Micro_DC_Motor_with_Encoder SJ01_SKU__FIT0450 - jimaobian/DFRobotWiki GitHub Wiki
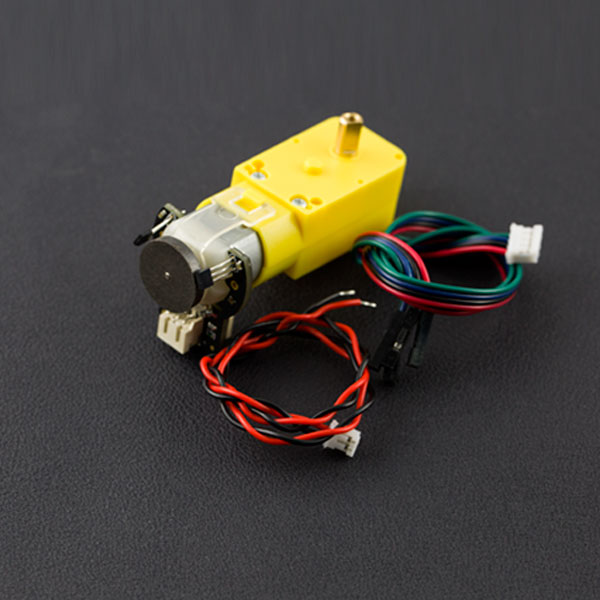

This is the DFRobot Micro DC geared motor with encoder. It is a motor with a 120:1 gearbox and an integrated quadrature encoder that provides a resolution of 16 pulse single per round giving a maximum output of 1920 within one round. With an Arduino controller and motor driver, applications for this might include a closed-loop PID control or PWM motor speed control. This motor is an ideal option for mobile robot projects. The copper output shaft, embedded thread and reinforced connector greatly extends the motor's service life.
- Gear ratio: 120:1
- No-load speed @ 6V: 160 rpm
- No-load speed @ 3V: 60 rpm
- No-load current @ 6V: 0.17A
- No-load current @ 3V: 0.14A
- Max Stall current: 2.8A
- Max Stall torque: 0.8kgf.cm
- Rated torque: 0.2kgf.cm
- Encoder operating voltage: 4.5~7.5V
- Motor operating voltage: 3~7.5V (Rated voltage 6V)
- Operating ambient temperature: -10~+60℃
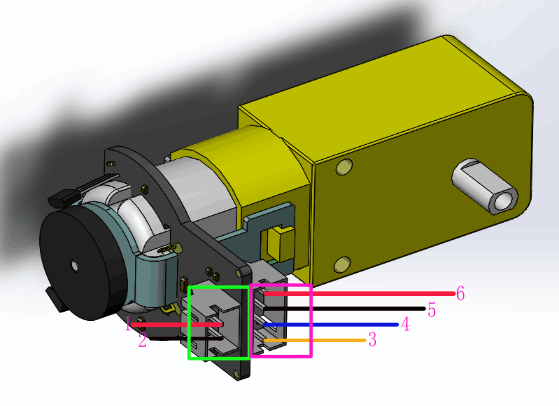 |
|-----------|--------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| **Grade** | **Name** | **Functional Description** |
| 1 | Motor power supply pin + | 3-7.5V,Rated voltage6V |
| 2 | Motor power supply pin - | |
| 3 | Encoder A phase output | Changes square wave with the output frequency of Motor speed |
| 4 | Encoder B phase output | Changes square wave with the output frequency of Motor speed(interrupt port) |
| 5 | Encoder supply GND | |
| 6 | Encoder supply + | 4.5-7.5V | |
-
hardware
- DFRduino UNO x1
- DC power supply x1
- L298 x1
-
software
- Arduino IDE Download Arduino IDE
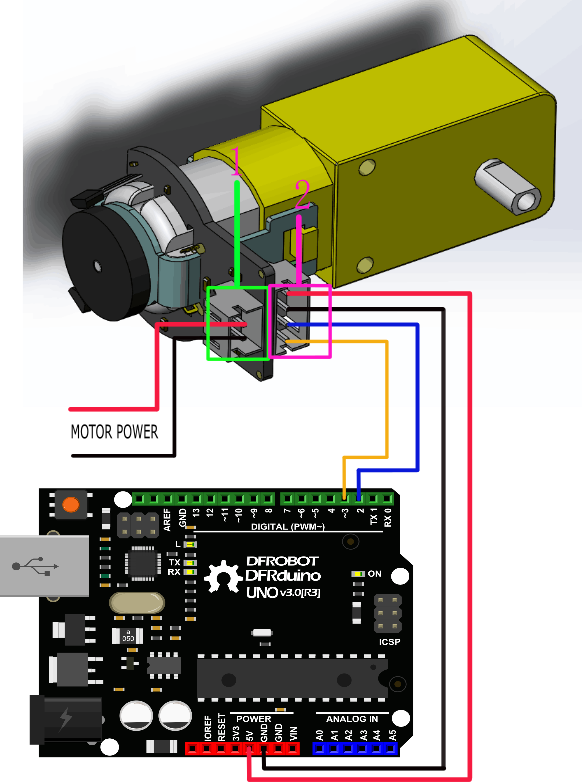
This tutorial is about Encoder usage. We are using D2&D3 as driving pins, you can select other ones, but it requires at least 1 interrupt pin. (We selected D2, Interrupt 0 in this tutorial).
