Planar impact in Lagrangian mode - isale-code/isale-wiki GitHub Wiki
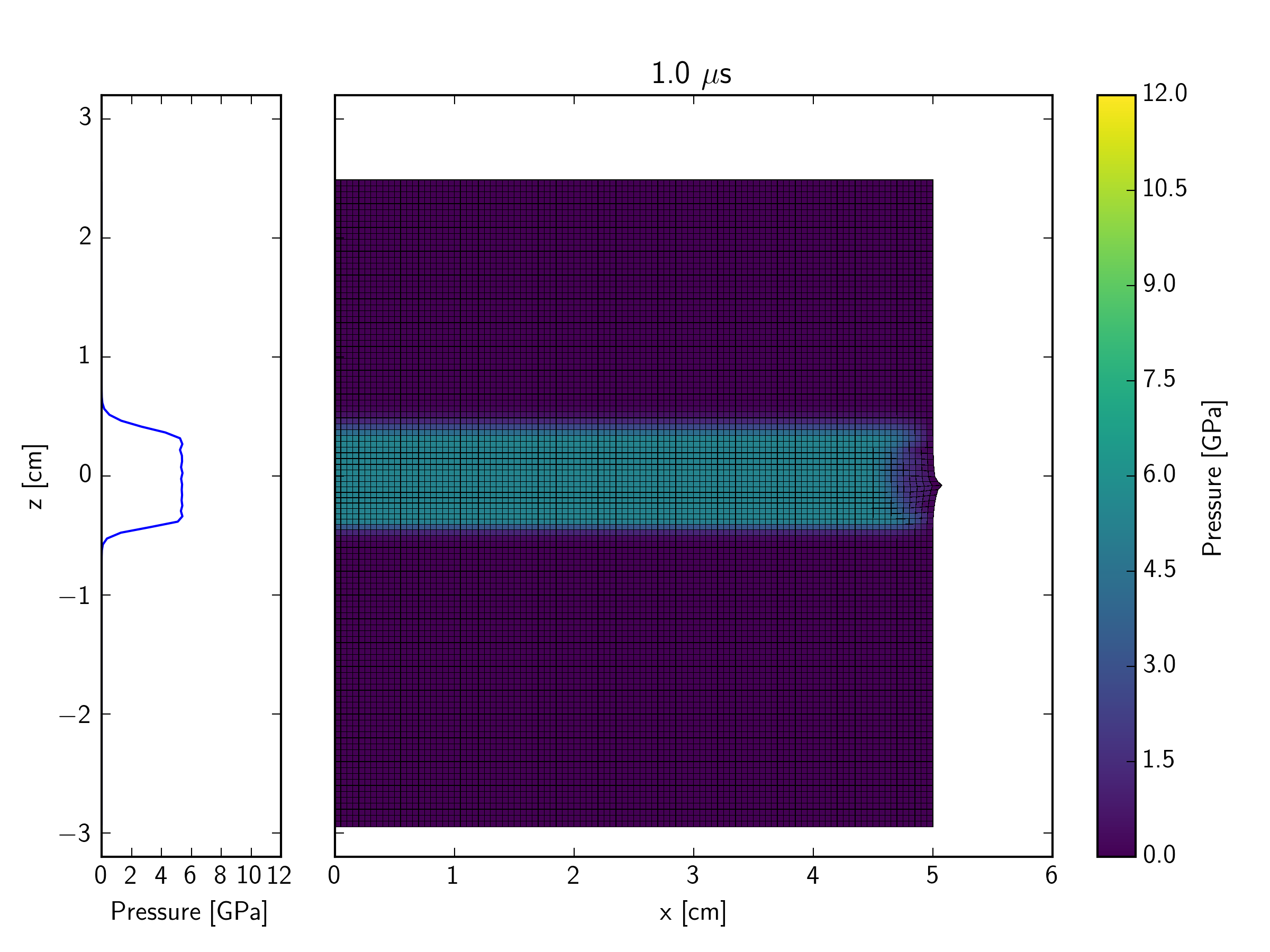
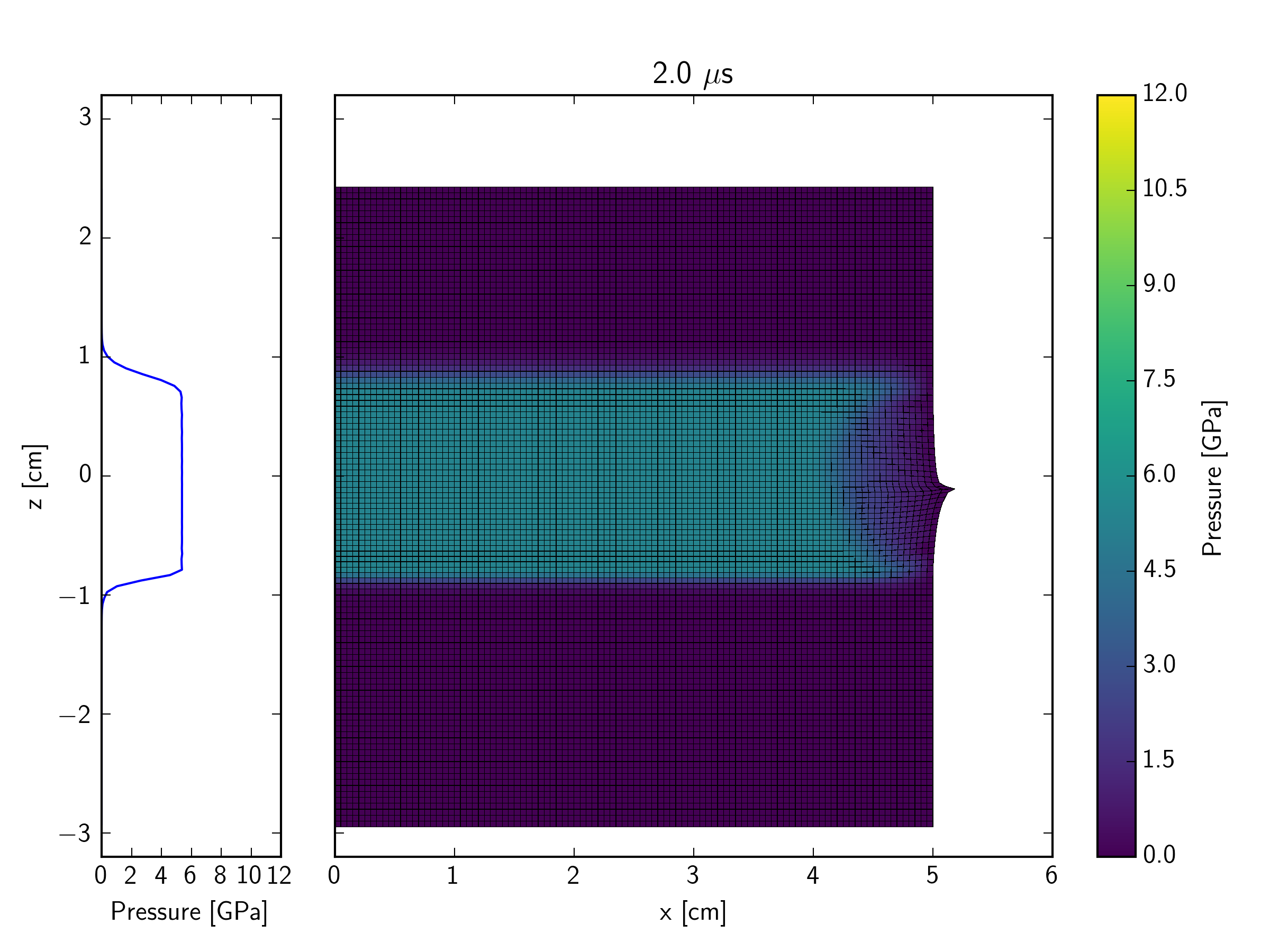
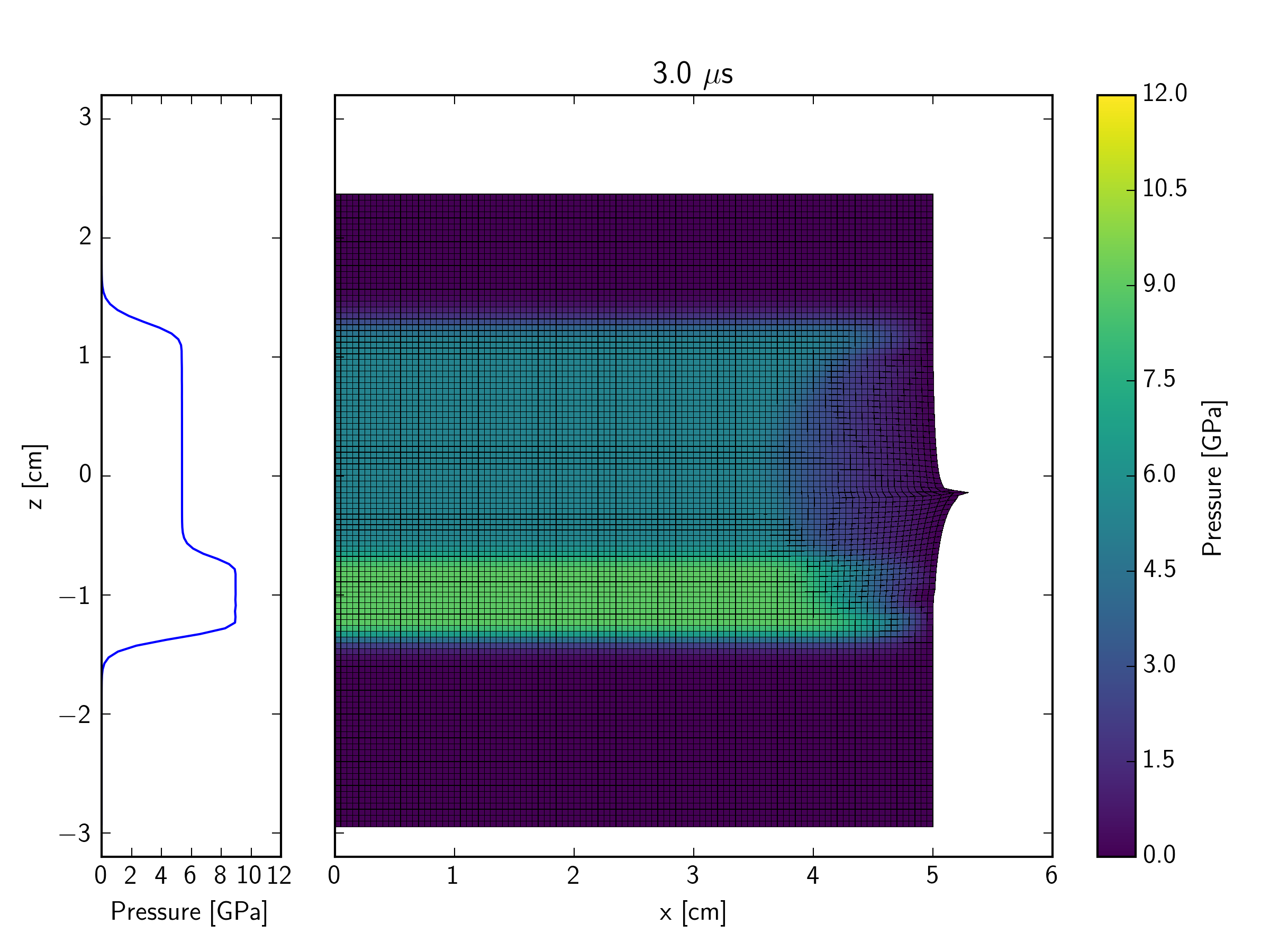
