MSP V2 - iNavFlight/inav GitHub Wiki
This page describes MSPV2 (MultiWii Serial Protocol Version 2). MSP is the remote messaging protocol used by INAV and other flight controllers such as MultiWii, CleanFlight and BetaFlight.
MSPV2 was introduced in INAV 1.73 for legacy commands, and is fully implemented (16bit commands) after 1.73 (i.e. 1.74 development branch and successors). An MSP API version of 2 or greater indicates MSPV2 support.
MSP is a request-response protocol. MSP defines the side sending the request as "MSP Master" role and the side generating a response as "MSP Slave" role.
A specific device may function as both "MSP Master" and "MSP Slave" or implement only one role, depending on requirements. Generally, a Groundstation software is an "MSP Master" and FC is an "MSP Slave", however in some use-cases a FC or any other device may be required to act as an "MSP Master" and "MSP Slave" concurrently.
The reasons for introducing a incrementally improved version of MSP include:
- Limited message IDs. MSP v1 provided 255 message IDs; between INAV and BetaFlight (CleanFlight), this space is almost exhausted.
- Limited message size. MSP v1 is limited to 255 byte message payloads. This is already a problem and can only get worse. The extant attempt to address this limitation in MSP v1 (the JUMBO frame extension) is a 'band-aid' and still suffers from the next restriction.
- Weak check-summing. MSP v1 uses a simple XOR checksum. This is vulnerable to simple communications errors (transposed bits). It can fail to detect common transmission corruptions.
MSP V2 addresses these shortcomings:
- 16bit message space. 65535 message IDs. For backwards compatibility, message IDs 0-255 map onto the analogous MSP v1 messages.
- 16bit payload.
- crc8_dvb_s2 checksum algorithm. This is a single byte CRC algorithm that is much more robust than the XOR checksum in MSP v1.
| Offset | Usage | CRC | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | $ | Same lead-in as V1 | |
| 1 | X | 'X' in place of v1 'M' | |
| 2 | type | '<' / '>' / '!' see Message Types | |
| 3 | flag | ✔ | uint8, flag, See Message Flags |
| 4 | function | ✔ | uint16 (little endian). 0 - 255 is the same function as V1 for backwards compatibility |
| 6 | payload size | ✔ | uint16 (little endian) payload size in bytes |
| 8 | payload | ✔ | n (up to 65535 bytes) payload |
| n+8 | checksum | uint8, (n= payload size), crc8_dvb_s2 checksum |
The fields marked with a ✔ are included in the checksum calculation.
| Identifier | Type | Can be sent by | Must be processed by | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| '<' | Request | Master | Slave | |
| '>' | Response | Slave | Master | Only sent in response to a request |
| '!' | Error | Master, Slave | Master, Slave | Response to receipt of data that cannot be processed (corrupt checksum, unknown function, message type that cannot be processed) |
Message flags are used to fine-tune the behaviour of the message exchange, often for use cases that do not require the integrity guarantees of a request - response protocol.
These flags are primarily intended to be used by RC radio systems and not by general consumers who should ensure that the flag value is set to zero to avoid unintended behaviours.
| Flag | Bit / Mask value | Status | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
NO_REPLY |
0 / 0x1
|
Implemented | Do not send a reply |
ILMI |
1 / 0x2
|
Implemented for INAV 8 | "In-Line Message identifier"; intended for radio system that inject transient messages into an extant message stream for private usage. |
Note that for INAV 8 and later, the flag field is returned, unaltered in the response (unless NO_REPLY was also set.) |
The normative reference for MSP V2 message flags is the enumeration mspFlags_e in the source code file src/main/msp/msp.h.
- Defined flag enumerations are reserved for specific use cases
- "Normal" consumers (GCS, Configurators, Remote Management etc.) should set the flag to zero.
- Setting values other than those defined in
src/main/msp/msp.his undefined behaviour. However if you have a use case, bits not defined inmspFlags_emay be used by applications.
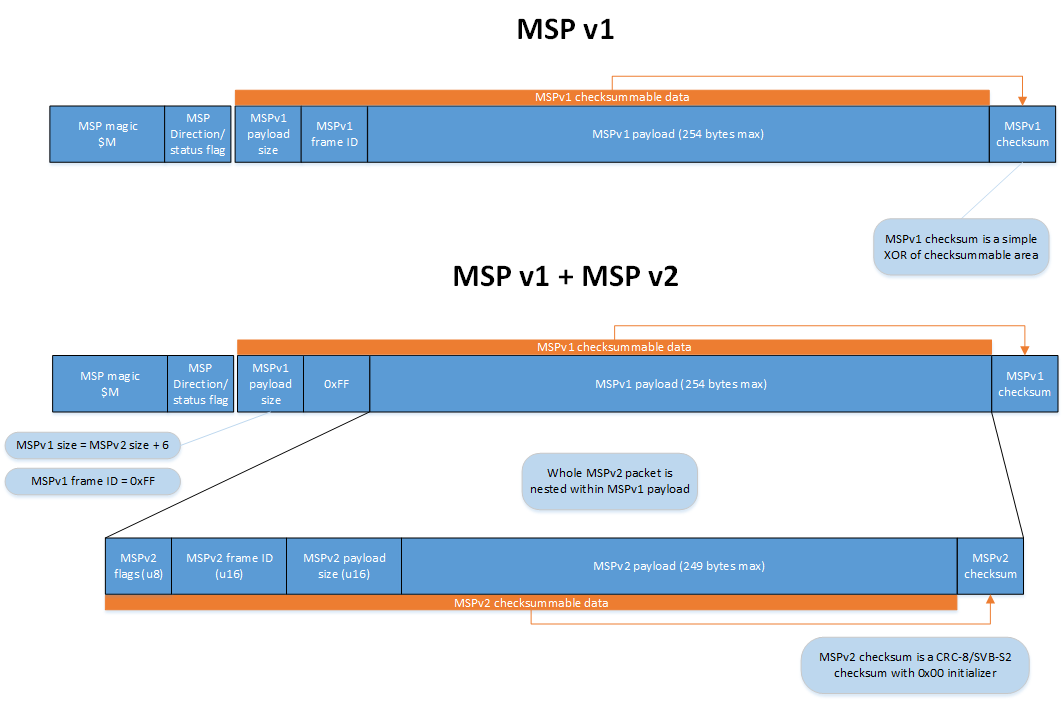
It is possible to encapsulate V2 messages in a V1 message in a way that is transparent to the consumer. This is implemented by setting the V1 function id to 255 and creating a payload of a V2 message without the first three header bytes. Thus a V1 consumer would see a not understood message rather than a communications error. This is not encouraged; rather it is preferred that MSP consumers should implement V2.
