4WD_Mobile_Platform_SKU_ROB0022 - jimaobian/DFRobotWiki GitHub Wiki
This Kit will teach you how to build a automatic obstacle - avoidance robot which is achieved on the platform of the Turtle Robot,based on ultrasonic sensor as distance measuring device,and combined with servo. === STEP1: Assemble Robot ===
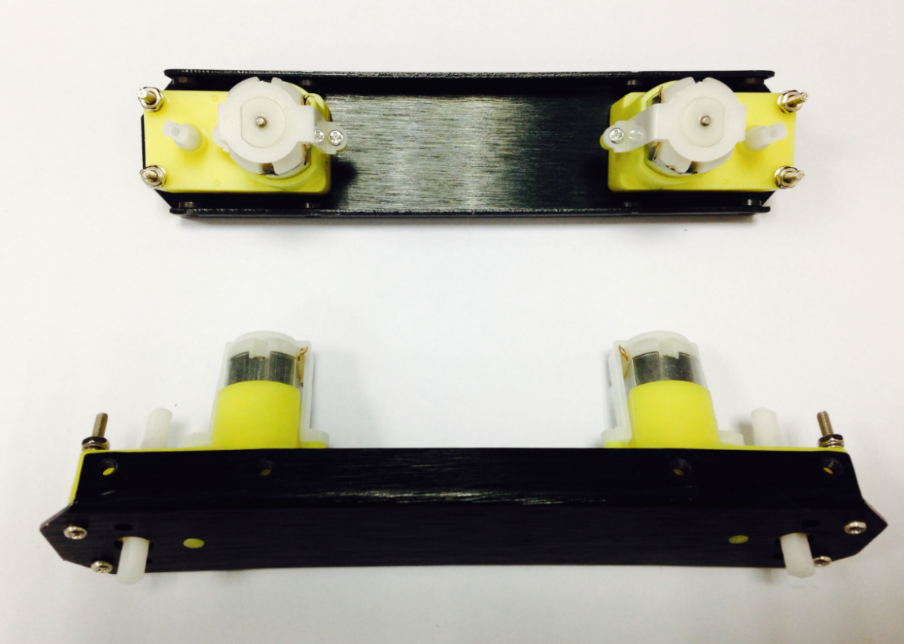
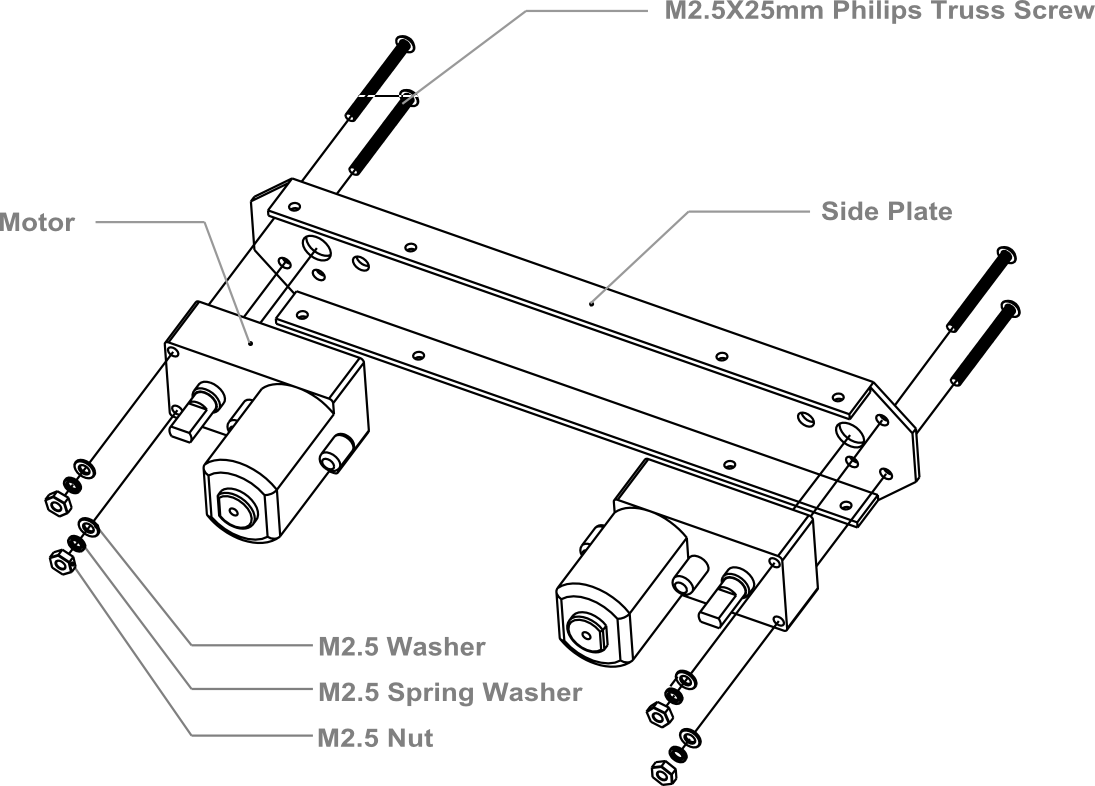
1.Assemble Your Own Motor
Look in your parts bag for eight long screws. These are used to fix and secure the motors in place. Place the motors in the correct alignment, then screw them into place as shown in the picture below.
Please note that washers and gaskets are also included in the parts bag. Washers can be used to increase friction, which helps fasten the motors into place. The gaskets help prevent the screw nuts from loosening and falling off due to the Pirate’s movements and collisions.

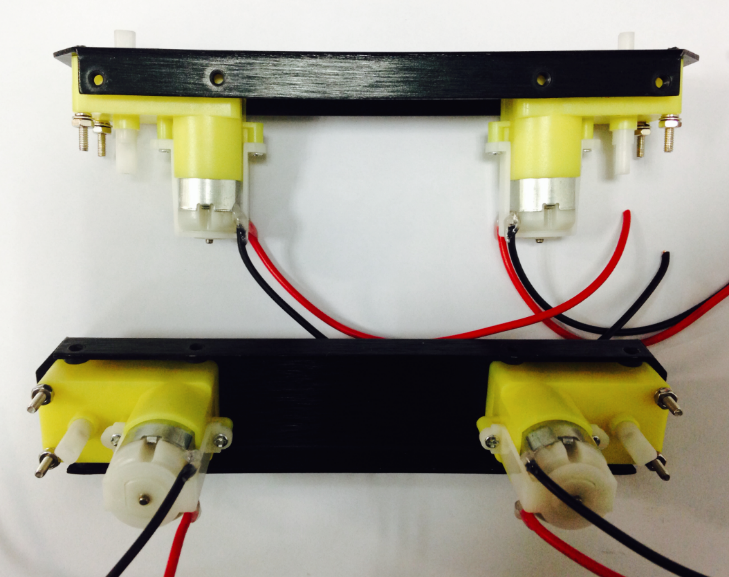
2.Soldering the Cables
Take the black and red wires out of the parts bag. Attach one black and one red cable (15 cm long) to each motor (4 motors in total). Then use your wire stripper to strip the insulation at both ends of the wires (make sure not to strip too much—refer to the pictures below). Next, solder the wires onto the pins affixed to the motors. Repeat the soldering process for all four motors.
