GPS_Module_With_Enclosure_(SKU_TEL0094) - jimaobian/DFRobotWiki GitHub Wiki

You must have used a GPS receiver. It is easy to be found in most place, such as smartphones, cars, and computers. They are used to track your loaction all over the globe. GPS Receiver for Arduino is a unit embedding GPS module and antenna in a small foot-print enclosure. By using TinyGPS library, Arduino can retrieve geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude, altitude), speed, heading and GMT time. The update rate is an important performance index of a GPS receiver. Most GPS in mobile phones provide an update rate of 1Hz, which means, only one set of data can be retrieved in one second. For GPS receivers with 1~10Hz, the data interval is much reduced and thus can be used for more demanding applications (e.g. on fast-moving vehicles). For more details ,please refer to the Documents as attached below.
- UBX-G7020-KT solution
- 1Hz(default) ~ 10Hz output
- 9600bps(default) [support:4800 ,9600 ,19200 ,38400 ,57600 ,115200 ,230400 ,460800,921600] TTL serial interface
- 5v @ 30mA (support 3.3~5v)
- 56-Channel receiver
- Extremely high sensitivity -161dBm
- Accuracy 2.5m (Autonomous) / <2m[SBAS]
- Operating temperature: -40°C to 85°C
- Hot Start : 1s
- Warm Start : 28s
- Cold Start : 29s
- Module Size 28*28*8.6mm
- Enclosure Size 37x48x16mm
- LED indicator
Item tracking Aircraft Control
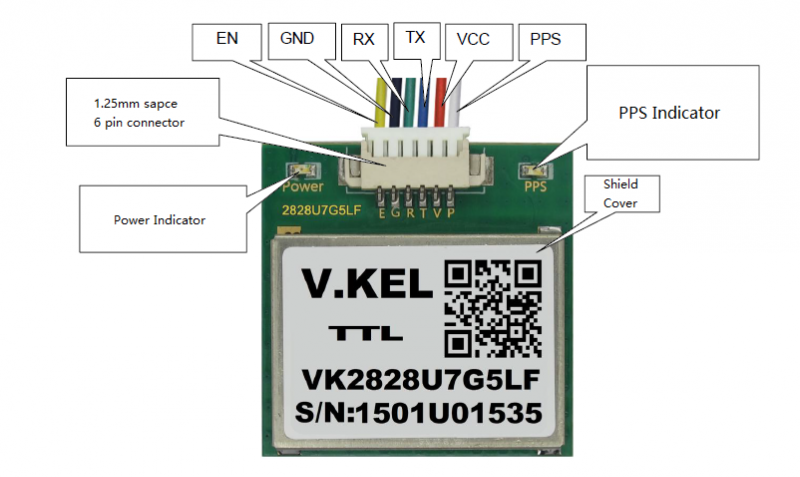
| Pin Name | Color | Description |
| PPS | White | time standard pulse output |
| VCC | Red | Power Supply Input 3.3V-5.V |
| TX | Blue | UART/TTL Interface |
| RX | Green | UART/TTL Interface |
| GND | Black | GND |
| EN | Yellow | Enable Pin.The device is in shutdown mode when voltage to this pin is LOW and enable when is HIGH or floating |
To use, simply create an instance of an object like this:
#include "TinyGPS.h"
TinyGPS gps;Feed the object serial NMEA data one character at a time using the encode() method. (TinyGPS does not handle retrieving serial data from a GPS unit.) When encode() returns “true”, a valid sentence has just changed the TinyGPS object’s internal state. For example:
void loop()
{
while (Serial.available())
{
int c = Serial.read();
if (gps.encode(c))
{
// process new gps info here
}
}
}You can then query the object to get various tidbits of data. To test whether the data returned is stale, examine the (optional) parameter “fix_age” which returns the number of milliseconds since the data was encoded.