Notice: attachInterrupt() 
If using an Arduino UNO and you want to use interrupt port 0 (Int.0), you need to connect digital pin D2 on the board. The following code is only used in UNO and Mega2560. If you want to use Arduino Leonardo, you should change digital pin D3 instead of digital pin D2.
See the link for details http://arduino.cc/en/Reference/AttachInterrupt
//The sample code for driving one way motor encoder
const byte encoder0pinA = 2;//A pin -> the interrupt pin 0
const byte encoder0pinB = 3;//B pin -> the digital pin 3
byte encoder0PinALast;
int duration;//the number of the pulses
boolean Direction;//the rotation direction
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(57600);//Initialize the serial port
EncoderInit();//Initialize the module
}
void loop()
{
Serial.print("Pulse:");
Serial.println(duration);
duration = 0;
delay(100);
}
void EncoderInit()
{
Direction = true;//default -> Forward
pinMode(encoder0pinB,INPUT);
attachInterrupt(0, wheelSpeed, CHANGE);
}
void wheelSpeed()
{
int Lstate = digitalRead(encoder0pinA);
if((encoder0PinALast == LOW) && Lstate==HIGH)
{
int val = digitalRead(encoder0pinB);
if(val == LOW && Direction)
{
Direction = false; //Reverse
}
else if(val == HIGH && !Direction)
{
Direction = true; //Forward
}
}
encoder0PinALast = Lstate;
if(!Direction) duration++;
else duration--;
}Code 1 phenomenon: Explanation: Serial data, when the motor forward, the output value> 0, when the motor reverse rotation, digital output <0. The faster the motor speed, the greater the absolute value of number.

PID control: PID algorithm to control the motor speed by L298P DC motor driver board
- Motor power port is connected to the L298 drive motor M1 port
- Download and install Arduino PID
//The sample code for driving one way motor encoder
#include <PID_v1.h>
const byte encoder0pinA = 2;//A pin -> the interrupt pin 0
const byte encoder0pinB = 3;//B pin -> the digital pin 3
int E_left =5; //The enabling of L298PDC motor driver board connection to the digital interface port 5
int M_left =4; //The enabling of L298PDC motor driver board connection to the digital interface port 4
byte encoder0PinALast;
double duration,abs_duration;//the number of the pulses
boolean Direction;//the rotation direction
boolean result;
double val_output;//Power supplied to the motor PWM value.
double Setpoint;
double Kp=0.6, Ki=5, Kd=0;
PID myPID(&abs_duration, &val_output, &Setpoint, Kp, Ki, Kd, DIRECT);
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);//Initialize the serial port
pinMode(M_left, OUTPUT); //L298P Control port settings DC motor driver board for the output mode
pinMode(E_left, OUTPUT);
Setpoint =80; //Set the output value of the PID
myPID.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);//PID is set to automatic mode
myPID.SetSampleTime(100);//Set PID sampling frequency is 100ms
EncoderInit();//Initialize the module
}
void loop()
{
advance();//Motor Forward
abs_duration=abs(duration);
result=myPID.Compute();//PID conversion is complete and returns 1
if(result)
{
Serial.print("Pluse: ");
Serial.println(duration);
duration = 0; //Count clear, wait for the next count
}
}
void EncoderInit()
{
Direction = true;//default -> Forward
pinMode(encoder0pinB,INPUT);
attachInterrupt(0, wheelSpeed, CHANGE);
}
void wheelSpeed()
{
int Lstate = digitalRead(encoder0pinA);
if((encoder0PinALast == LOW) && Lstate==HIGH)
{
int val = digitalRead(encoder0pinB);
if(val == LOW && Direction)
{
Direction = false; //Reverse
}
else if(val == HIGH && !Direction)
{
Direction = true; //Forward
}
}
encoder0PinALast = Lstate;
if(!Direction) duration++;
else duration--;
}
void advance()//Motor Forward
{
digitalWrite(M_left,LOW);
analogWrite(E_left,val_output);
}
void back()//Motor reverse
{
digitalWrite(M_left,HIGH);
analogWrite(E_left,val_output);
}
void Stop()//Motor stops
{
digitalWrite(E_left, LOW);
}Code 2 phenomenon: The code PID value has been set as 80, so the motor will stabilize at about 80 rpm. If outside forces such as changes in motor drive voltage, the motor's resistance, etc affect the speed, the program will adjust the PWM value to stabilize the rotational speed at 80.
 shopping from dfrobot store or dfrobot distributor.
shopping from dfrobot store or dfrobot distributor.