| Note:Pay attention to the correct locations of the red and black wires when soldering. Please consult the following photos for details. |
image:Assemble Mobile Platform STEP2_1.png|1 image:Assemble Mobile Platform STEP2_2.jpg|2
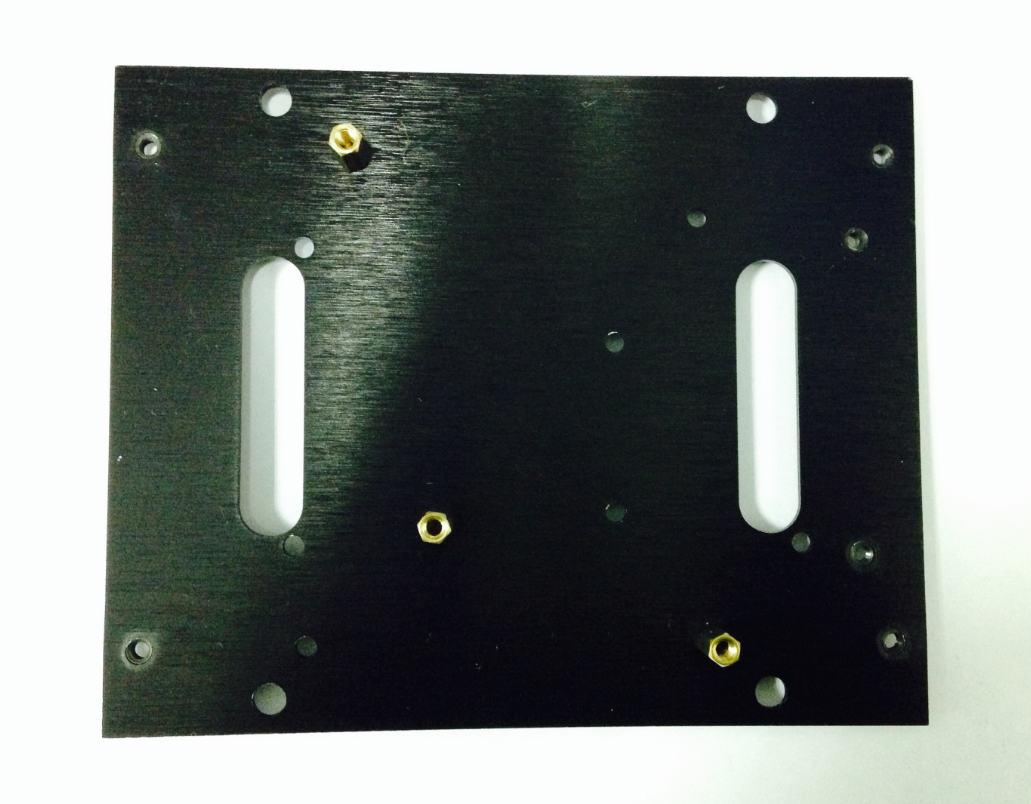
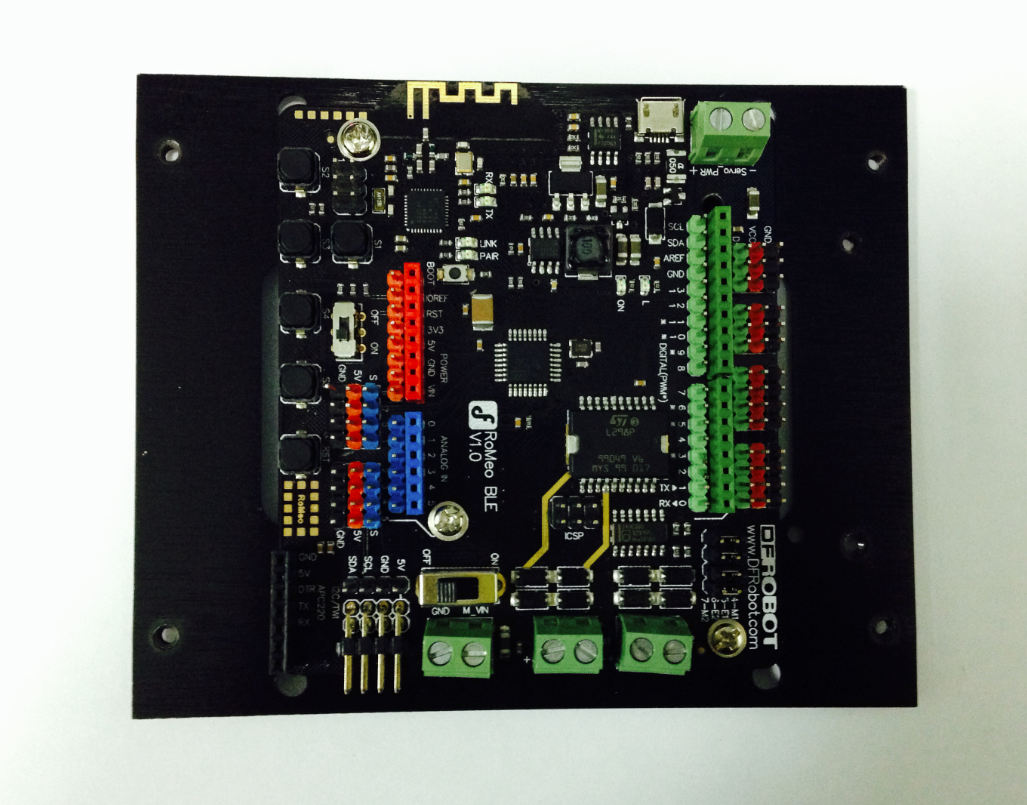
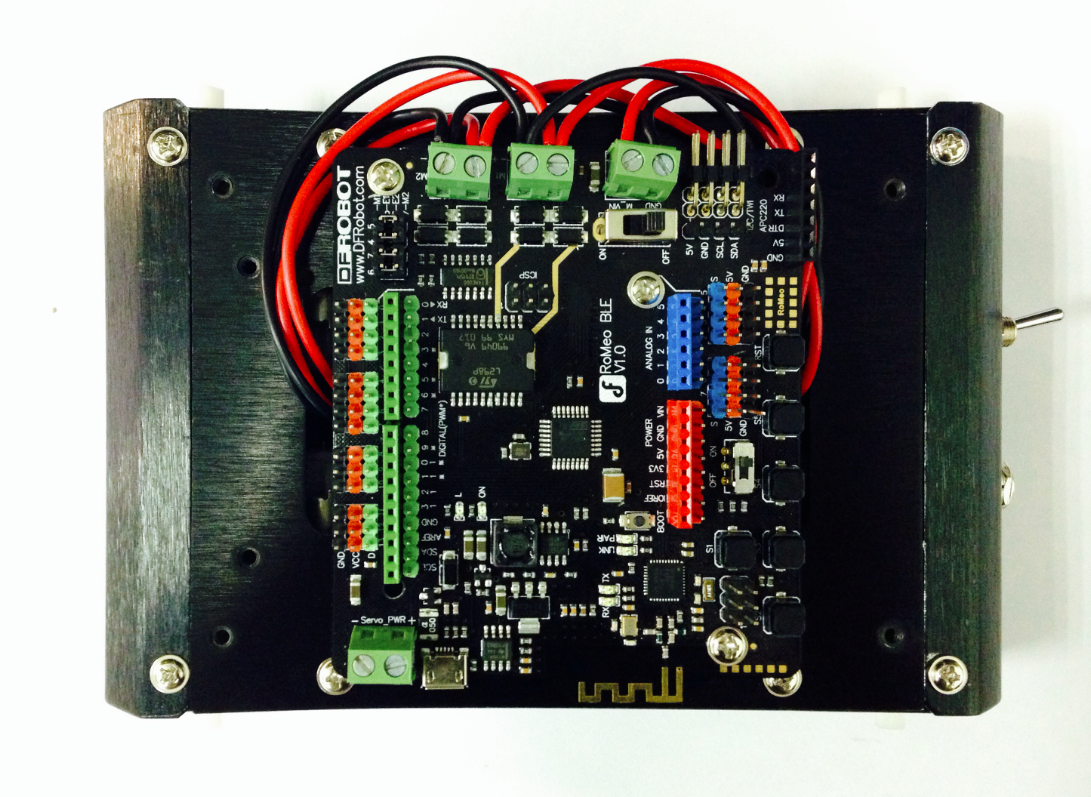
3.Assemble the Romeo BLE controller
Look in your parts bag for three copper supports. Those 1cm-long supports are used to fasten the Romeo controller board. As shown in the picture below, there are three holes in the controller board. Place the three copper supports into the holes, then fasten them into place with the appropriate screws.