long lat, lon;
unsigned long fix_age, time, date, speed, course;
unsigned long chars;
unsigned short sentences, failed_checksum;
// retrieves +/- lat/long in 100000ths of a degree
gps.get_position(&lat, &lon, &fix_age);
// time in hhmmsscc, date in ddmmyy
gps.get_datetime(&date, &time, &fix_age);
// returns speed in 100ths of a knot
speed = gps.speed();
// course in 100ths of a degree
course = gps.course();GPS with LCD Module Sample

| - - GPS** | - - Arduino** |
| VCC | VCC |
| GND | GND |
| RX | TX |
| TX | RX |
Library:TinyGPS V1.3
#include <TinyGPS.h>
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
TinyGPS gps;
LiquidCrystal lcd(8, 9, 4, 5, 6, 7); //LCD driver pins
int led = 13;
long lat, lon;
unsigned long fix_age, time, date, speed, course;
unsigned long chars;
unsigned short sentences, failed_checksum;
//int year;
//byte month, day, hour, minute, second, hundredths;
int DEG;
int MIN1;
int MIN2;
void LAT(){ //Latitude state
DEG=lat/1000000;
MIN1=(lat/10000)%100;
MIN2=lat%10000;
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // set the LCD cursor position
lcd.print("LAT:");
lcd.print(DEG);
lcd.write(0xDF);
lcd.print(MIN1);
lcd.print(".");
lcd.print(MIN2);
lcd.print("' ");
}
void LON(){ //Longitude state
DEG=lon/1000000;
MIN1=(lon/10000)%100;
MIN2=lon%10000;
lcd.setCursor(0,1); // set the LCD cursor position
lcd.print("LON:");
lcd.print(DEG);
lcd.write(0xDF);
lcd.print(MIN1);
lcd.print(".");
lcd.print(MIN2);
lcd.print("' ");
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); //Set the GPS baud rate.
pinMode(led, OUTPUT);
lcd.begin(16, 2); // start the library
lcd.setCursor(0,0); // set the LCD cursor position
lcd.print("GPS test"); // print a simple message on the LCD
delay(2000);
}
void loop()
{
while (Serial.available())
{
digitalWrite(led, HIGH);
int c = Serial.read(); // Read the GPS data
if (gps.encode(c)) // Check the GPS data
{
// process new gps info here
}
}
digitalWrite(led, LOW);
gps.get_position(&lat, &lon, &fix_age); // retrieves +/- lat/long in 100000ths of a degree
gps.get_datetime(&date, &time, &fix_age); // time in hhmmsscc, date in ddmmyy
//gps.crack_datetime(&year, &month, &day, //Date/time cracking
//&hour, &minute, &second, &hundredths, &fix_age);
LAT();
LON();
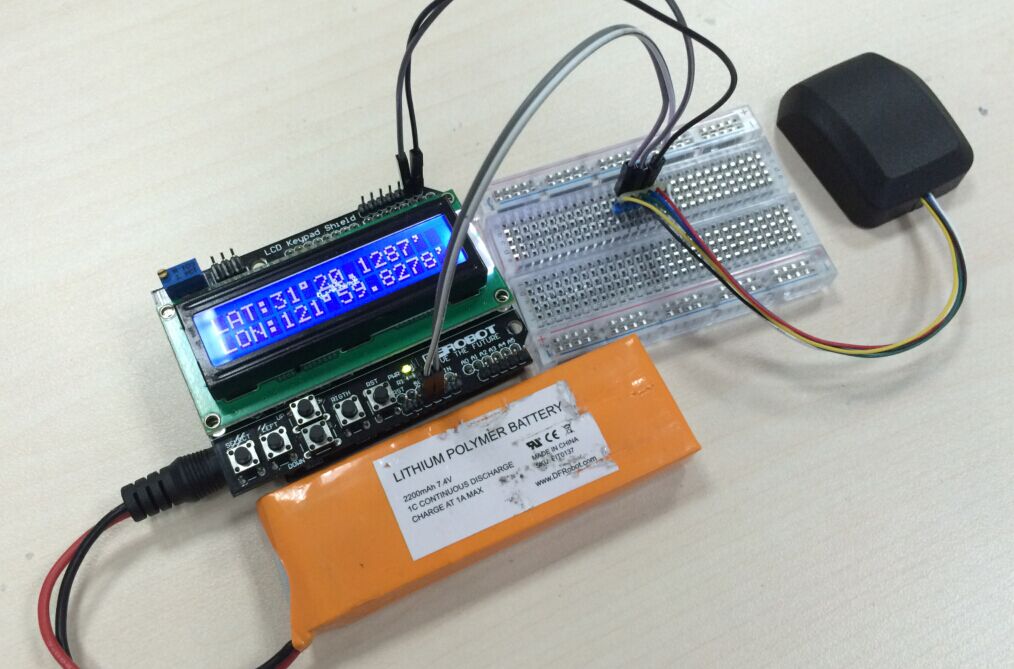
}As shown in the picture above , you can get GPS data on the LCD screen.
Library TinyGPS VK2828U7G5LF datasheet VKEL GPS Test Assistant
 shopping click to buy on dfrobot store
shopping click to buy on dfrobot store
category: Product Manual category: TEL Series category: Wireless