Multi Cloud - ganeshahv/Contrail_SRE GitHub Wiki
AWS
Azure
-

-
Azure only supports Availability Zones in certain regions.
-
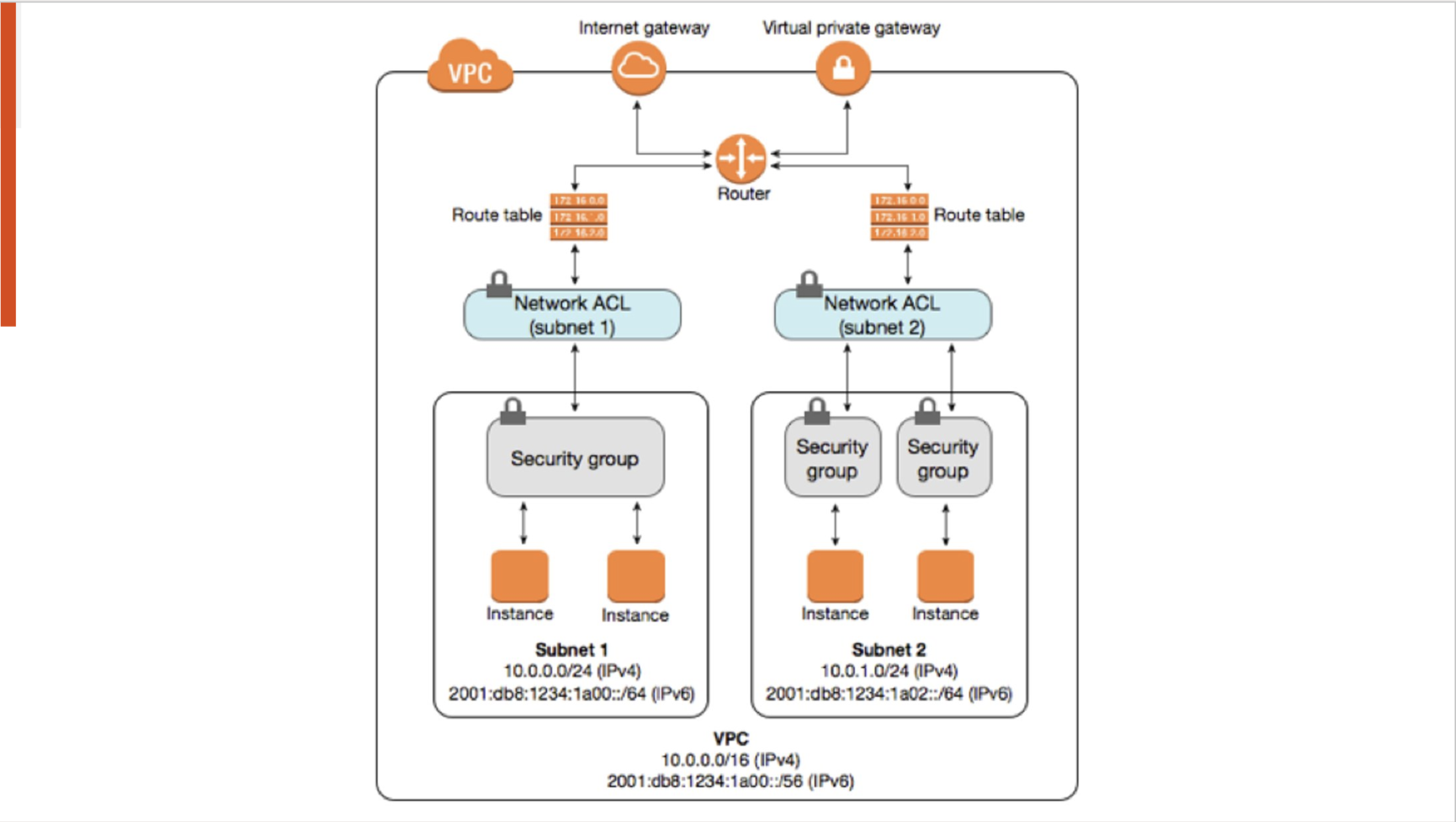
Virtual Network Gateways are used for Hybrid Connectivity termination constructs for VPN or Express Route.
-
ResourceGroup groups items together for better organization control of a specific workload.
-
AD Tenant is the top level organizational structure in Azure.
-
Azure Virtual WAN as a platform does not provide encryption within the cloud, a multi-cloud architecture, nor supports 3rd party devices in the HUB.
-
ExpressRoute circuit in Azure can terminate on ExpressRoute Gateway or Virtual Network Gateway.
-
NVA in Azure is a 3rd party device in the Azure marketplace.