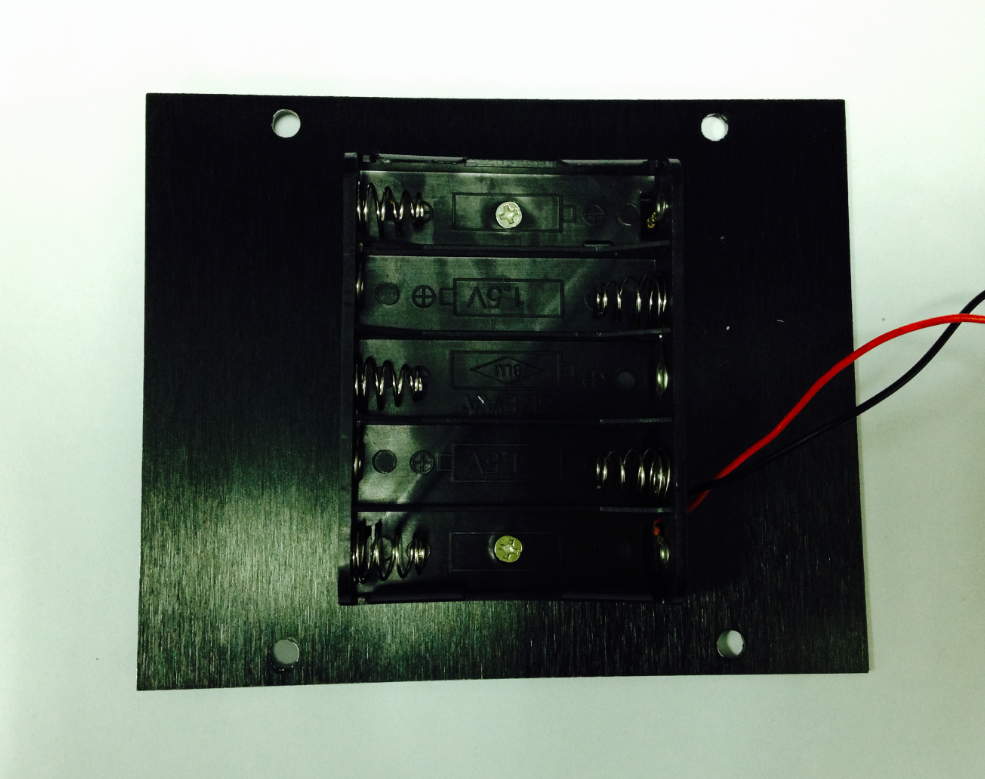
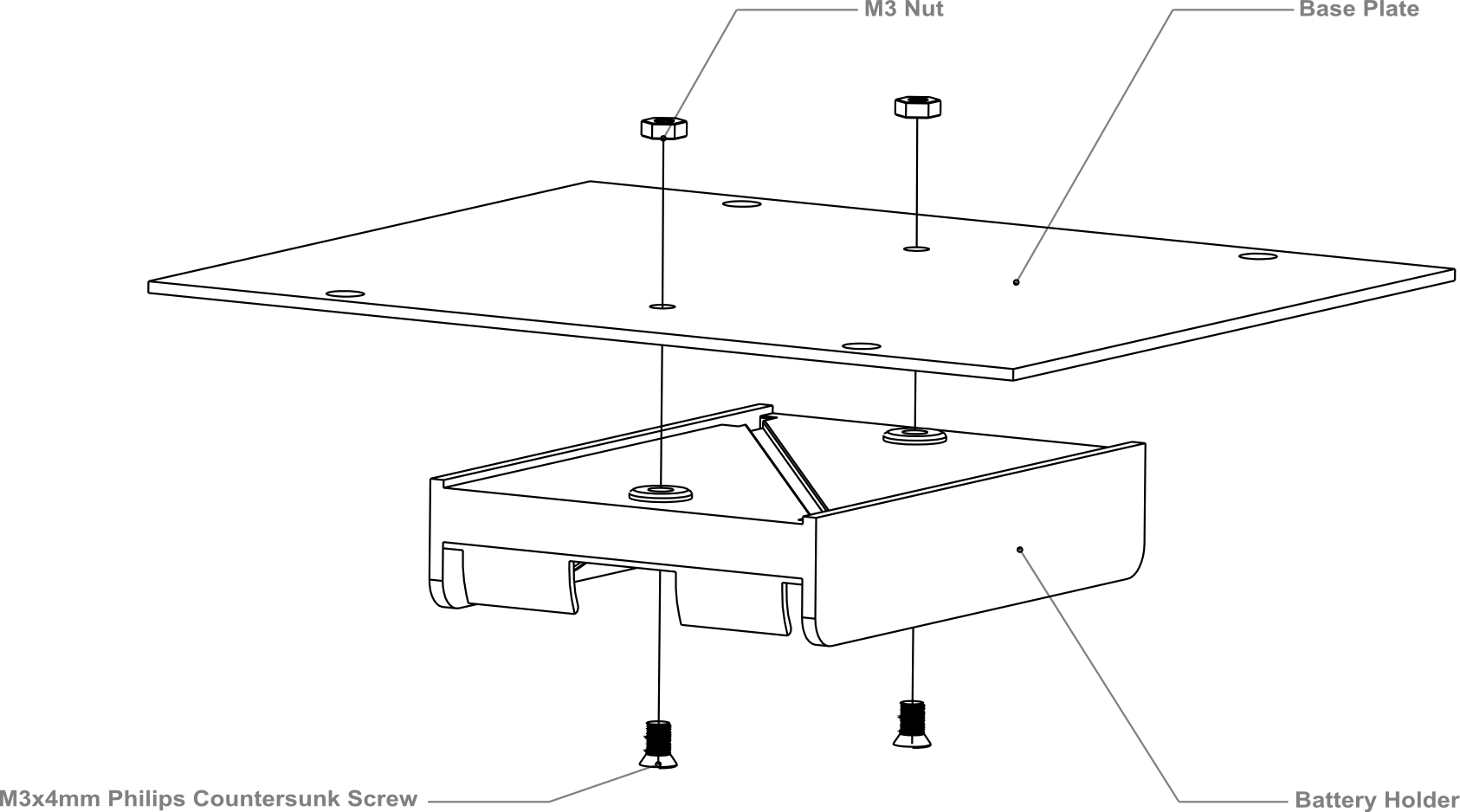
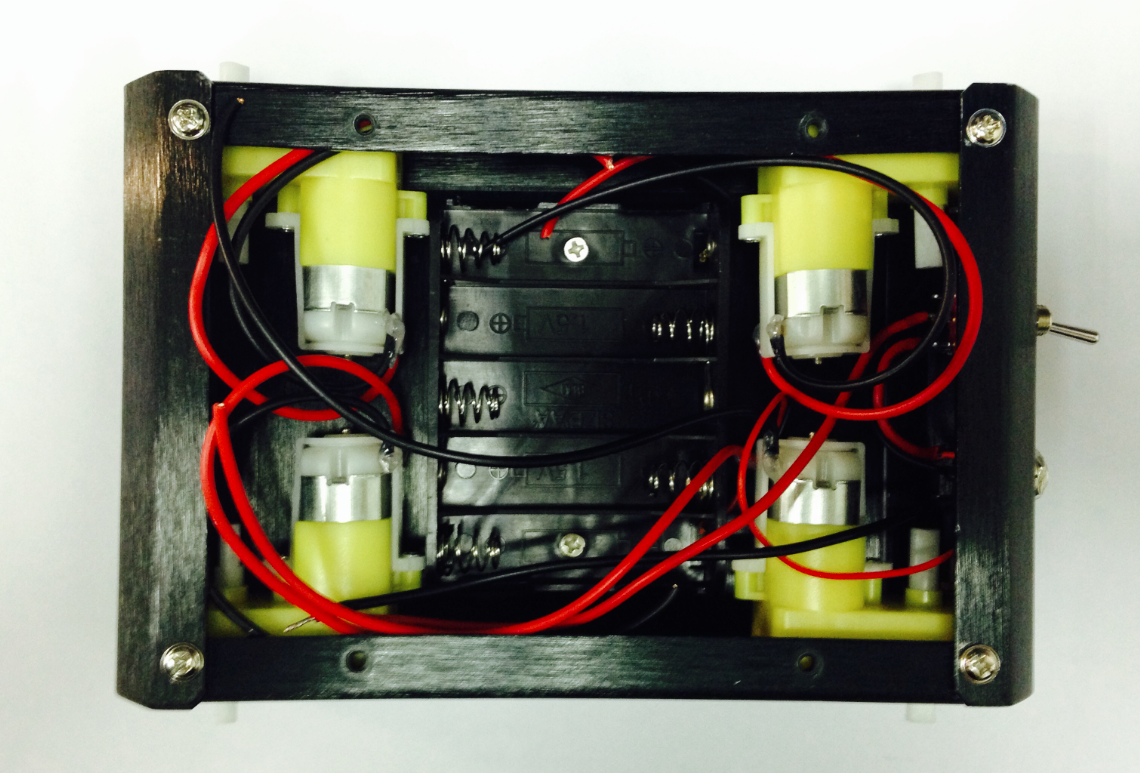
4.Assemble the Battery Box
Take out two countersunk screws (their heads are flat). Then follow the steps shown in the picture below and affix the battery to the car base.

