SDLC for App Development - johnverz22/appdev-lessons GitHub Wiki
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a structured process used for developing software applications. It provides a systematic way to plan, create, test, and deploy software, ensuring high quality and reliability. For beginners, here’s a detailed explanation of the SDLC phases, simplified for better understanding:
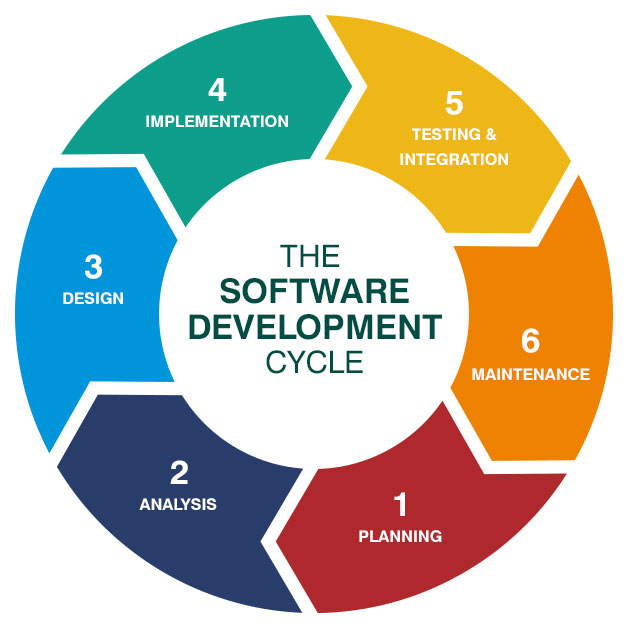
1. Planning
- Purpose: Determine the goal of the software project and its feasibility.
- Activities:
- Identify the problem or need for the software.
- Define objectives: What the software should achieve.
- Perform feasibility studies: Check if the project is economically, technically, and operationally viable.
- Plan resources, time, and cost estimates.
- Outcome: A project plan that acts as a roadmap for the entire process.
2. Requirement Analysis
- Purpose: Understand what the users need the software to do.
- Activities:
- Gather requirements through interviews, surveys, and user meetings.
- Document functional requirements (what the software should do) and non-functional requirements (e.g., performance, security).
- Create a Software Requirements Specification (SRS) document.
- Outcome: Clear, detailed requirements that guide the next steps.
3. Design
- Purpose: Develop a blueprint for the software system.
- Activities:
- Define the system architecture (how components interact).
- Choose technologies, tools, and programming languages.
- Create diagrams such as flowcharts, ERDs (Entity-Relationship Diagrams), or UML (Unified Modeling Language) diagrams.
- Design user interfaces (UI) and user experiences (UX).
- Outcome: Design documents, prototypes, or mockups.
4. Implementation (Coding)
- Purpose: Build the actual software based on the design.
- Activities:
- Write code according to design specifications.
- Divide tasks among developers if working in teams.
- Follow coding standards and use version control (e.g., Git).
- Outcome: The first version of the software, also known as the "build."
5. Testing
- Purpose: Ensure the software works correctly and meets requirements.
- Activities:
- Perform different types of testing, such as:
- Unit Testing: Testing individual components or modules.
- Integration Testing: Ensuring components work together.
- System Testing: Checking the entire system's functionality.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Getting feedback from end-users.
- Identify and fix bugs or errors.
- Perform different types of testing, such as:
- Outcome: A stable, bug-free product ready for deployment.
6. Deployment
- Purpose: Deliver the software to users.
- Activities:
- Release the software to production environments.
- Provide installation guides or set up the system for users.
- Offer training or documentation for end-users if needed.
- Monitor the system after release for any issues.
- Outcome: The software is live and available to users.
7. Maintenance
- Purpose: Keep the software updated and functional over time.
- Activities:
- Fix any new bugs or issues reported by users.
- Add new features or enhancements based on feedback.
- Ensure the software remains compatible with new technologies.
- Perform regular updates for security and performance.
- Outcome: A long-lasting and up-to-date software product.
Benefits of Using SDLC
- Clarity and Organization: Each phase has a clear objective.
- Risk Management: Early detection of issues reduces risks.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Proper planning minimizes waste.
- High Quality: Regular testing ensures reliability.
SDLC Models
Beginners should also know there are different models for implementing the SDLC. These include:
- Waterfall Model: Linear and sequential, moving step-by-step through phases.
- Agile Model: Iterative and flexible, focusing on small, incremental changes.
- Spiral Model: Combines iterative development with risk management.
- V-Model: Emphasizes verification and validation at each stage.
Tips for Beginners
- Think of SDLC as a story: You plan (idea), write (code), and edit (test) your project before publishing (deploy) it.
- Always document your work in each phase.
- Focus on teamwork, especially during planning, design, and testing.
- Learn basic tools for coding (e.g., IDEs, Git), testing (e.g., Selenium), and deployment (e.g., Docker).