-
SNAT required for traffic symmetry and User Defined Route Management at scale are the challenges with using an NVA to provide spoke to spoke communication in Azure.
GCP
- GCP private dedicated connectivity is referred to as Cloud Interconnect.
- A Virtual Machine is an example of a Zonal Resource.
- A VPC is an example of a Global Resource.
- For a single user, GCP resources are structurally organized in a Project.
- Auto Mode in GCP means subnets are created in each region.
- GCP supports dynamic routes within the cloud.
OCI
- Virtual cloud networks are called VCN in OCI.
- OCI subnets are not tied to Availability Domains.
- There can be 5 DRGs in an OCI Region.
- Overlapping IPs are not allowed when peering VCNs in OCI.
- In OCI you need to specify a Compartment ID when creating resources.
MCNA
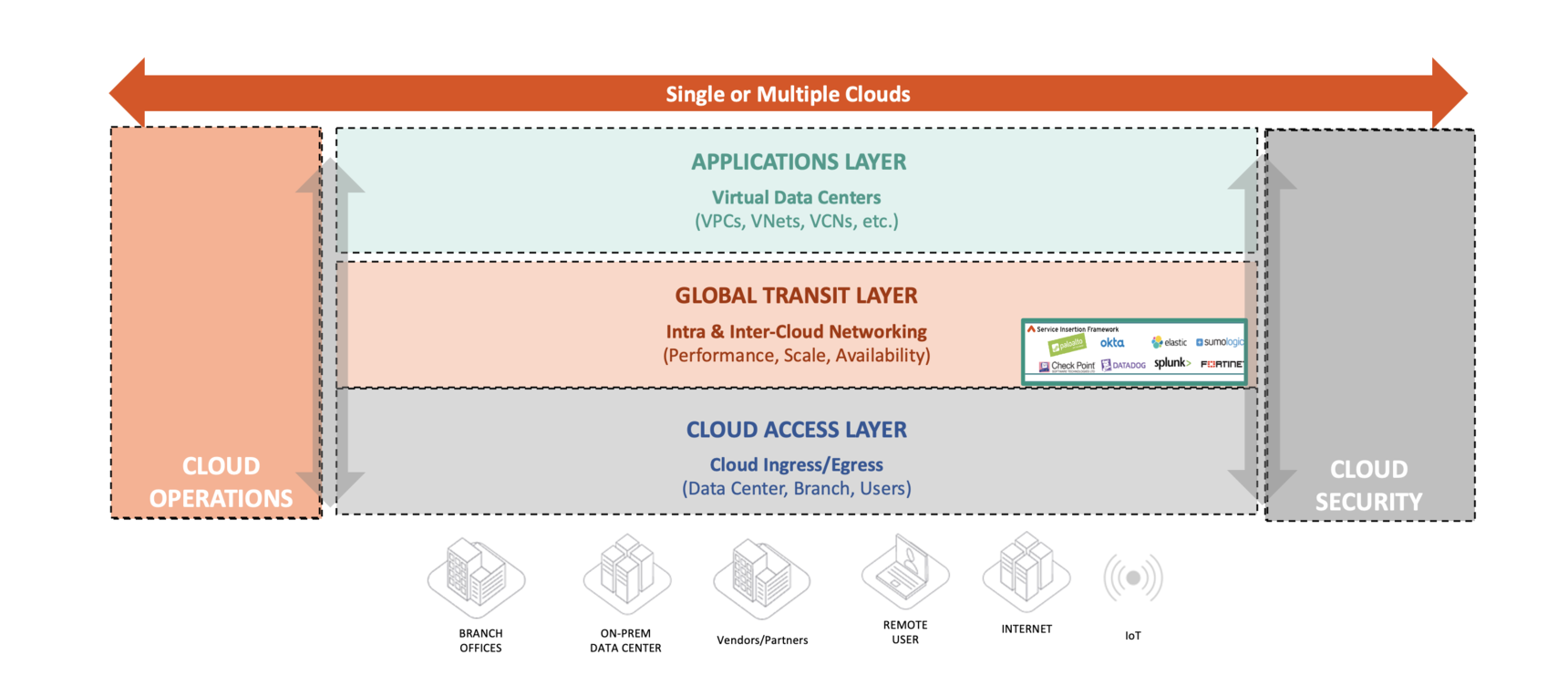
- Cloud Core, Operations, and Access are the main pillars of the MCNA.
- Security and Visibility is inserted throughout the MCNA Architecture.
- Normalized Data Plane, Centralized Control Plan which are repeatable across cloud providers is a benefit of having a Multi-Cloud Network Architecture
- Go Build, Vendor Lock In and Black Box are some of the Customer Challenges in cloud.