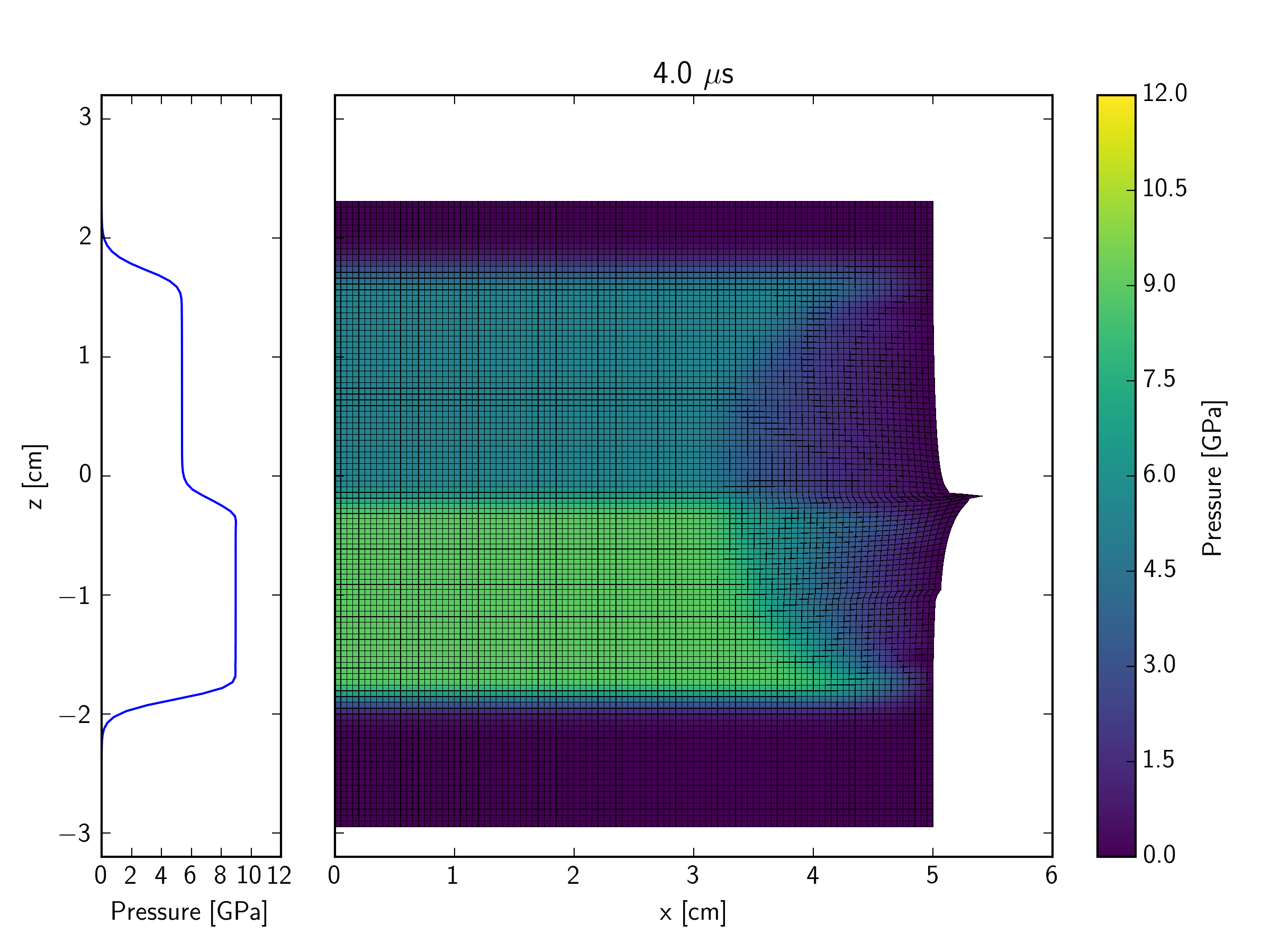
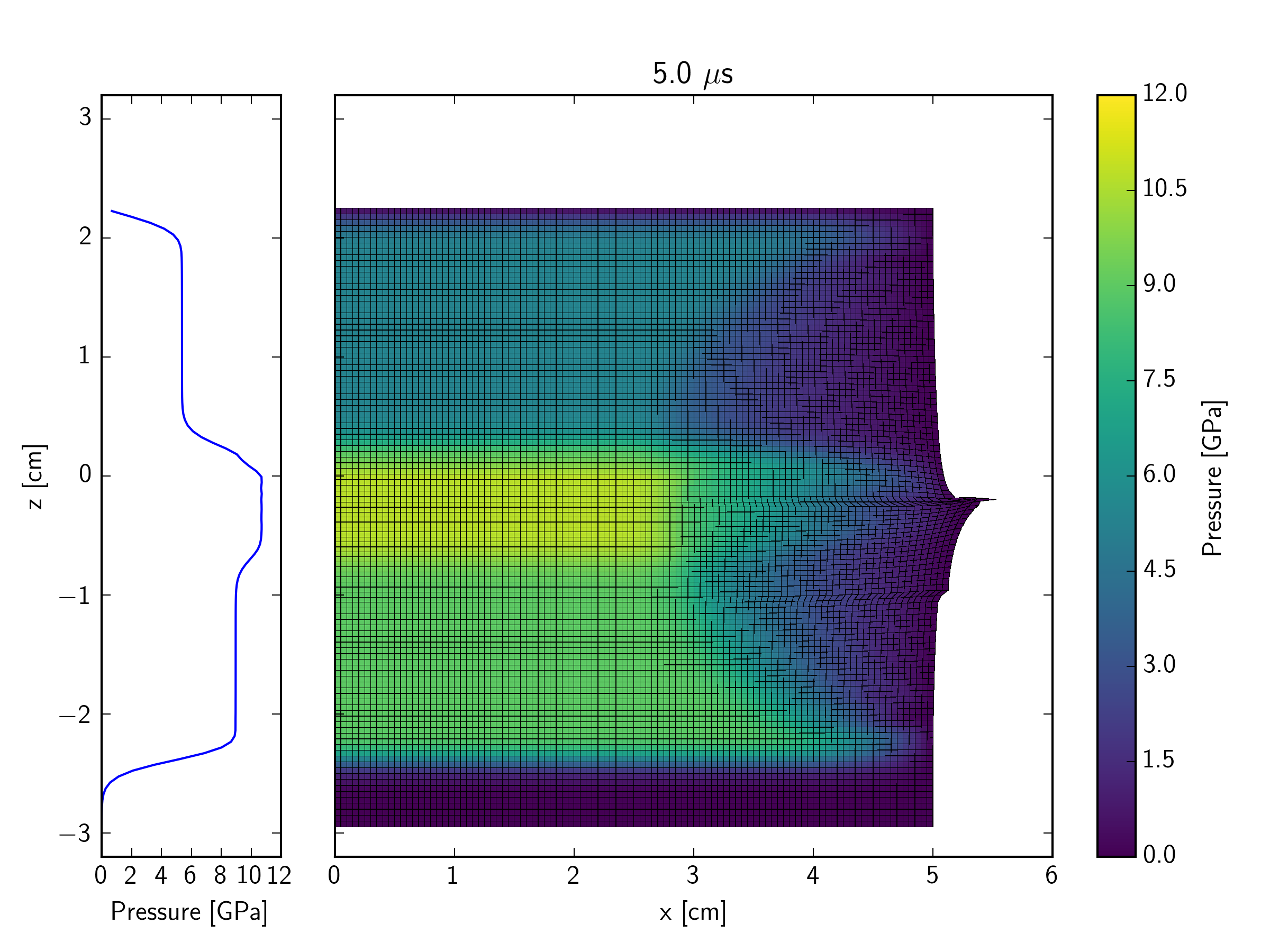
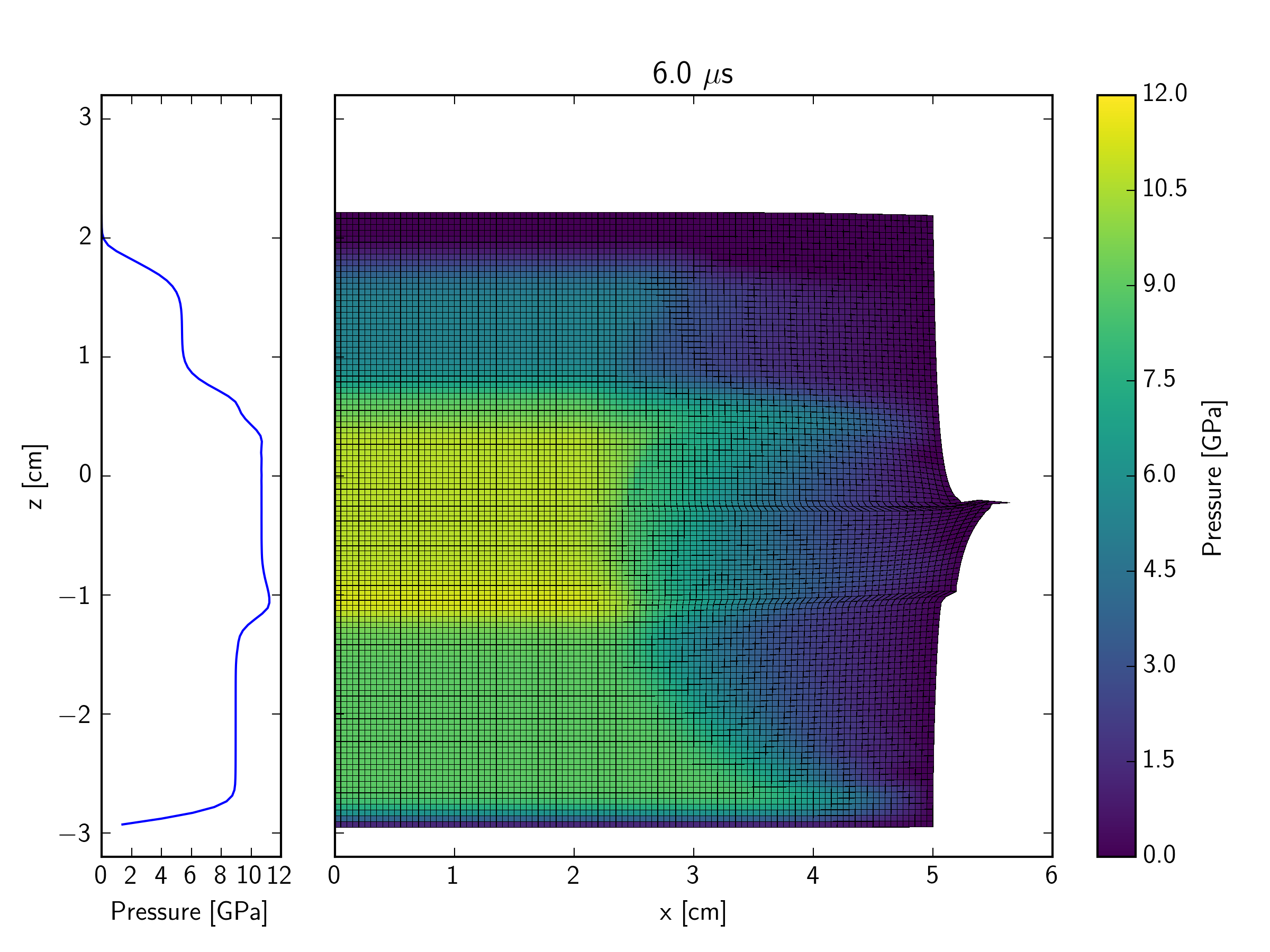
This example simulates, in a Lagrangian representation, the impact of an iron plate hitting a quartzite target at 600 m/s, with an iron buffer plate behind the target. The impact initiates a shock wave which travels through the quartzite target. At the interface between the back of the target and an iron buffer plate, the shock wave reflects back into the target and transmits a shock wave into the buffer. As the initial shock wave reaches the back of the impacting plate, a release wave is sent back through the impactor, and into the target. In contrast to the Eulerian simulation, the right edge of the mesh in the Lagrangian version is a free surface. This implies that a release wave is also generated at the edge of contact plane between the impactor and target; this propagates in towards the symmetry axis at the same time that the shock is propagating into the target and projectile.
