,效果同 -
print('返回两个集合的差集 set1.difference(set2)', set1.difference(set2))
print('返回两个集合的差集 set2.difference(set1)', set2.difference(set1))
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
# 移除两个集合中都存在的元素
set1.difference_update(set2)
print('移除set1中set1和set2都存在的元素 set1.difference_update(set2)', set1)
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
set2.difference_update(set1)
print('移除set2中set1和set2都存在的元素 set2.difference_update(set1)', set2)
# 移除元素
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
# 移除指定元素
set1.discard(10)
print("移除的元素不存在时不报错 set1.discard(10):", set1)
set1.remove(6)
print("移除的元素不存在时报错 set1.remove(6):", set1)
# 随机移除元素
set1.pop()
print('随机移除元素后的set1 set1.pop():', set1)
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
set3 = {5, 6, 10}
set4 = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
print('返回多个集合的交集,set1不变 set1.intersection(set2,set3,set4):', set1.intersection(set2,set3,set4), set1)
set1.intersection_update(set2,set3,set4)
print('set1变为set1与其他集合的交集 set1.intersection_update(set2,set3,set4):', set1)
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6}
print('判断两个集合是否包含相同元素,如果包含返回False set2.isdisjoint(set1):', set2.isdisjoint(set1))
# 子集判断
print('判断set1是否是set2的子集 set1.issubset(set2):', set1.issubset(set2))
print('判断set2是否是set1的子集 set2.issubset(set1):', set2.issubset(set1))
# 父集判断
print('判断set1是否是set2的父集 set1.issuperset(set2):', set1.issuperset(set2))
print('判断set2是否是set1的父集 set2.issuperset(set1):', set2.issuperset(set1))
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 9}
print("异或运算 set1.symmetric_difference(set2):", set1.symmetric_difference(set2))
set1.symmetric_difference_update(set2)
print("异或运算后将相同部分移除,不同部分添加到set1中 set1.symmetric_difference_update(set2):", set1)
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}
set3 = {5, 6, 10}
print('计算集合的合集 set1.union(set2, set3):', set1.union(set2, set3))
set1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set2 = {5, 6, 10}
set1.update(set2)
print('将set2中的元素添加到set1中 set1.update(set2):', set1)
print('set.clear() 和 set.copy()用法同列表')
输出结果
添加元素 set1.add(0) {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
返回两个集合的差集 set1.difference(set2) {0, 1, 2, 3}
返回两个集合的差集 set2.difference(set1) {8, 9, 7}
移除set1中set1和set2都存在的元素 set1.difference_update(set2) {1, 2, 3}
移除set2中set1和set2都存在的元素 set2.difference_update(set1) {7, 8, 9}
移除的元素不存在时不报错 set1.discard(10): {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
移除的元素不存在时报错 set1.remove(6): {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
随机移除元素后的set1 set1.pop(): {2, 3, 4, 5}
返回多个集合的交集,set1不变 set1.intersection(set2,set3,set4): {5, 6} {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}
set1变为set1与其他集合的交集 set1.intersection_update(set2,set3,set4): {5, 6}
判断两个集合是否包含相同元素,如果包含返回False set2.isdisjoint(set1): False
判断set1是否是set2的子集 set1.issubset(set2): False
判断set2是否是set1的子集 set2.issubset(set1): True
判断set1是否是set2的父集 set1.issuperset(set2): True
判断set2是否是set1的父集 set2.issuperset(set1): False
异或运算 set1.symmetric_difference(set2): {1, 2, 3, 9}
异或运算后将相同部分移除,不同部分添加到set1中 set1.symmetric_difference_update(set2): {1, 2, 3, 9}
计算集合的合集 set1.union(set2, set3): {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
将set2中的元素添加到set1中 set1.update(set2): {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 10}
set.clear() 和 set.copy()用法同列表