- Transit is the most important aspect of any multi-cloud network.
- The Cloud Core layer of the MCNA provides Normalized Data plane across clouds.
- Cloud Access in MCNA provides common access for SDWAN, Direct Connect options from cloud providers and VPN connectivity.
- The core principal of MCNA is a multi-cloud network and security framework for consistent deployment across clouds.
Aviatrix
-
Aviatrix Systems is the pioneer of Multi-Cloud Network Architecture (MCNA).
-
MCNA provides a consistent and repeatable architecture across multiple clouds.
-
Aviatrix implements a data plane through dynamic and software-defined routing with a centralized control plane.
-
Security is built into the network architecture through segmentation, encryption, ingress and egress filtering, and security services insertion.
-
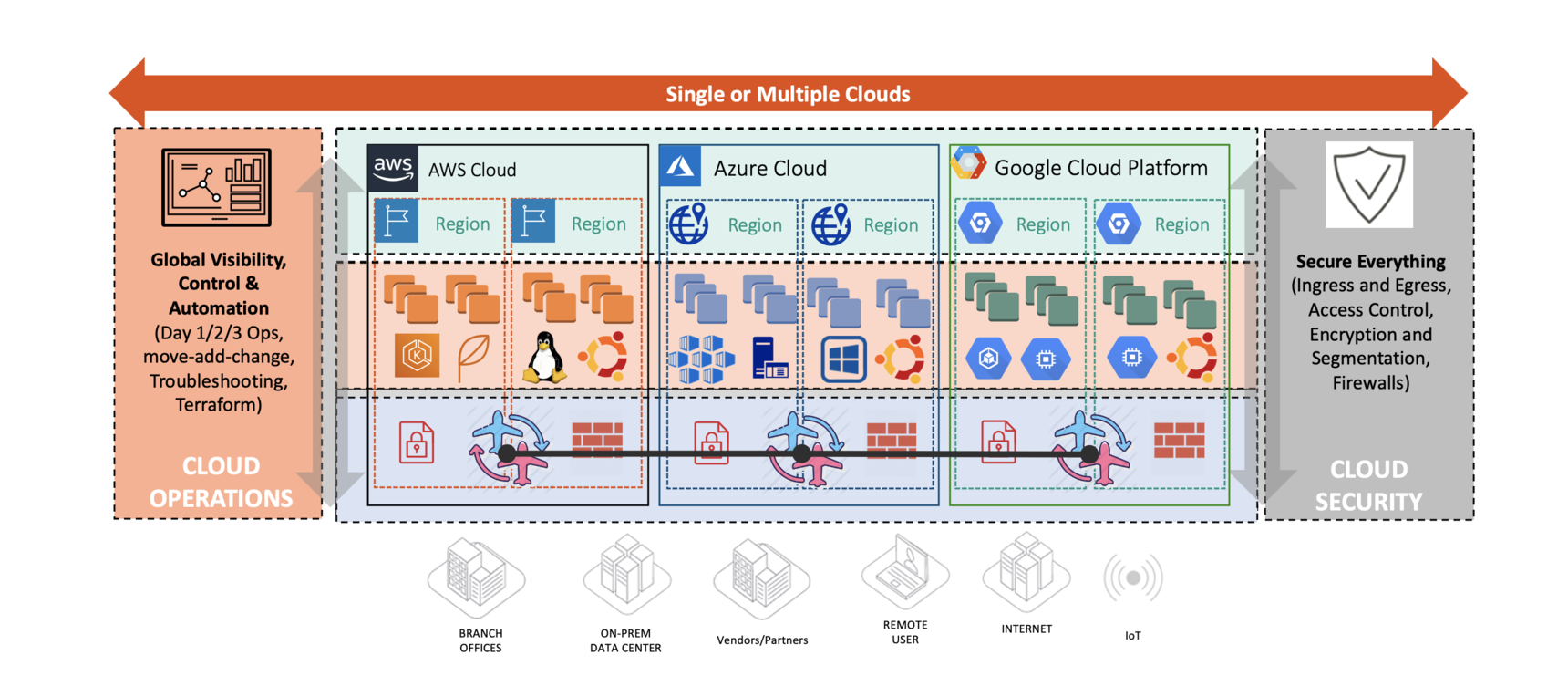
MCNA architecture defines four distinct layers at a high level. These are Cloud Core, Cloud Security, Cloud Access, and Cloud Operations.
-
-
-
A centralised controller is also the entry-point for multi-cloud automation, which can be done using APIs or Terraform.
-
The Aviatrix gateways act as a Distributed and Common Data-Plane.
-
Aviatrix services are also integrated with AWS GuardDuty to block malicious activity automatically at the Virtual Private Cloud network level.