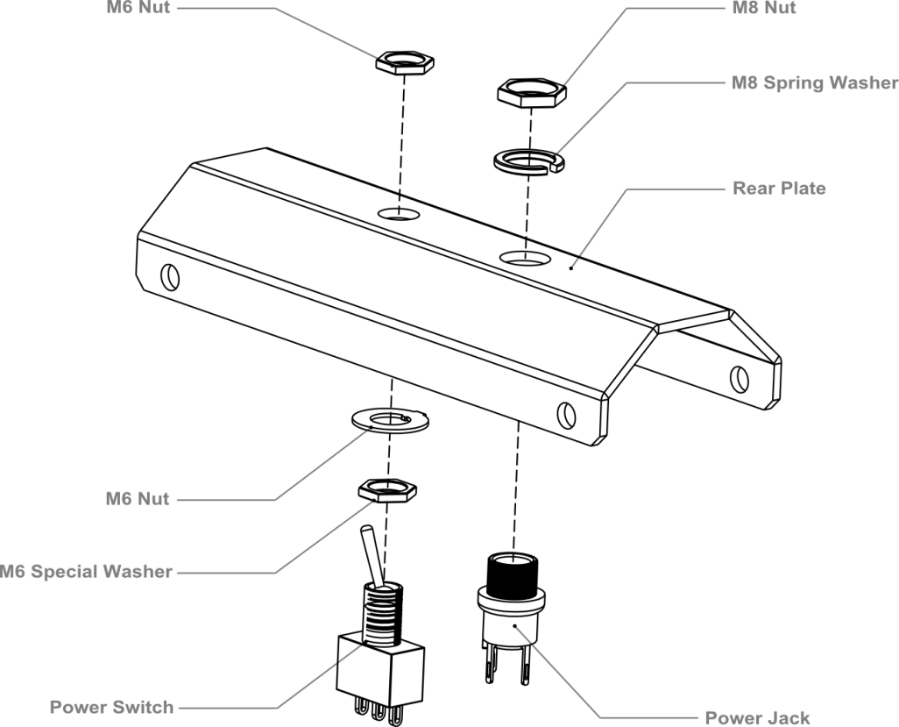
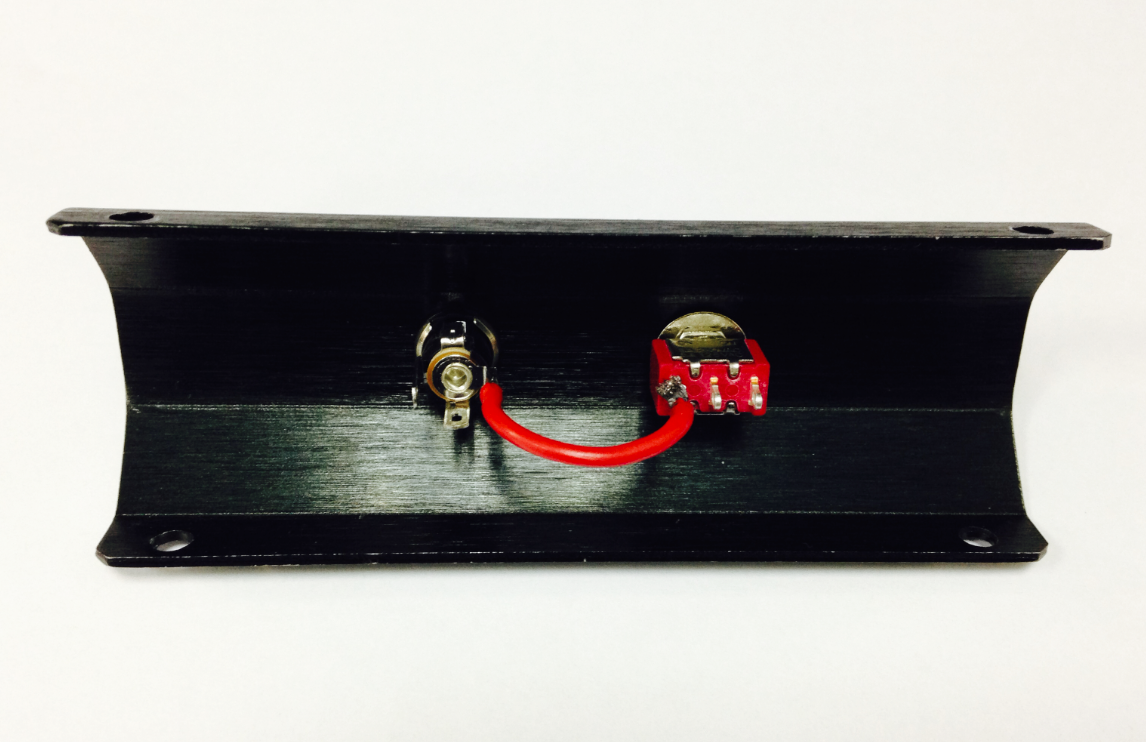
5.Crafting the Power Switch
Batteries are the essential lifeblood of robots. To control power usage, we need to use a power switch: the switch turns off power when not in use, thus preserving electricity and battery life. Refer to the picture below before assembling and installing the power switch.
Please pay attention to the sequence of the gaskets and screw nuts when assembling the switch.
After assembling the switch, we want to start soldering its wires. Take some of the remaining wire leftover from before. Strip the wiring off both ends of the cables so that the inside of the wire is exposed (same process as with the motors before). We want to solder the exposed end of the wires to the pins on the switch. When soldering, it’s very important that we note the position of the switch’s pins.
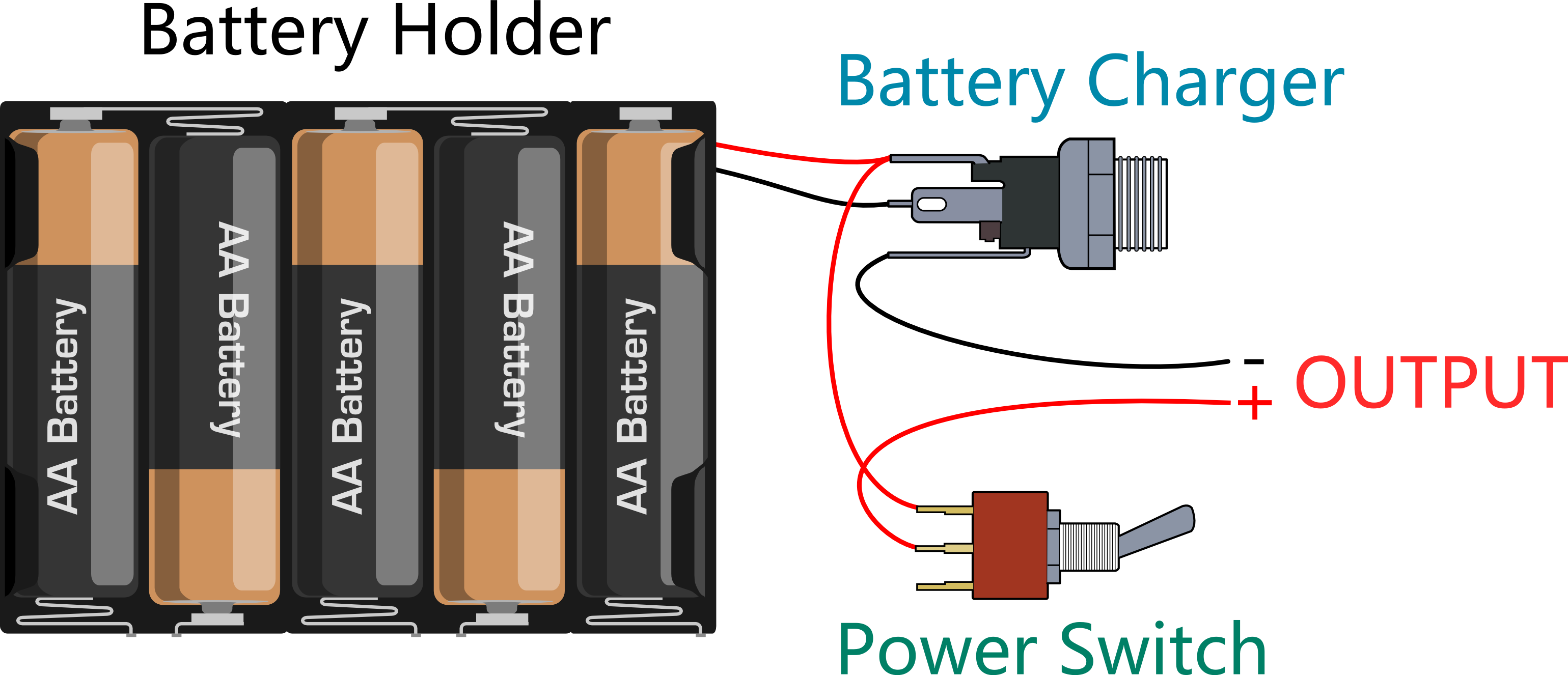
Let’s do this step by step. a)Connect the switch to the battery charger. Pay attention to the exact location of both items.

b)Solder the red cables connecting the switch with the battery charger as shown in the picture below.
Here’s another picture to make things clearer.