This example illustrates the limitations of the Lagrangian approach for simulating high-deformation processes. It can be used as a template for simple numerical planar-impact experiments analogous to laboratory plate impact experiments. However, note that in this example the strength of each material is neglected.
Go to the relevant example directory
cd /share/examples/planar_lagrangian_2D
Run iSALE2D. The simulation will take several minutes, so this should be run in the background.
./iSALE2D &
Go into the Plotting directory and produce images of the simulation to visualise the pressure field and a line graph of the pressure pulse at x=0 (output in @Pressure/@).
python Plotting/Pressure.py
Below are highlighted the model options that differ from the Eulerian version of this example
------------------- General Model Info --------------------------------- MODEL Modelname : Planar-Lagrangian
A cylindrical mesh geometry with a cell size of 0.5 mm and no extension zones. There are fewer cells in the vertical.
------------------- Mesh Geometry Parameters --------------------------- GRIDH horizontal cells : 0 : 100 : 0 GRIDV vertical cells : 0 : 110 : 0 GRIDSPC grid spacing : 5.D-4 CYL Cylind. geometry : 1.0D0
The set-up type is @DEFAULT@ with no gravity field. The ALE model is set to @LAGRANGE@.
------------------- Global setup parameters ----------------------------- S_TYPE setup type : DEFAULT ALE_MODE Eul/Lag/ALE : LAGRANGE T_SURF Surface temp : 293.D0 GRAD_TYPE gradient type : NONE
A single impactor object strikes a two layer target. The iron impactor has a @PLATE@ geometry (extending the full width of the mesh) with a half-thickness if 26 cells. The impactor velocity is 0.6 km/s vertically down. In the target, the bottom iron layer extends from cell 1 to cell 40; above this is a quartzite layer, extending from cell 41 to cell 60.
------------------- Projectile ("Object") Parameters --------------------
OBJNUM number of objects : 1
OBJRESH CPPR horizontal : 26
OBJVEL object velocity : -6.D2
OBJMAT object material : iron___
OBJTYPE object type : PLATE
------------------- Target Parameters ----------------------------------
LAYNUM layers number : 2
LAYPOS layer position : 40 : 60
LAYMAT layer material : iron___ : quarzit
The simulation duration is 6 microseconds, with output saved every 0.1 microseconds.
------------------- Time Parameters ------------------------------------ TEND end time : 6.D-6 DTSAVE save interval : 1.D-7
Boundary conditions differ in the Lagrangian version. The top, bottom and right boundaries are all free surfaces.
------------------- Boundary Condition Parameters ---------------------- BND_L left : FREESLIP BND_R right : FREESURFACE BND_B bottom : FREESURFACE BND_T top : FREESURFACE
Deactivate the deviatoric stress model.
------------------- Control parameters (global) ------------------------ STRESS Consider stress : 0
Strengthless iron and quartzite material models are used, with ANEOS-derived EoS tables.
----------------------------------------------------------- MATNAME Material name : iron___ : quarzit EOSNAME EOS name : iron___ : quarzit EOSTYPE EOS type : aneos : aneos STRMOD Strength model : NONE : NONE DAMMOD Damage model : NONE : NONE ACFL Acoustic fluidisation : NONE : NONE PORMOD Porosity model : NONE : NONE THSOFT Thermal softening : NONE : NONE LDWEAK Low density weakening : NONE : NONE ----------------------------------------------------------- POIS pois : 5.0000D-01 : 5.0000D-01 CHEAT C_heat : 4.4000D+02 : 1.0000D+03
The figures below show the pressure contours. The mesh is also shown so that the deformation of cells can be observed. Not long after the end of this simulation, the right edge of the mesh becomes so distorted that the calculation would grind to a halt (because of the time-step restriction enforced by the very small cell size).