-
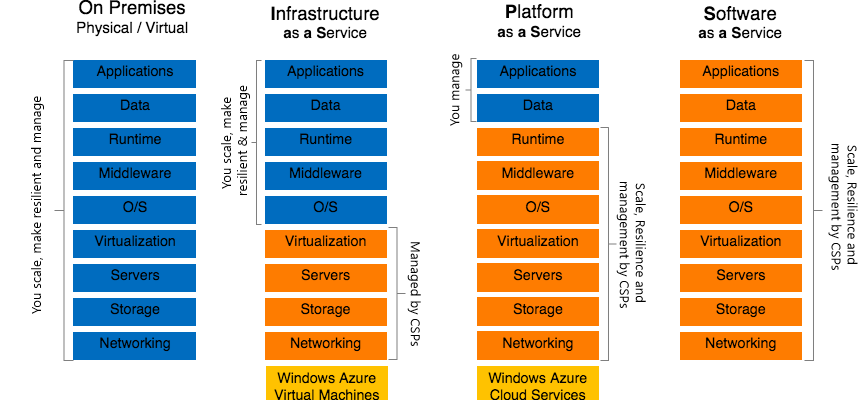
ACE
- Aviatrix Transit Solution is built using Aviatrix IPSEC for encryption by default with option for high performance.
- Cloud environments are not natively encrypted, are limited to 1.25G and tied to a single core within compute.
- Controller, Gateways and Co-Pilot are the components within the Aviatrix Platform.
- Native solutions build tunnels across a single core only limiting the IPSEC to 1.25G.
- The Aviatrix FQDN Egress Filter supports both centralized and distributed egress methods.
- Aviatrix can extend native AWS features like Guard Duty to provide enforcement of alerts.
- Aviatrix Transit provides End to End Encryption, is repeatable across Clouds and ensures complete visibility and control.
- With Aviatrix HPE, customers can get near line rate encryption within the cloud, between clouds and between on-prem and cloud.
- Aviatrix can provide filtering of partner route advertisements through a BGP Approval Process.
- Challenges with inserting firewalls in the cloud include:
- Repackaged Firewall Solution from on-prem world
- Native Firewall Solutions are primarily L4 firewalls
- Customer required to configure and manage routing
- Aviatrix can achieve 70G throughput with Firenet
- The Aviatrix Site to Cloud offers support for Network Address Translation (NAT), TCP and UDP tunnels and a template driven manner for configuration.
- Aviatrix Firenet can orchestrate the firewall deployment, firewall routing, and VNET/VPC routing for NGFW insertion.
- The Aviatrix User VPN solution allows profile based granular access control.
- DUO, Okta, AD and SAML are some of the 3rd party integrations available for Aviatrix User VPN.
- Security Domains allow customers to group VPC/VNETs with common security properties for access.
- Aviatrix Site 2 Cloud can also be used to onboard IoT devices.
- Aviatrix Private S3 solution provides private access (RFC1918 only) to S3 buckets without the need of public addresses.
- Aviatrix is a multi-cloud Terraform provider.
- Aviatrix can provide packet captures of live traffic.
- Aviatrix uses a Lambda script, an S3 bucket and an auto scaling group for Controller HA in AWS.
- Flight Path provides a visual walk-through based on source and destination to highlight path issues.
- Limited visibility into native constructs and lack of standard troubleshooting tools like ping, traceroute, etc. are some operational challenges that customers face in the cloud.
- The Aviatrix controller can perform auditing of routing constructs. This ensures that no new routes have been added, that can affect end to end network correctness.
- Common troubleshooting tasks like ping and traceroute can be run from any Aviatrix gateway.
- Aviatrix upgrades are hitless.
- Customers can spin up a single Aviatrix controller and on-board multiple cloud accounts for management.
- CoPilot must be deployed only once to gain visibility across your multi-cloud network.
- CoPilot topology can provide customized visibility options, custom tagging of resources and diagnostic functions from gateways.
- CoPilot provides geolocation features for data traffic.
- Aviatrix FlowIQ provides netflow data across the multi-cloud network for all traffic seen by gateways.
- Flow IQ will provide summarization of netflow data but for specific records we must perform tasks on the gateways.
- Aviatrix CoPilot provides intelligent visibility into cloud networks through dynamic topology, netflow, troubleshooting.
- CoPilot allows for custom filters to limit data to defined resources, applications, and flows.
- A single controller is needed to run a multi-cloud environment consisting of OCI, Azure and GCP.
- CloudFormation template from docs.aviatrix.com is the recommended or easiest way of deploying the Aviatrix controller in AWS.
- Aviatrix Controller cannot be deployed in a on-prem DC.