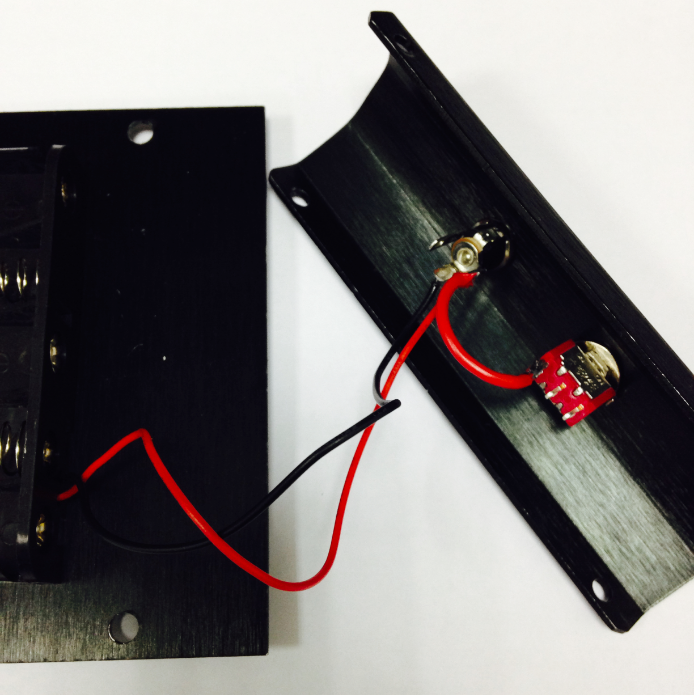
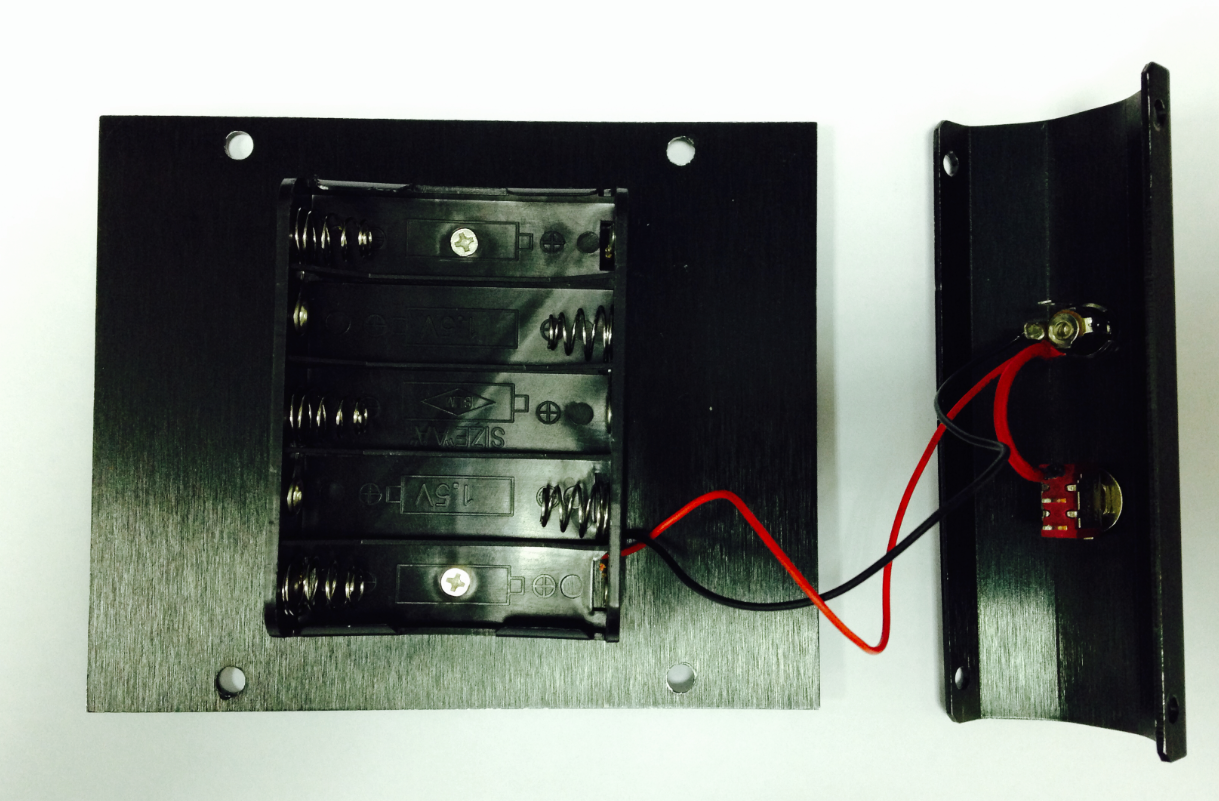
c)Finally, take one red cable and one black cable. Attach one end of one cable to the negative pole of the battery charger and one end of the other cable to the positive pole of the battery charger. Then attach the other ends of both cables to the Romeo BLE controller.
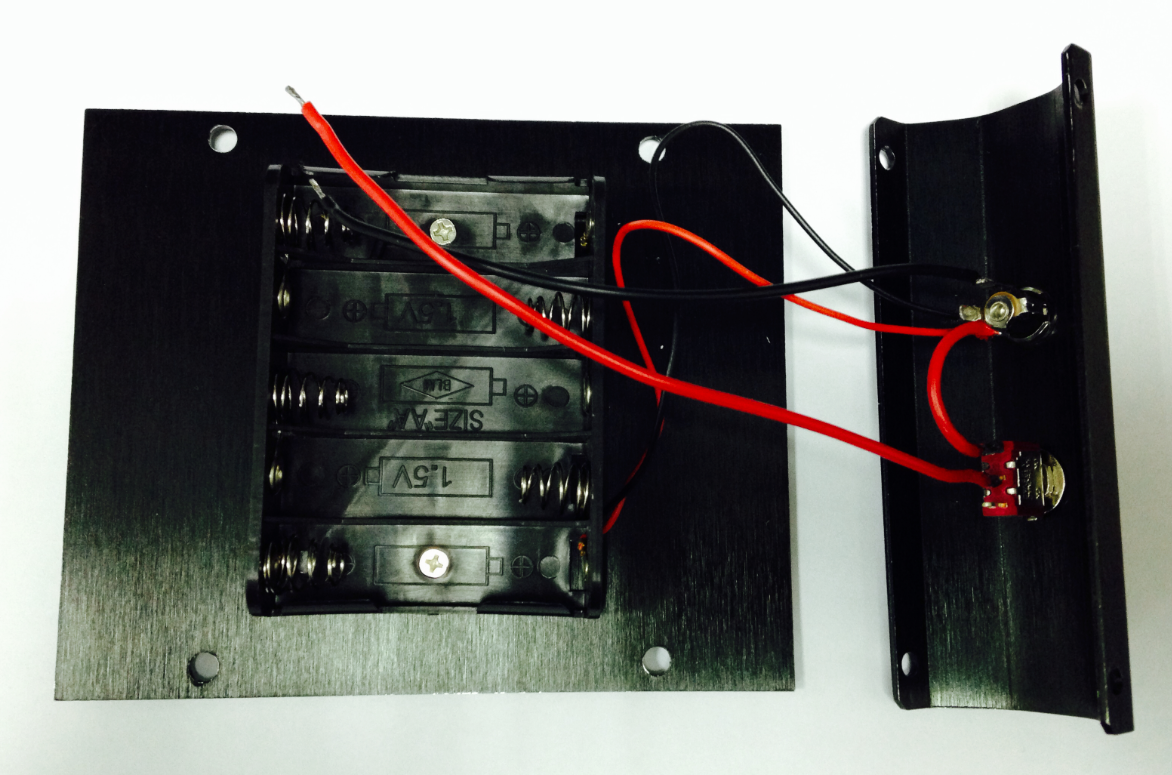
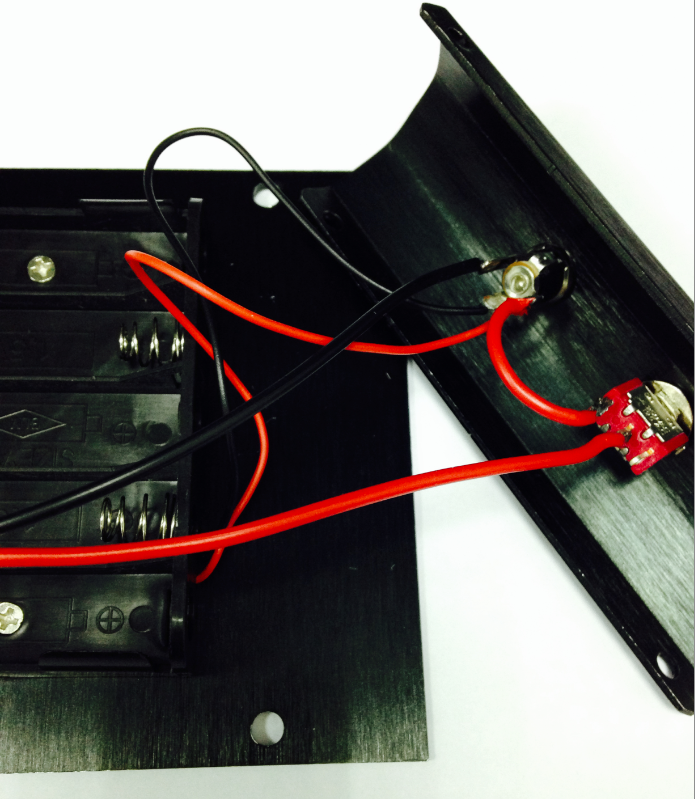
Looking at this enlarged picture should give you a better idea of how the wires should be connected. After soldering, make sure to check and see if your wiring between the battery and Romeo controller is consistent from start to finish and matches with the above pictures.
