Read 07 301 - jserpa-p/lisbon-ops-301n1_Reading GitHub Wiki
What is a Server
A server is a computer program or device that provides a service to another computer program and its user, also known as the client. In a data center, the physical computer that a server program runs on is also frequently referred to as a server. That machine might be a dedicated server or it might be used for other purposes.
NGINX
NGINX is open source software for web serving, reverse proxying, caching, load balancing, media streaming, and more. It started out as a web server designed for maximum performance and stability.
The goal behind NGINX was to create the fastest web server around, and maintaining that excellence is still a central goal of the project.
Network Architectures
The three-tier architecture
- Core
- Distribution
- Access
SDN (Software Defined Networking)
- Networking devices have different functional planes os operation (data, control and managment planes)
- Split the functions into seperate logical units
Spine and Leaf architecture
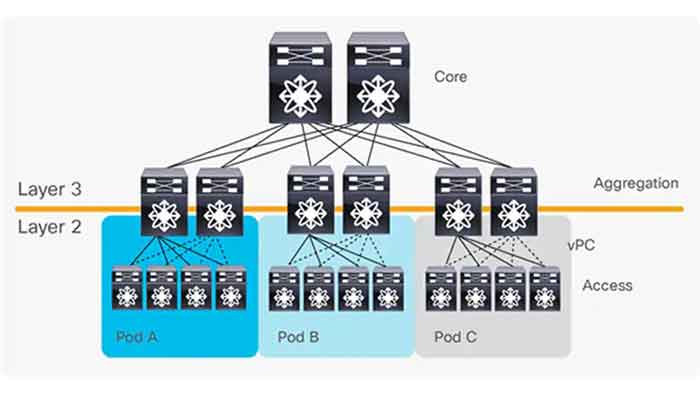
Advantages
- Simple cabling
- Reduntant
- Fast
Disadvantages
- Additional switches may be costly
Networking Devices
- Hub (OSI Layer 1)
- Bridge (OSI Layer 2)
- Switch (OSI Layer 2)
- Router (OSI Layer 3)
- Access Point (OSI Layer 2)
- Cable Modem
- DSL Modem
- Repeater
- Converting Media
Network Connectors
- LC (Local Connector)
- ST (Straight Tip)
- SC (Subscriber Connectors)
- MT-RJ (Mechanical Transfer Registered Jack)
- UPC (Ultra Polished Connector)
- APC (Angled Polished Connector)
- RJ11 (Registered Jack type 11)
- RJ45 (Registered Jack type 45)
- F-connector
Ethernet Standards
Ethernet is the most popular networking technology
10 and 100 megabit ethernet
- 10BASE-T (twisted pair)
- 100BASE-TX
- 1000BASE-T (gigabit Ethernet over Category 5 cabling)
- 10GBASE-T
- 40GBASE-T
- 100BASE-FX
- 100BASE-SX
- 1000BASE-SX
- 1000BASE-LX
- 10GBASE-SR
- 10GBASE-LR (Long Range)
WDN
Wavelength-Division Multiplexing, where we can have bidirectional communication over a single stranded fiber for multiple types of signals. This uses different wavelengths for each carrier that we happen to be sending across that fiber. You can think of this as sending different colors of a signal over the same strand of fiber.