HardwareSetup - graznik/librsswitch GitHub Wiki
Using the transmitter of a remote control
###Advantages
- No separate module has to be bought.
###Disvantages
- The remote control cannot be used any more.
###Proceeding The remote control of the REV 008345 devices consists of two printed circuit boards (PCBs), one with the encoder chip and one with a 433 MHz sender module.
In order to use the tranmitter PCB with the Raspberry Pi, the remote control has to be opened and the transmitter has to be unsoldered from the encoder PCB. Afterwards the transmitter has to be connected to the P1 header of the Raspberry Pi.
Although the remote controls normally work with a 12 V battery supply, the 5 V of the Raspberry Pi is sufficient to operate the transmitter module.
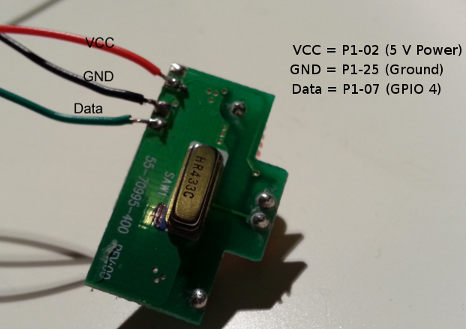
- VCC has to be connected to P1-02 (5 V Power)
- GND has to be connected to P1-25 (Ground)
- Data has to be connected to P1-07 (GPIO 4)
Using a common transmitter
###Advantages
- The remote control is leaved untouched
- The modules are very cheap
###Disvantages
- A separate module has to be bought
###Proceeding The xbay offers cheap 433 MHz transmitters, a search with those keywords should come up with a lot of devices for about 2 USD.
The transmitter has to be connected the P1 header of the Raspberry Pi, the pinning is the same as for the REV transmitter above:
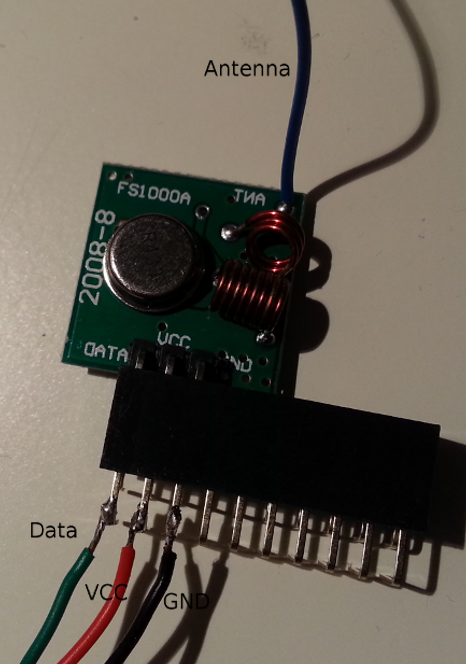
- VCC has to be connected to P1-02 (5 V Power)
- GND has to be connected to P1-25 (Ground)
- Data has to be connected to P1-07 (GPIO 4)