6.Assemble the Car Base
Using eight M3x6mm screws, attach the side plates to the front and back bumper plates as shown by the diagram below.
| Note: When tightening the screws during this step, make sure not to fully tighten the screws at first — this way, we can easily detach the top board in later steps should we need to make adjustments. |
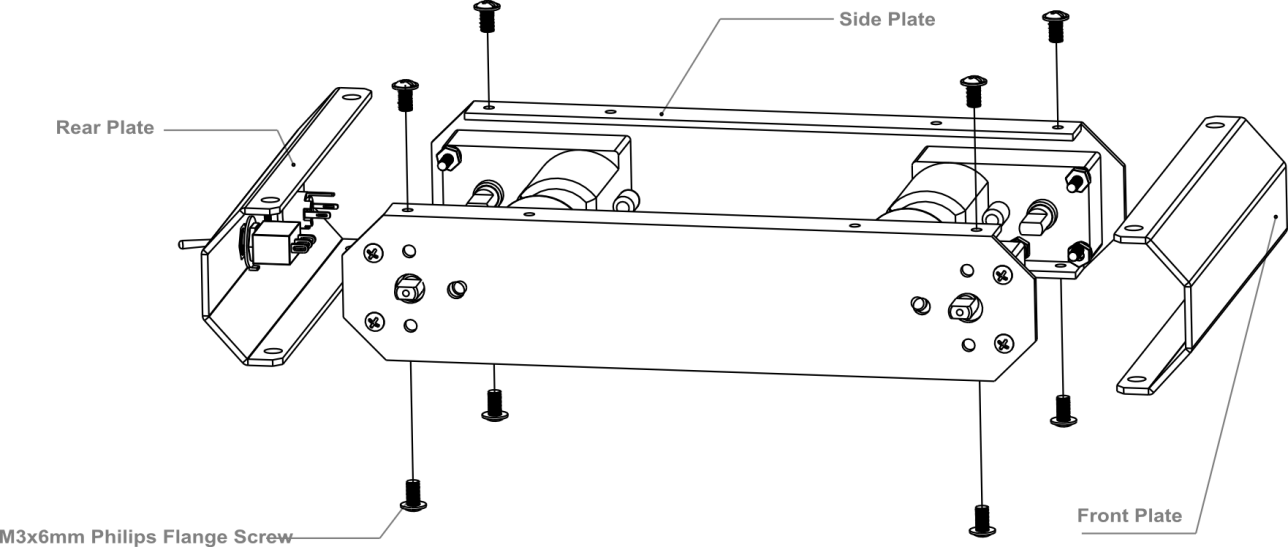
Then, re-attach the base plate to the body of the car as shown in the picture below.
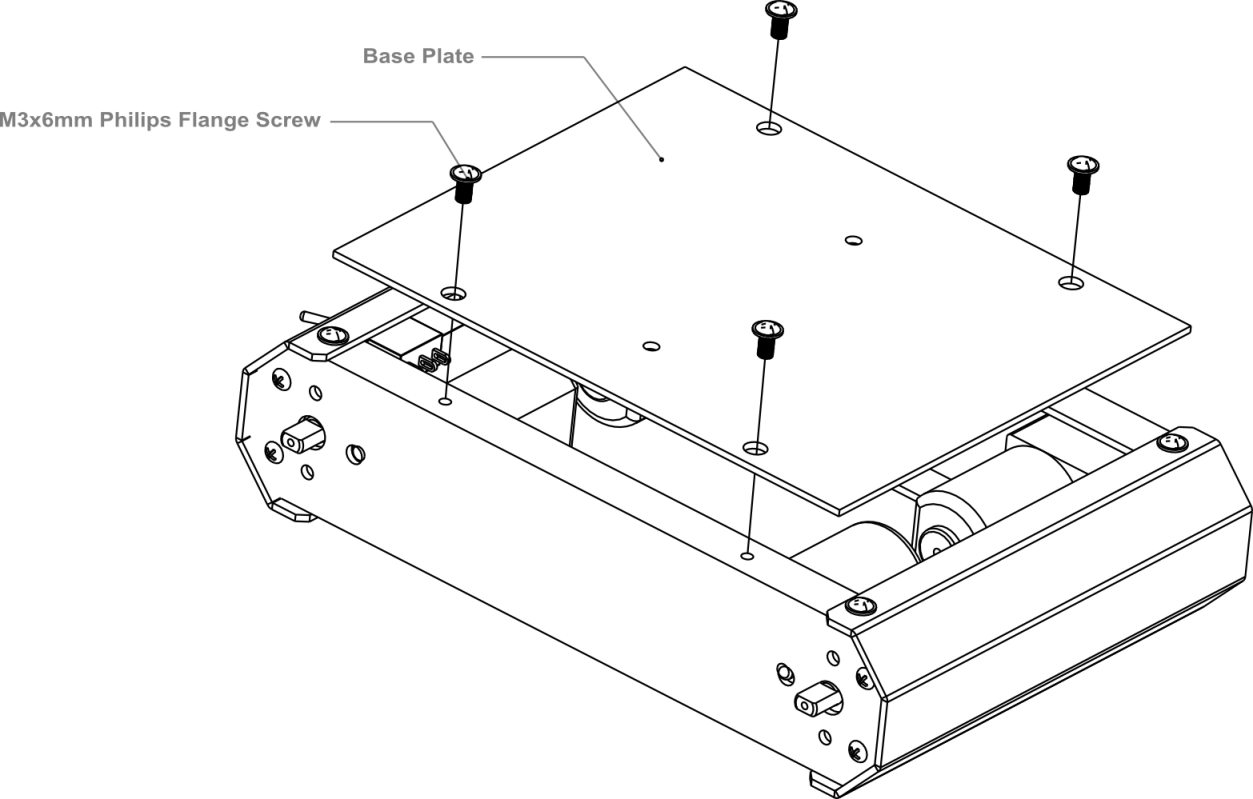
This is what the car base should like after it’s been assembled — remember to install the battery pack!
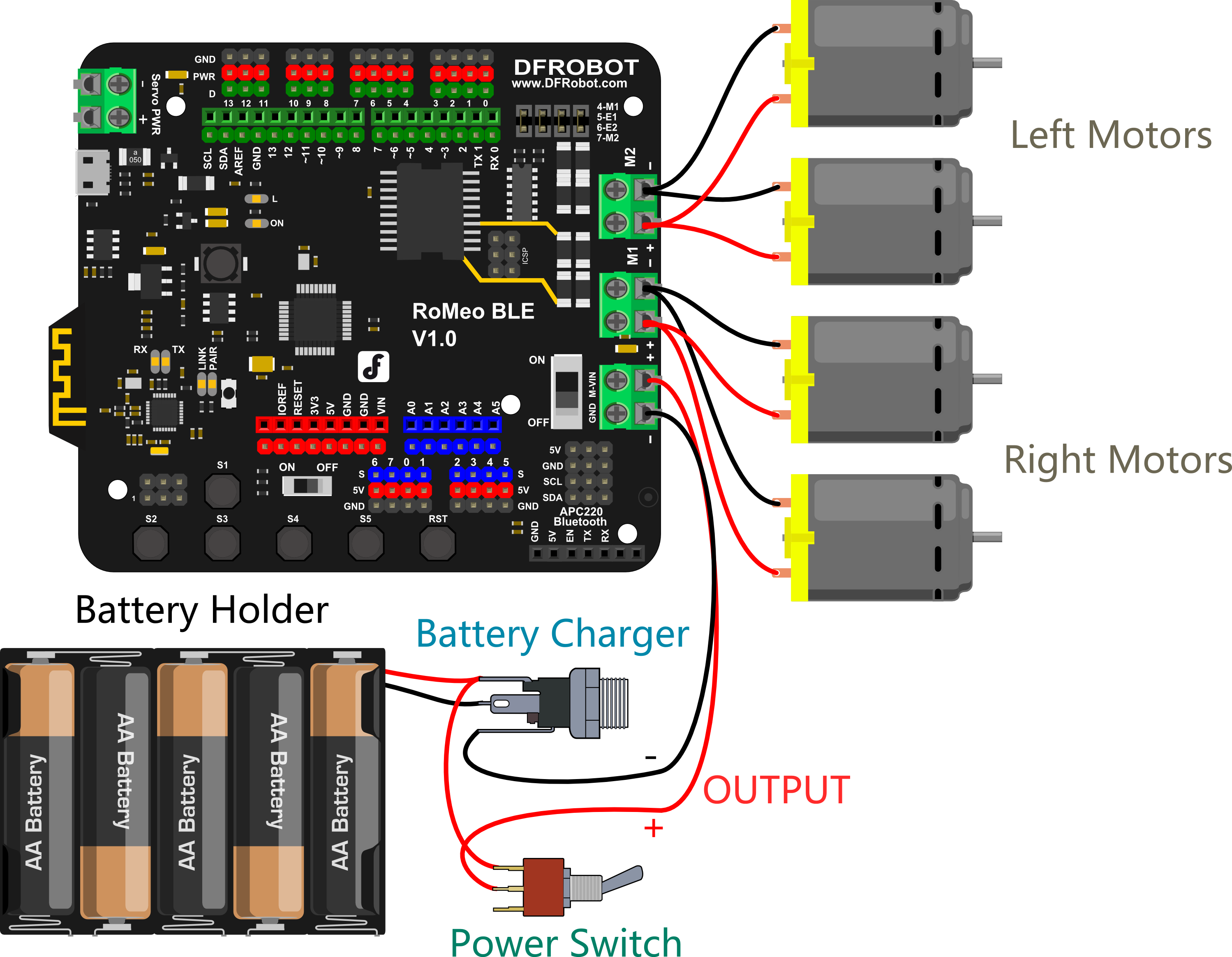
7.Connect the Motors with the Microcontroller Board
Now we need to the motors with the microcontroller board. Carefully follow the following diagram: the left motor’s red and black wires should be soldered into M2; the right motor’s red and black wires should be soldered to M1. Pay special attention to the battery pack: the black wire should be soldered into the wire port reading GND, while the red wire should be soldered in the wire port labeled VND. Use your screwdriver to loosen and tighten the wire ports — make sure these ports are fastened well once the wires have been inserted.