As MSP V2 (function id: 100, payload size: 0)
"$X<\x00d\x00\x00\x00\x8F"
24 58 3c 00 64 00 00 00 8f
For a mythical V2 "Hello World" message with function id 0x4242 (note: this function id is not implemented in INAV), as MSPV2 (hex bytes), 18 byte payload, flag set to 0xa5:
24 58 3e a5 42 42 12 00 48 65 6c 6c 6f 20 66 6c 79 69 6e 67 20 77 6f 72 6c 64 82
And embedded in a V1 message (hex bytes):
24 4d 3e 18 ff a5 42 42 12 00 48 65 6c 6c 6f 20 66 6c 79 69 6e 67 20 77 6f 72 6c 64 82 e1
The V2 capable CGS mwp reports this as:
2017-08-11T19:50:12+0100 MSP_CMDS_HELLO_WORLD frame (18): flag=0xa5 "Hello flying world"
Note: This message function is NOT implemented in the FC. It is just a (temporary) test case in mwp.
The checksum should be initialised to zero. The following 'C' code snippet shows the INAV implementation.
uint8_t crc8_dvb_s2(uint8_t crc, unsigned char a)
{
crc ^= a;
for (int ii = 0; ii < 8; ++ii) {
if (crc & 0x80) {
crc = (crc << 1) ^ 0xD5;
} else {
crc = crc << 1;
}
}
return crc;
}
And pseudo-code usage:
int len; // payload size
uint8_t *msg = calloc(1, len+9); // allocation for message
msg[0] = '$';
...
// complete message content
uint8_t ck2 = 0; // initialise CRC
for (int i = 3; i < len+8; i++)
ck2 = crc8_dvb_s2(ck2, msg[i]); // loop over summable data
msg[len+8] = ck2;
As the MSP v1 JUMBO messages is not obviously documented elsewhere:
- This is a MSP v1
$M ...message - Set the function code as normal (0-255)
- Set the payload size to 255
- set the real real payload size as the first two bytes of the payload
- Then the real payload
- Then a MSP V1 XOR checksum as normal
One could embed a MSP V2 message within a MSP V1 JUMBO frame, but this is not likely to be well supported by consumers. If you need V2, please use it natively.
For INAV 1.8.0, MSP V2 messages have been defined (0x4242 is a joke, not a land grab). It is hoped that a message catalogue can be cooperatively developed by FC authors to avoid the current fragmentation in MSP V1.
Suggested approach is to allocate blocks of MSPv2 messages to certain firmwares - use high nibble of Function ID as firmware family identifier. This will allow up to 4096 firmware-specific messages.
| Function ID | Usage | Supports flags | FCs implementing | Documentation Link |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x0000-0x00FE | Legacy | ✘ | INAV, MultiWii, BetaFlight, Cleanflight, BaseFlight | Legacy and INAV Wiki |
| 0x1000-0x1EFF | Common messages | ✔ | INAV | INAV Wiki |
| 0x1F00-0x1FFF | Sensors connected via MSP | ✔ | INAV | INAV Wiki |
| 0x2000-0x2FFF | INAV-specific | ✔ | INAV | INAV Wiki |
| 0x3000-0x3FFF | Betaflight-specific, Cleanflight-specific | ? | Betaflight, Cleanflight |
For new developments targeting modern INAV, MSPV2 is the recommended message format. Applications seeking compatibility with MultiWii, INAV prior to INAV 2.0 or other, older FCs may wish to also implement MSPV1.
New INAV messages should be defined as MSPv2. This will avoid un-managed contention between Cleanflight derivative FCs in the legacy V1 space.
| Offset | Usage | CRC | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | $ | Lead in | |
| 1 | M | 'M' in place of v2 'X' | |
| 2 | type | '<' / '>' / '!' see Message Types | |
| 3 | payload size | ✔ | uint8 payload size in bytes |
| 4 | function | ✔ | uint8 |
| 5 | payload | ✔ | uint8 payload size in bytes |
| n+5 | checksum | uint8, (n= payload size), CRC XOR over indicated items |
The fields marked with a ✔ are included in the checksum calculation.
- Send
MSP_IDENTas MSPV1. The response will inform you if the "server" side is MW, old INAV, modern INAV or other (Cleanflight, Betaflight etc). - If the "server" is not MultiWII, send
MSP_API_VERSIONas MSPV1, otherwise proceed with V1 using only MW supported messages. - If the API_VERSION indicates MSPV2, switch to V2 to take advantage of more reliable CRC and newer messages.
- Continue with
MSP_FC_VARIANT,MSP_FC_VERSIONto determine the type and version / age of the "server" (Cleanflight family) FC. - You now have enough information to tailor your application to the FC's capabilities.