네번째스터디 : DFS & BFS - gomamon/twitch_algorithm GitHub Wiki
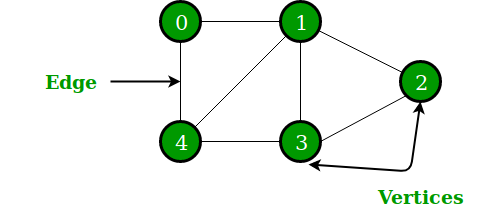
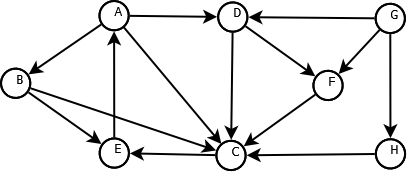
정점(node/ vertex)과 간선(edge)들의 집합!
인접 : 두 정점사이에 간선존재
경로:
{0,1,4,3}
-
방향성
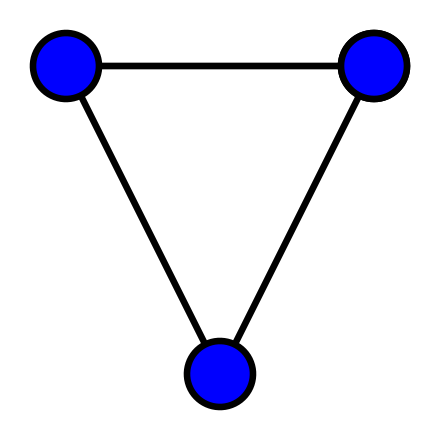
- 무방향그래프(undirected graph)
-
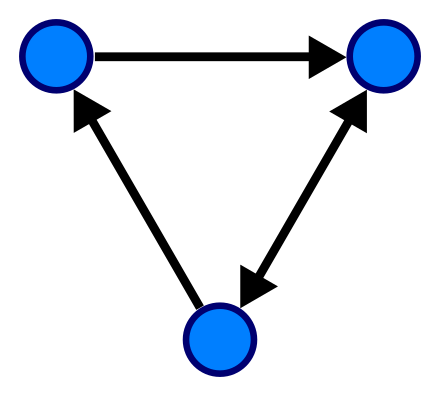
방향그래프(directed graph)
-
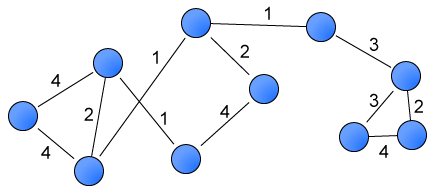
가중치 그래프 weighted graph
-
cycle graph
Does This graph has cycle?
- 인접행렬
0 1 2 3 4 5 0 1 0 1 1 2 1 3 4 5
인접 리스트
vector
/*
1 2
2 1
4 1
2 4
4 3
3 3
5 6
*/
vector < int > v[10000];
for(){
vv.resize(7)
scanf("%d %d",&a, &b);
vv[a].push_back(b);
vv[b].push_back(a);
}
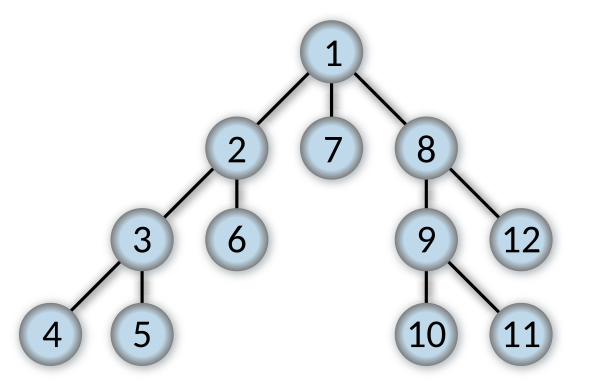
Depth-first search (DFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures.
//재귀
void dfs(int x){
printf("%d " ,x);
visit[x] = true;
for(int i = 0 ; i < (int)v[x].size(); ++i){
if(visit[v[x][i]] != true)
dfs(v[x][i]);
}
}
//stack
void dfs(){
stack< int > s;
printf("%d", V);
s.push(V);
while(!s.empty()){
int x = s.top();
if(!visit[x])
printf("%d", x);
visit[x] = true;
int chk = false;
for(int i=0; i< (int)v[x].size(); i++){
if(!visit(v[x][i])){
chk = true
s.push(v[x][i]);
break;
}
}
if (!chk)
s.pop();
}
}
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/11724
6 8
1 2
2 5
5 1
3 4
4 6
5 4
2 4
2 3
#include <vector>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector < vector<int> > c;
int n, m, u, v;
bool visited[1005];
int cnt;
void dfs(int start) {
visited[start] = true;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)c[start].size(); ++i) {
if (!visited[c[start][i]] )
dfs(c[start][i]);
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
c.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &u, &v);
c[u].push_back(v);
c[v].push_back(u);
}
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++) {
if (visited[i] == false)
{
dfs(i);
cnt++;
}
}
printf("%d\n", cnt);
}Breadth-first search (BFS) is an algorithm for traversing or searching tree or graph data structures.
void bfs(int V){
queue <int> que;
que.push(V);
visit[V]=true; //방문했어!
while(!que.empty()){
int x = que.front();
que.pop();
printf("%d ",x);
for(int i = 0 ;i < (int)v[x].size(); ++i){
if(visit[v[x][i]] != true){
que.push(v[x][i]);
visit[v[x][i]] = true;
}
}
}
}
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7569
#include <stdio.h>
#include <queue>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int t[102][102][102];
int dx[] = {0,0,1,-1,0,0};
int dy[] = {0,0,0,0,1,-1};
int dz[] = {1,-1,0,0,0,0};
int m,n,h;
int ans=0;
void bfs(){
queue < pair< int, pair<int, int> > > q;
for(int i=0 ; i<h ; i++){
for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++){
for(int k=0 ; k<m ; k++){
if(t[k][j][i]==1)
q.push( make_pair ( k , make_pair(j,i) ) );
}
}
}
while(!q.empty()){
int nowx = q.front().first;
int nowy = q.front().second.first;
int nowz = q.front().second.second;
for( int i=0 ; i < 6 ; i++ ){
if(nowx+dx[i] < m && nowx+dx[i] >= 0 &&
nowy+dy[i] < n && nowy+dy[i] >= 0 &&
nowz+dz[i] < h && nowz+dz[i] >= 0 &&
t[nowx+dx[i]][nowy + dy[i]][nowz+dz[i]]==0
)
{
t[nowx + dx[i]][nowy+dy[i]][nowz+dz[i]] = t[nowx][nowy][nowz]+1;
q.push( make_pair ( nowx + dx[i], make_pair( nowy+dy[i],nowz+dz[i] ) ) );
}
}
q.pop();
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d%d%d",&m,&n,&h);
for(int i=0 ; i<h ; i++){
for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++){
for(int k=0 ; k<m ; k++){
scanf("%d",&t[k][j][i]);
}
}
}
bfs();
for(int i=0 ; i<h ; i++){
for(int j=0 ; j<n ; j++){
for(int k=0 ; k<m ; k++){
if(t[k][j][i]==0){
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
ans = max(ans,t[k][j][i]);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",ans-1);
}