| Note: Make sure the wires from one motor (i.e. the left motor) are soldered into the motor port. (i.e. the M2 port on the diagram below — do not solder one motor’s wires into two separate ports.) |
After soldering the motor wires to the microcontroller board, we’re ready to attach the top plate to the base of the car. Before we attach the top plate, you have the option of attaching a sensor plate (see diagram below) — if you don’t plan to use sensors just yet, you can skip this extra step.
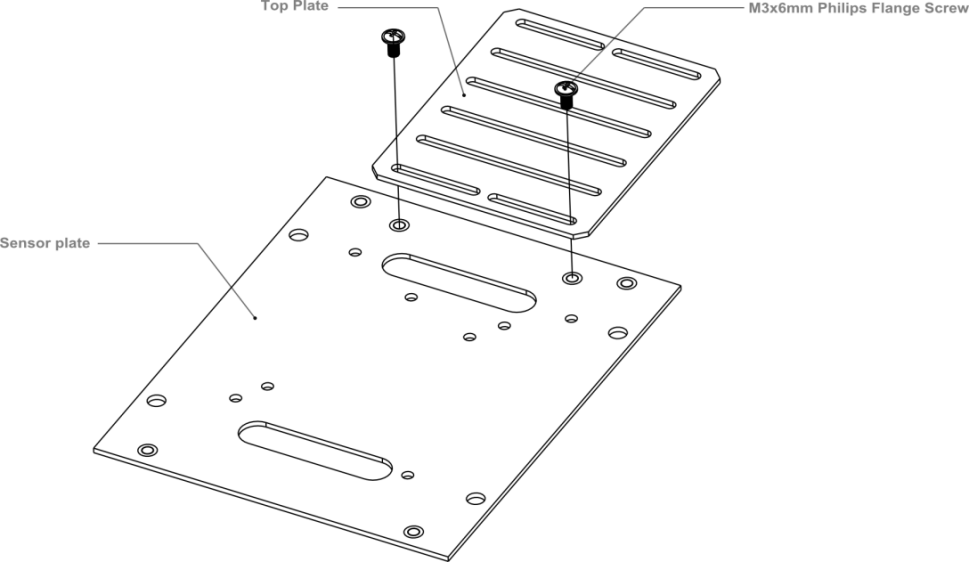

After attaching the top plate, your Pirate should resemble the picture below.
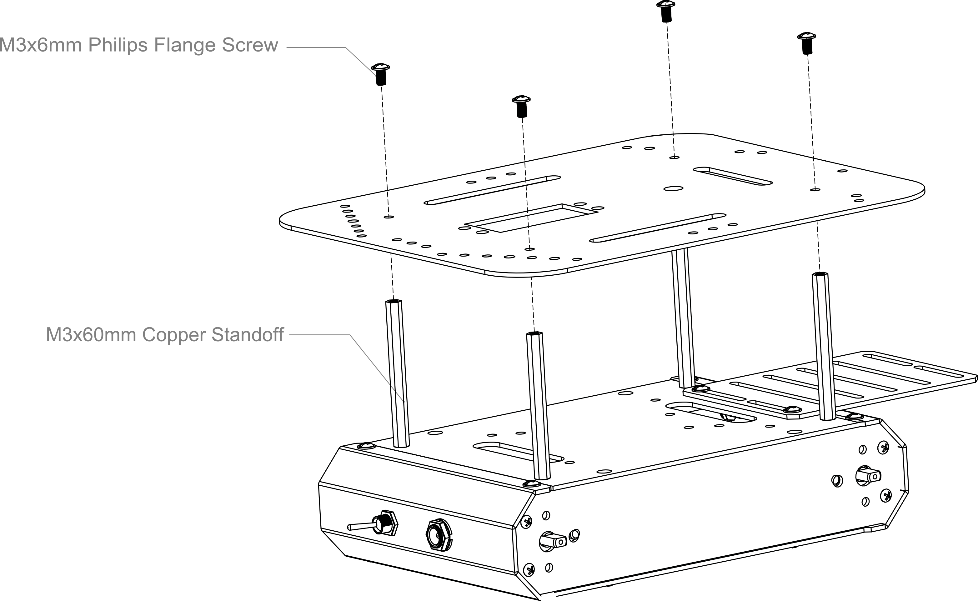
8.Attach an extra level to the Pirate
Find the four holes on the base’s top plate. Screw in the four M3x60mm Copper Standoffs, then attach the additional top plate as shown in the diagram below — use M3x6mm screws to affix the plate to the copper standoffs.
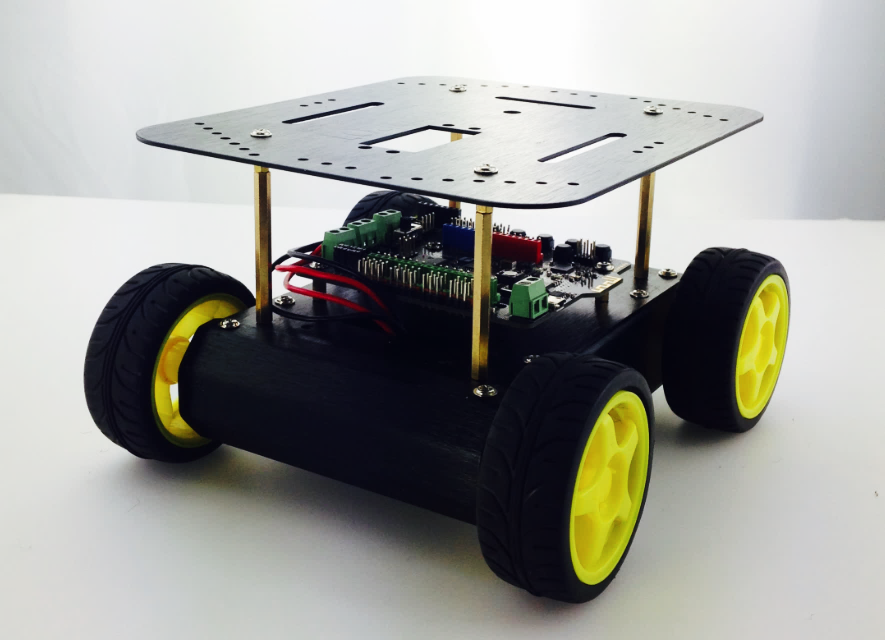
Toss some wheels on your Pirate and you’re ready to let it whip!

