Wireless_Power_(SKU_DFR0362) - jimaobian/DFRobotWiki GitHub Wiki
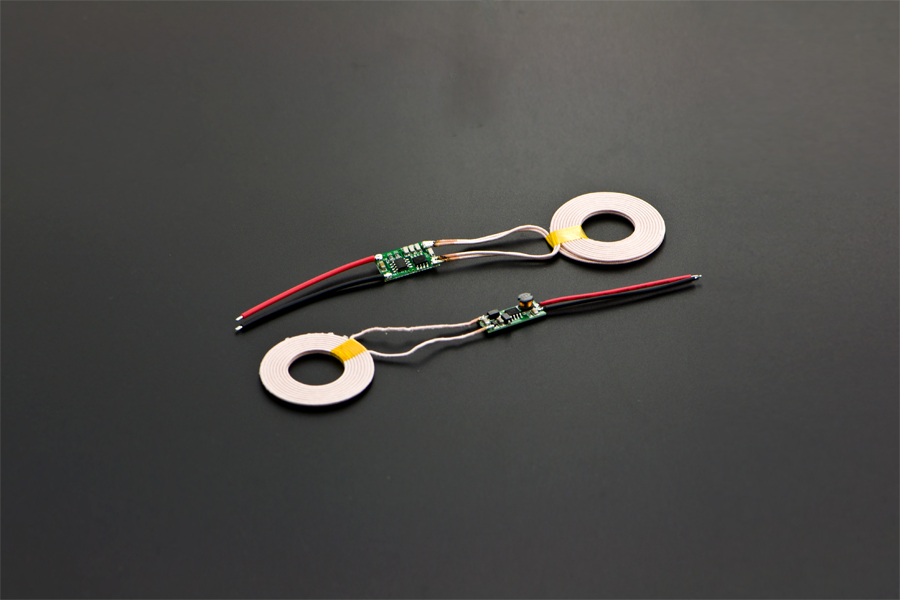
Wireless charging uses an electromagnetic field to transfer energy between two objects. This is usually done with a charging station. Energy is sent through an inductive coupling to an electrical device, which can then use that energy to charge batteries or run the device. This is a new wireless charging module, which could provides 5V@1A (MAX 1.2A) power output. It is using the new technology "resonant magnetic coupling, which will reduce the electricity consumption during power transmission. The transfer efficiency could arrive 90%. It could meet your most project requests.
- Operating Voltage (Input): 5V
- Operating Voltage (Output): 5V@1A (Max: 1.2A)
- Transmitting Terminal Size: 43mm(Outer diameter)*10mm(Inside diameter)*2.3mm(Thickness)
- Receiving Terminal Size: 43mm(Outer diameter)*10mm(Inside diameter)*2.3mm(Thickness)
- Operating Distance:2-10mm.
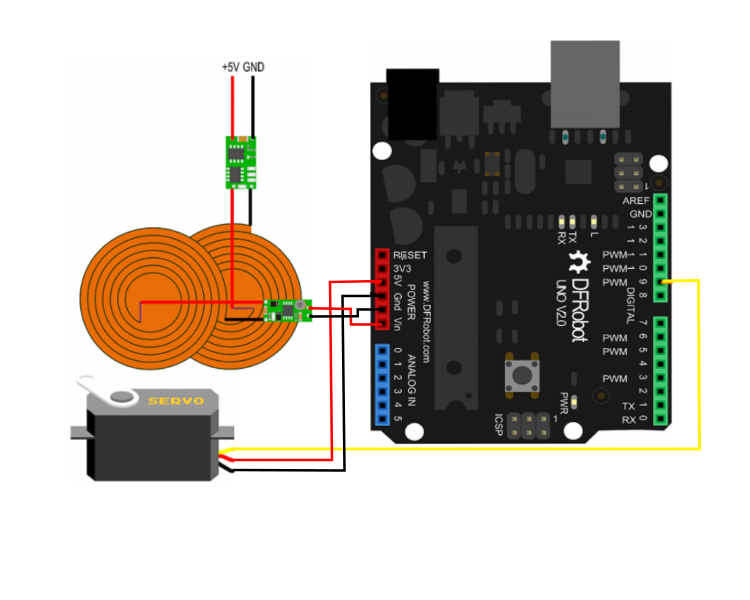
/******** start code ********/
/* Sweep
by BARRAGAN <http://barraganstudio.com>
This example code is in the public domain.
modified 8 Nov 2013
by Scott Fitzgerald
http://arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Sweep
*/
#include <Servo.h>
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
// twelve servo objects can be created on most boards
int pos = 0; // variable to store the servo position
void setup()
{
myservo.attach(9); // attaches the servo on pin 9 to the servo object
}
void loop()
{
for(pos = 0; pos <= 180; pos += 1) // goes from 0 degrees to 180 degrees
{ // in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
for(pos = 180; pos>=0; pos-=1) // goes from 180 degrees to 0 degrees
{
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
delay(15); // waits 15ms for the servo to reach the position
}
}
/******** end code ********/
 get it from wireless charging module 5v/1a or dfrobot distributor.
get it from wireless charging module 5v/1a or dfrobot distributor.