Read 04 301 - jserpa-p/lisbon-ops-301n1_Reading GitHub Wiki
Read 04
VirtualBox Network Settings
VirtualBox network modes:
- Not Attached
- NAT
- NAT Network
- Bridged Adapter
- Internal Network
- Host-Only Adapter
- Generic Driver
Virtual Network Adapters
Each VirtualBox VM can use up to eight virtual network adapters, each of which in turn is referred to as a network interface controller (NIC). Just 4 can be configured with VirtualBox GUI but all 8 can bu configured with the VBoxManage modifyvm command. VBoxManage is a command line management tool
Types of Virtual Network Adapters in VirtualBox
A virtual network adapter is a software-emulated physical device. There are six virtual adapter types that can be virtualized by VirtualBox.
- AMD PCnet-PCI II (Am79C970A)
- AMD PCnet-FAST III (Am79C973)
- Intel PRO/1000 MT Desktop (82540EM)
- Intel PRO/1000 T Server (82543GC)
- Intel PRO/1000 MT Server (82545EM)
- Paravirtualized Network Adapter (virtio-net)
Comparison of VirtualBox Network Modes
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is a process of intercepting traffic addressed to the appropriate IP address and port in addition to redirecting that traffic to a different IP address and/or port.
- SSH access
- HTTP access
Network Topologies
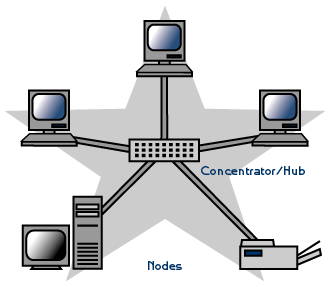
- Star
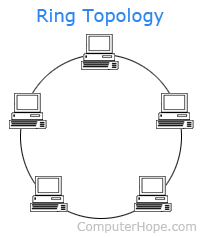
- Ring
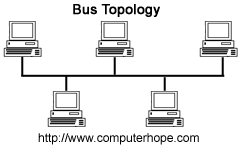
- Bus
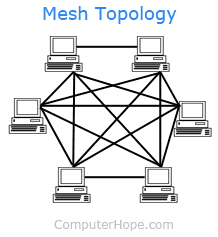
- Mesh
Routing Technologies
The hop
Whenever we talk about what the next hop might be for a particular piece of traffic, we’re referring to what router this traffic is going to. Whenever we hit that destination router or destination gateway, that is the next hop in the communication.
Configuring the next hop
Every router needs to be configured with some type of routing table, so that any inbound communication knows where to go as its next hop. A router that’s not configured properly or has an incorrect next hop will end up sending traffic down the wrong part of the network, or it may create a routing loop where traffic simply bounces back and forth until it’s discarded by the router.
Dynamic Routing
Which routing protocol to use?
1- Are you trying to determine where a route might be based on the state of that link, whether the link is up or down? 2- Is the important determination based on how far away that particular connection might be? 3- Is distance something relating to the number of hops between one point and another? 4- Is it related to the speed of the communication between those connections?
Distance-vector routing protocol
- Information passed between routers contain networks details
- Usually automatic
- Good for smaller networks
- RIP (Routing Information Protocol)
Link state routing protocol
- Information passed between routers is related to the current conectivity
- Consider the speed of the link
- Very scalable
- OSPF (Open Shortest Path First)
Hybrid routing protocol
- BGP (Border Gateway Protocol)
- A little link-state, a little distance-vector
Network Switching Overview
The switch
- Forward or drop frames
- Gather a constantly updating list of MAC addresses
- Maintain a loop-free environment
Learning the MACs
- Switches examine incoming traffic
- Adds unknown MAC addresses to the MAC address table
- The switch does not always have the MAC address on the table
- When in doubt, send the frame to everyone
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)
- Determine a MAC address based on an IP address
- arp -a
NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol)
- No broadcast
- Neighbor MAC Discovery
- SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration)
- DAD (Duplicate Address Detection)
- There's no ARP in IPv6
- NS (Neighbor Solicitation)
- NA (Neighbor Advertisement)
Power over Ethernet PoE
This allows us to connect devices such as access points, voice over IP phones, and other devices by simply plugging in an ethernet connection.