Upload the Code
int speedPin_M1 = 5; //M1 Speed Control
int speedPin_M2 = 6; //M2 Speed Control
int directionPin_M1 = 4; //M1 Direction Control
int directionPin_M2 = 7; //M1 Direction Control
void setup(){
}
void loop(){
carAdvance(150,150);
delay(1000);
carBack(150,150);
delay(1000);
carTurnLeft(150,150);
delay(1000);
carTurnRight(150,150);
delay(1000);
}
void carStop(){ // Motor Stop
digitalWrite(speedPin_M2,0);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,LOW);
digitalWrite(speedPin_M1,0);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,LOW);
}
void carTurnLeft(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Turn Left
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed); //PWM Speed Control
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,LOW);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,HIGH);
}
void carTurnRight(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Turn Right
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,HIGH);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,LOW);
}
void carBack(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Move backward
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,LOW);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,LOW);
}
void carAdvance(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Move forward
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,HIGH);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,HIGH);
}
1. Fixed Ultrasonic Sensor Position
Please see the Installation Manual
2. Fixed Servo Position
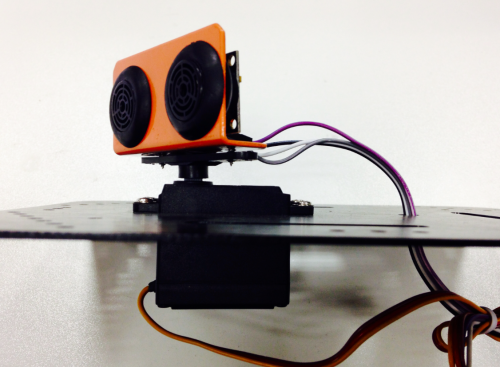

=== STEP4: Debug Ultrasonic Sensor and Servo ===
1. Hardware Connection
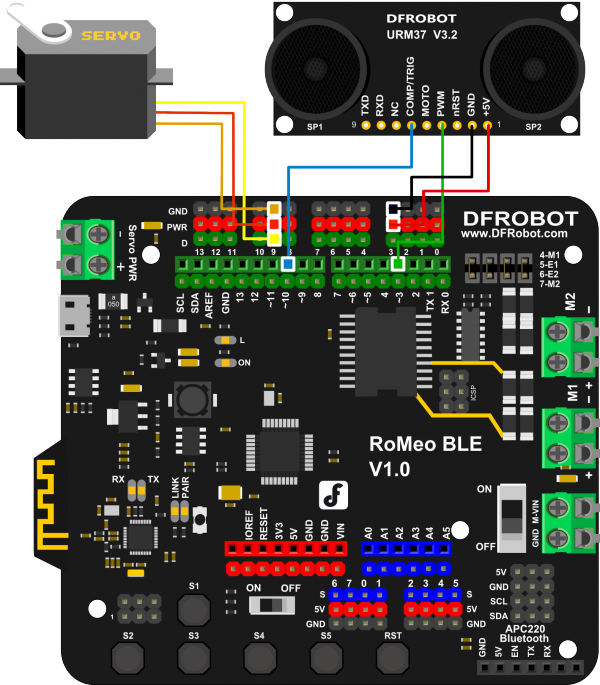
2. Upload Code
Download the library firstly.Metro libray
#include <Servo.h>
#include <Metro.h>
Metro measureDistance = Metro(50);
Metro sweepServo = Metro(20);
unsigned long actualDistance = 0;
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int pos = 60;
int sweepFlag = 1;
int URPWM = 3; // PWM Output 0-25000US,Every 50US represent 1cm
int URTRIG= 10; // PWM trigger pin
uint8_t EnPwmCmd[4]={0x44,0x02,0xbb,0x01}; // distance measure command
void setup(){ // Serial initialization
myservo.attach(9);
Serial.begin(9600); // Sets the baud rate to 9600
SensorSetup();
}
void loop(){
if(measureDistance.check() == 1){
actualDistance = MeasureDistance();
// Serial.println(actualDistance);
// delay(100);
}
if(sweepServo.check() == 1){
servoSweep();
}
}
void SensorSetup(){
pinMode(URTRIG,OUTPUT); // A low pull on pin COMP/TRIG
digitalWrite(URTRIG,HIGH); // Set to HIGH
pinMode(URPWM, INPUT); // Sending Enable PWM mode command
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
Serial.write(EnPwmCmd[i]);
}
}
int MeasureDistance(){ // a low pull on pin COMP/TRIG triggering a sensor reading
digitalWrite(URTRIG, LOW);
digitalWrite(URTRIG, HIGH); // reading Pin PWM will output pulses
unsigned long distance=pulseIn(URPWM,LOW);
if(distance==50000){ // the reading is invalid.
Serial.print("Invalid");
}else{
distance=distance/50; // every 50us low level stands for 1cm
}
return distance;
}
void servoSweep(){
if(sweepFlag ){
if(pos>=60 && pos<=120){
pos=pos+1; // in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
}
if(pos>119) sweepFlag = false; // assign the variable again
}else {
if(pos>=60 && pos<=120){
pos=pos-1;
myservo.write(pos);
}
if(pos<61) sweepFlag = true;
}
}
3. Adjust the servo position
Method 1: Reinstall wheel Method 2: Adapt your code accordingly
1. Fix the expansion board
Uplpad the code
#include <Servo.h>
#include <Metro.h>
Metro measureDistance = Metro(50);
Metro sweepServo = Metro(20);
int speedPin_M1 = 5; //M1 Speed Control
int speedPin_M2 = 6; //M2 Speed Control
int directionPin_M1 = 4; //M1 Direction Control
int directionPin_M2 = 7; //M1 Direction Control
unsigned long actualDistance = 0;
Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
int pos = 60;
int sweepFlag = 1;
int URPWM = 3; // PWM Output 0-25000US,Every 50US represent 1cm
int URTRIG= 10; // PWM trigger pin
uint8_t EnPwmCmd[4]={0x44,0x02,0xbb,0x01}; // distance measure command
void setup(){ // Serial initialization
int i;
for(i=4;i<=7;i++)
pinMode(i, OUTPUT);
myservo.attach(9);
Serial.begin(9600); // Sets the baud rate to 9600
SensorSetup();
myservo.write(90);
delay(3000);
}
void loop(){
if(measureDistance.check() == 1){
actualDistance = MeasureDistance();
Serial.println(actualDistance);
// delay(100);
}
if(sweepServo.check() == 1){
servoSweep();
}
if(actualDistance <= 30){
myservo.write(90);
if(pos>=90){
carBack(150,150);
delay(600);
carTurnRight(150,150);
delay(600);
}else{
carBack(150,150);
delay(600);
carTurnLeft(150,150);
delay(600);
}
}else{
carAdvance(150,150);
delay(100);
}
// carBack(150,150);
}
void SensorSetup(){
pinMode(URTRIG,OUTPUT); // A low pull on pin COMP/TRIG
digitalWrite(URTRIG,HIGH); // Set to HIGH
pinMode(URPWM, INPUT); // Sending Enable PWM mode command
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
Serial.write(EnPwmCmd[i]);
}
}
int MeasureDistance(){ // a low pull on pin COMP/TRIG triggering a sensor reading
digitalWrite(URTRIG, LOW);
digitalWrite(URTRIG, HIGH); // reading Pin PWM will output pulses
unsigned long distance=pulseIn(URPWM,LOW);
if(distance==50000){ // the reading is invalid.
Serial.print("Invalid");
}else{
distance=distance/50; // every 50us low level stands for 1cm
}
return distance;
}
void carStop(){ // Motor Stop
digitalWrite(speedPin_M2,0);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,LOW);
digitalWrite(speedPin_M1,0);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,LOW);
}
void carTurnLeft(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Turn Left
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed); //PWM Speed Control
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,LOW);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,HIGH);
}
void carTurnRight(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Turn Right
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,HIGH);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,LOW);
}
void carBack(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Move backward
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,LOW);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,LOW);
}
void carAdvance(int leftSpeed,int rightSpeed){ //Move forward
analogWrite (speedPin_M2,leftSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M1,HIGH);
analogWrite (speedPin_M1,rightSpeed);
digitalWrite(directionPin_M2,HIGH);
}
void servoSweep(){
if(sweepFlag){
if(pos>=60 && pos<=120){
pos=pos+5; // in steps of 1 degree
myservo.write(pos); // tell servo to go to position in variable 'pos'
}
if(pos>119) sweepFlag = false; // assign the variable again
}
else {
if(pos>=60 && pos<=120){
pos=pos-5;
myservo.write(pos);
}
if(pos<61) sweepFlag = true;
}
}
Your own car was born!
| Q 1. The servo twitched rapidly and the ultrasonic sensor produced inaccurate readings while the motors were running, how to solve this problem? |
**A:**You can add a 0.1uF capacitor between each motor's positive and negative pole.
 get it from dfrobot store or dfrobot distributor.
get it from dfrobot store or dfrobot distributor.